Application of Phospholipase pldζ1 Gene in Improving Salt Tolerance of Plants
A technology of salt tolerance and genetics, applied in the field of plant molecular breeding and biology, can solve problems such as complex molecular mechanisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] PLDζ1 Gene Cloning and Overexpression Enhance Plant Salt Tolerance
[0031] 1. Cloning of full-length cDNA of PLDζ1 gene and construction of plant overexpression vector:
[0032] Total RNA was extracted from the leaves of japonica rice Dongjin, and the first-strand cDNA was synthesized by reverse transcription RT-PCR using mRNA as a template, and then the cDNA was used as a template, using PLDζ1 sequence-specific primers PLDζ1FZ: 5'-GGGGTACCATGCAAGAATATCTGAACC-3' and PLDζ1RZ: 5'-CGGGATCCATGGAAAACTTGTGGAG-3' was amplified by PCR, and the amplified target fragment included the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The amplified target fragment was inserted into the restriction site of the plant overexpression vector pU1301D1 (modified by pCAMBIA1301, Hajdukiewicz et al., The small, versatile pPZPfamily of Agrobacterium binary vectors for plant transformation. PlantMol. Biol. 1994, 25: 989-994) Between Kpn I and BamH I, the pU1301D1:PLDζ1 recombinant plasmid was obtained. After ...
Embodiment 2
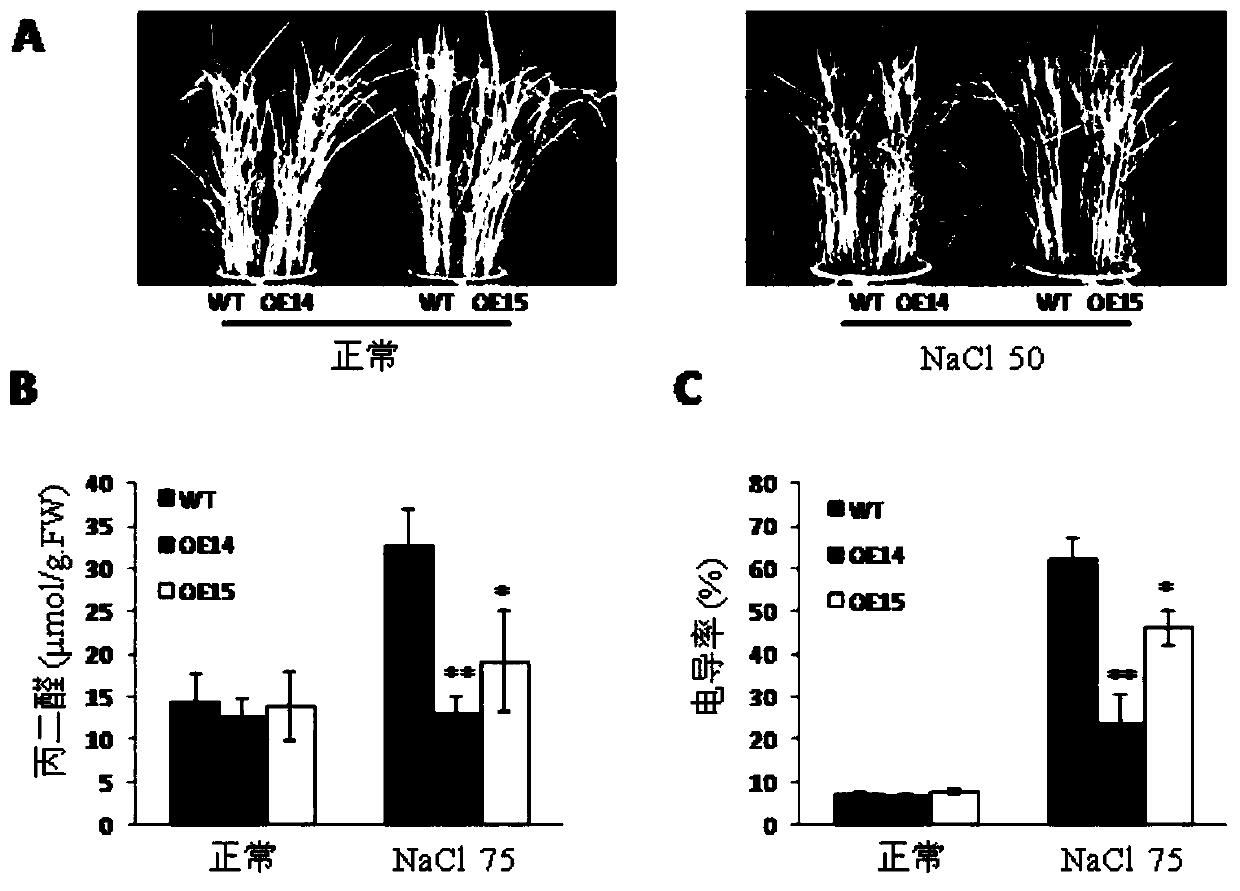
[0044] Overexpression of PLDζ1 enhances salt tolerance of plants
[0045] Two PLDζ1-OE independent strains OE-14 and OE-15 of the PLDζ1 overexpression rice transformed plants created in Example 1 were randomly selected for detailed analysis, and the non-transformed regenerated plants (wild type, WT) that had also undergone the tissue culture process were randomly selected. As a control, it was treated with different concentrations of NaCl solution (0, 50, 75mM) for one month at the tillering stage. The results found that under normal conditions, PLDζ1 overexpressed plants had no significant difference in plant height, leaf plasma membrane permeability, and malondialdehyde content between the corresponding wild-type plants. significantly higher than that of the wild type, and its leaf plasma membrane permeability and malondialdehyde content were significantly lower than those of the non-transformed wild type ( figure 1 ). After one month of 75mM NaCl treatment, the malondiald...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Isolation, Identification and Functional Identification of PLDζ1 Deletion Mutant
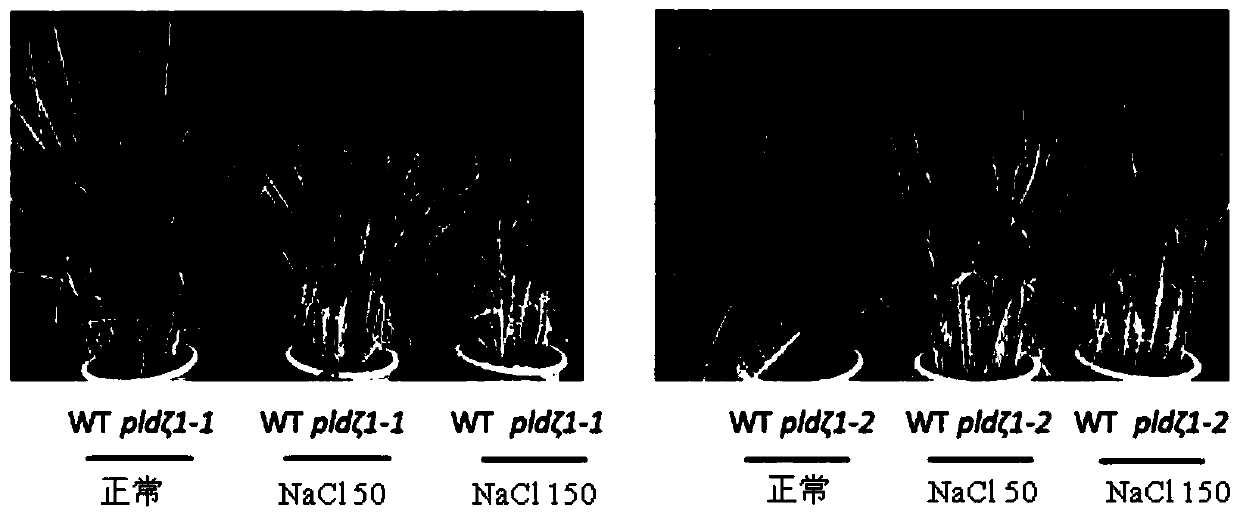
[0048] 1. Isolation, identification and phenotype observation of mutant pldζ1:
[0049] In order to further verify and analyze the function of the PLDζ1 gene, the present invention isolated and obtained two independent mutant lines with T-DNA inserted into different sites of PLDζ1, named pldζ1-1 and pldζ1-2 respectively, wherein the T-DNA of pldζ1-1 was inserted into It is located in the 3'-UTR region of PLDζ1, while the T-DNA insertion of pldζ1-2 is located in the third intron of PLDζ1. The effect of T-DNA insertion on the expression of PLDζ1 was analyzed by semi-quantitative RT-PCR. The results showed that there was a small amount of expression of PLDζ1 in the pldζ1-1 homozygous mutant, but it was significantly lower than that of the wild type, while in the pldζ1-2 homozygous mutant PLDζ1mRNA could not be detected, which belonged to complete deletion mutant.
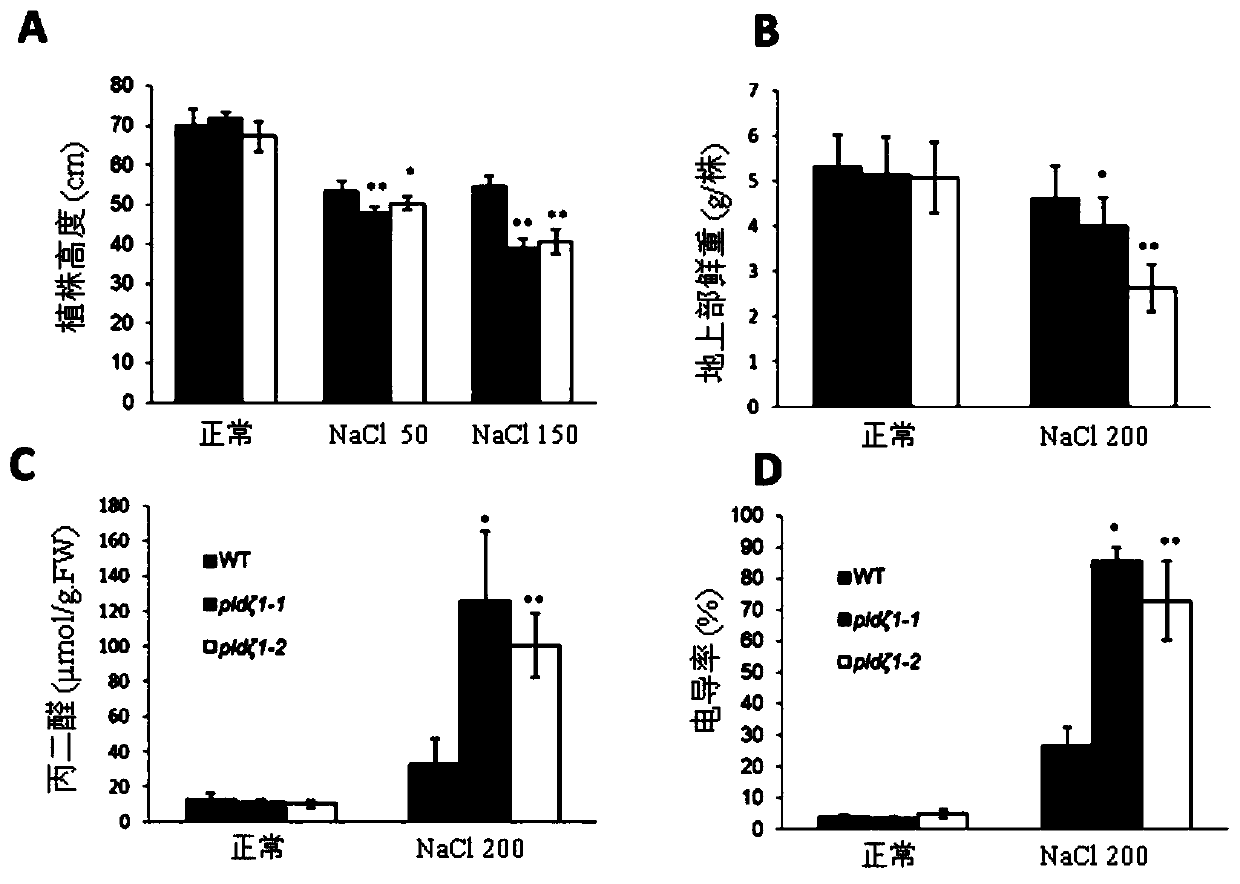
[0050] The analysis show...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com