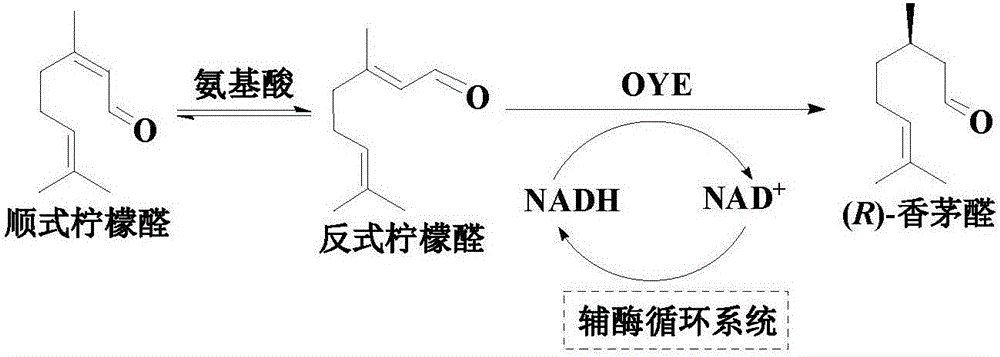
An enzymatic citral asymmetric reduction method capable of increasing optical purity of (R)-citronellal
A technology of optical purity and citral, applied in fermentation and other fields, can solve problems such as low yield and expensive catalyst
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
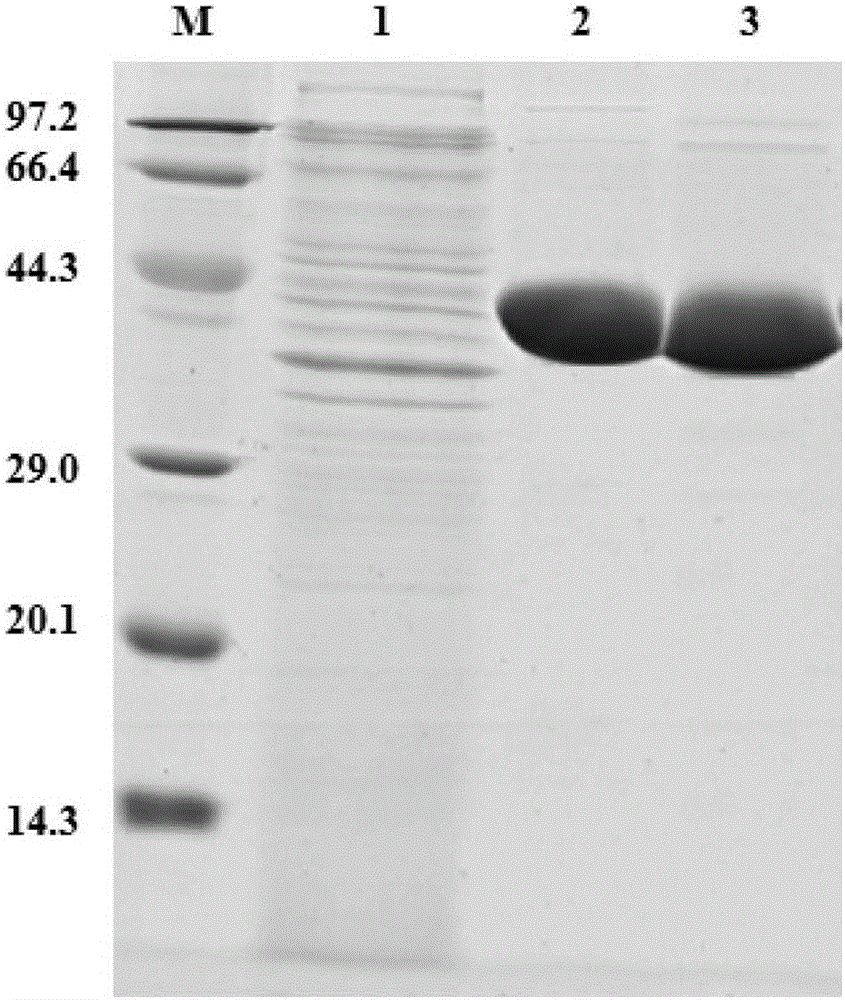
[0028] Example 1: Expression and purification of Saccharomyces cerevisiae enol reductase OYE1 and formate dehydrogenase FDHCB derived from Candida boidinii
[0029] (1) Construction and inducible expression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae enol reductase OYE1 Escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria
[0030] Saccharomyces cerevisiae enol reductase OYE1 gene oye1 was amplified by PCR with the designed primers F1 and R1 using the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CICC 1002 genomic DNA purchased from the China Industrial Microorganism Collection and Management Center as a template. shown in Table 1.
[0031] Table 1 PCR amplification reaction system
[0032]
[0033] The primers were as follows: F1, 5'-ATGCCATTTGTTAAGGACTTTA-3'; R1, 5'-TTAATTTTTGTCCCAACCGA-3'. The PCR reaction process was as follows: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 min; then, denaturation at 94°C for 30s, renaturation at 57°C for 30s, and hold at 72°C for 1 min as a cycle, repeating this cycle 35 times; finally, ho...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2: Enzyme activity assay of Saccharomyces cerevisiae enol reductase OYE1
[0041] The standard enzyme activity assay system (2mL) contains 0.4mM NADH, 100μg / mL Saccharomyces cerevisiae enolate reductase OYE1, and 20mM citral (citral was added in the form of 1M substrate solution prepared with octanol, and the amount of the substrate solution was added). In terms of the amount of citral, the final concentration in the reaction system was 20 mM), and 50 mM PIPES buffer (pH 7.0) was used as the reaction medium; the concentrations all refer to the final concentration in the assay system. The reaction was carried out at 30 °C, NADH was added last, and the enzymatic activity (the molar coefficient of NADH ε) was determined by detecting the change of the absorbance value of the reaction system at 340 nm per minute. 340 =6.3mM -1 cm -1 ). Units of activity (U) are defined as the amount of enzyme required to consume 1 μmol of NADH per minute.
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: Characterization of Catalytic Properties of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Enol Reductase OYE1
[0043] The total volume of the standard catalytic system is 10 mL, including 20 mM citral respectively (citral is added in the form of a 1M substrate solution prepared with octanol, and the added amount of the substrate solution is based on the amount of citral, and the final concentration in the reaction system is 20 mM) , 0.25mMNAD +, 100 mM sodium formate, 0.3 U / mL OYE1, 0.5 U / mL FDHCB, and 50 mM PIPES buffer (pH 7.0) as the reaction medium. The optimization of the conditions for the asymmetric reduction reaction was carried out on a water-bath shaker with a rotation speed of 200 rpm. The reaction solution was extracted with ethyl acetate, and the obtained organic phase was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and then the substrate citral and the product (R)-citronellal were quantitatively determined by gas chromatography.
[0044] The detection conditions of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com