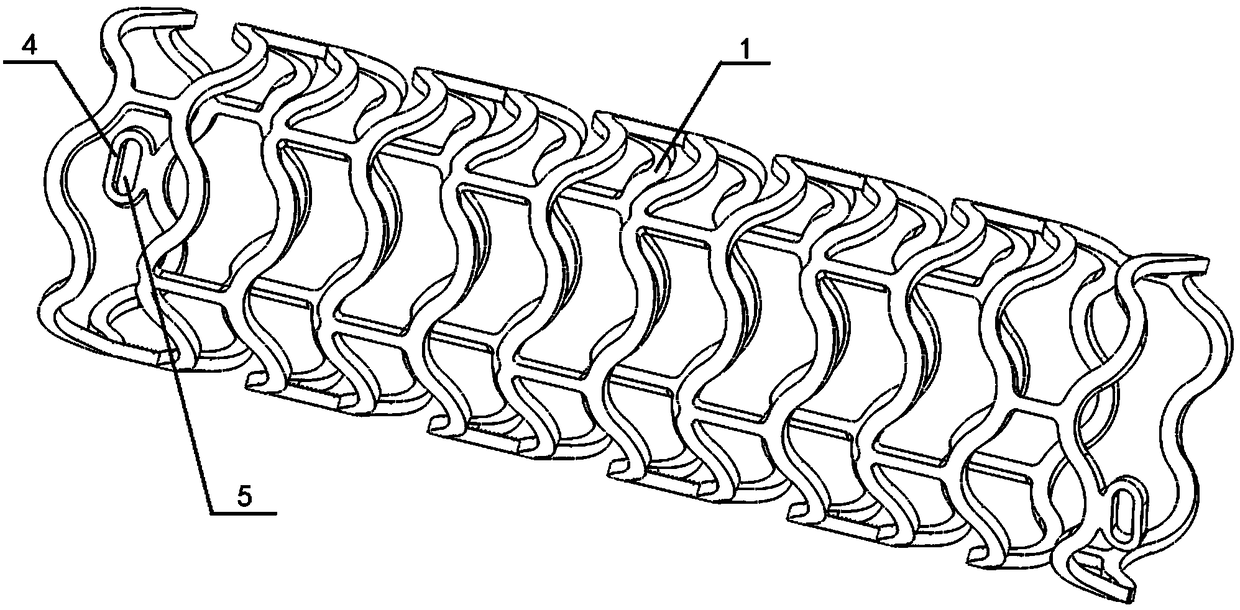
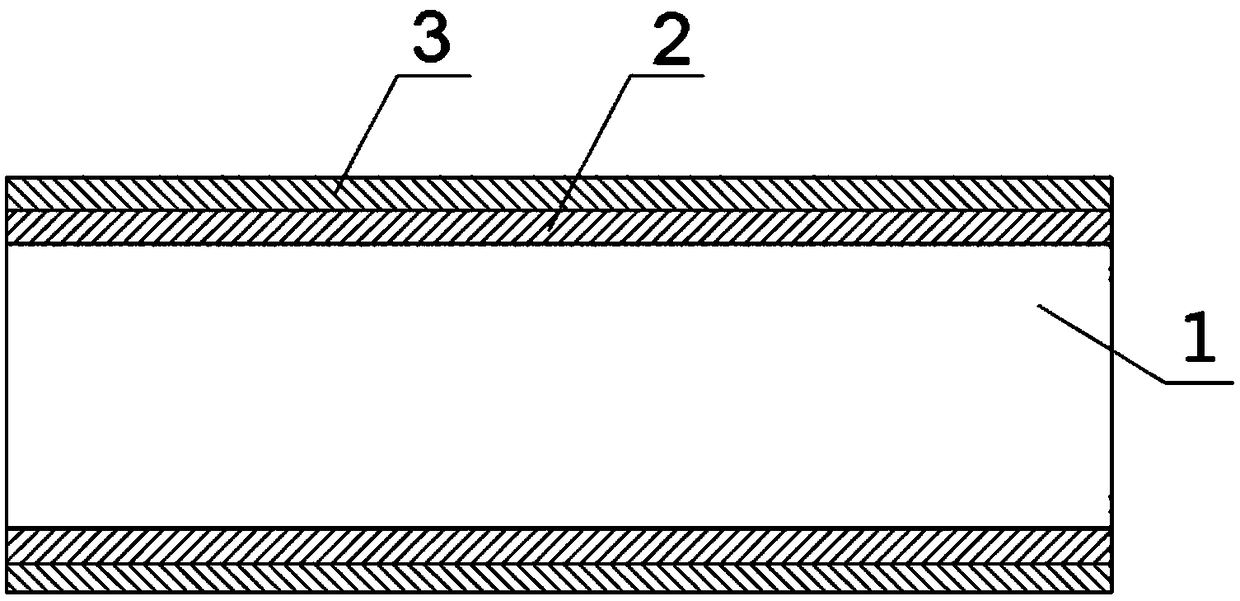
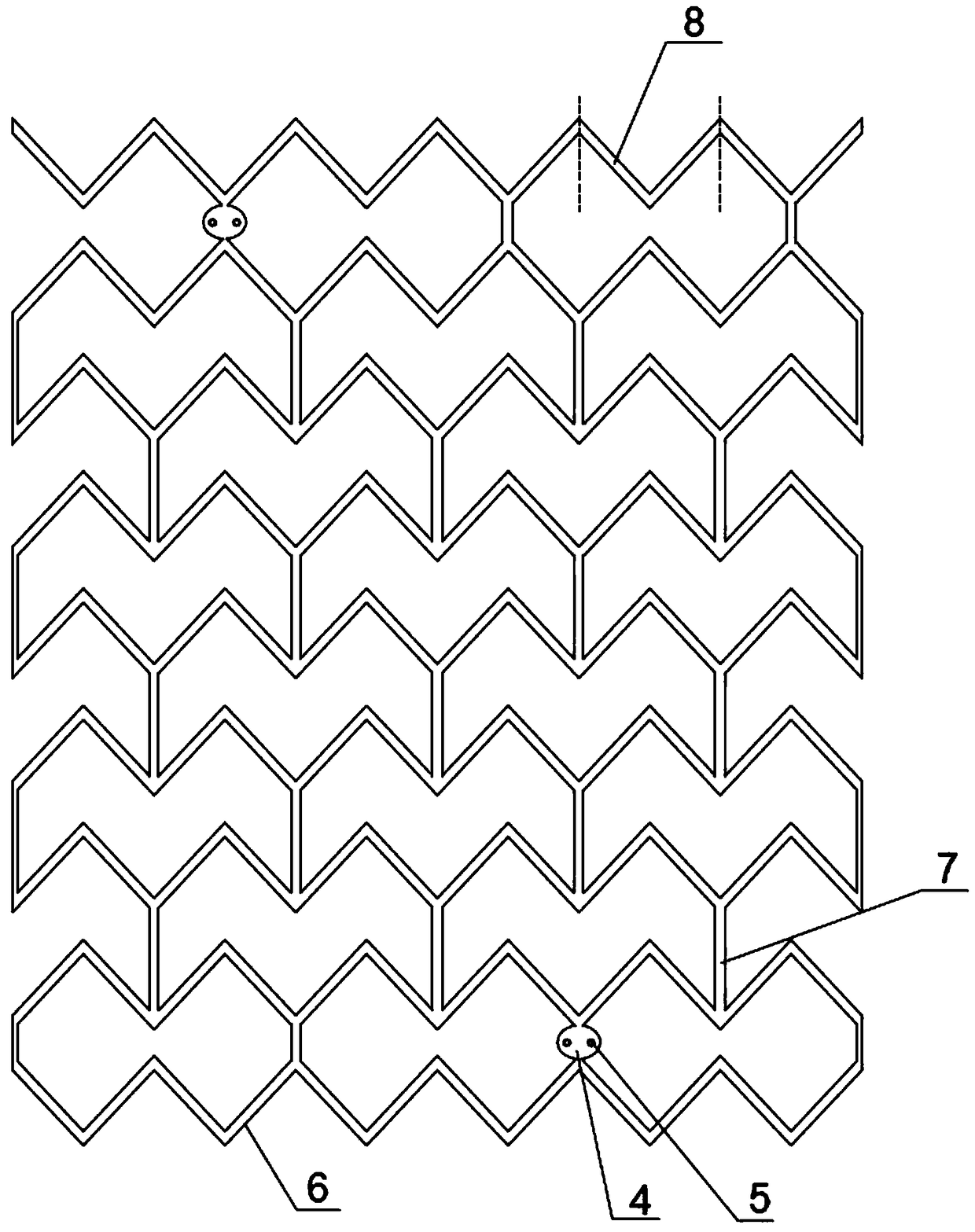
Fully degradable vascular stent for treatment of vascular diseases and preparation method thereof
A vascular stent, fully degradable technology, applied in the field of three types of medical devices, can solve problems such as hindering the recovery of vascular function, and achieve the effects of convenient operation and use, stable performance and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] A preparation method for a fully degradable vascular stent for treatment of vascular diseases, comprising the following steps:
[0067] 1) Raw material preparation:
[0068] Take polylactic acid as raw material A, and the number average molar molecular weight of polylactic acid is 100,000;
[0069] 2) Processing into pipes:
[0070] First heat the raw material A to a molten state, the heating temperature is 200 ° C, fill the molten material into the pipe forming mold, and then cool it naturally until the internal temperature of the material drops to room temperature, that is, it is processed into a cylindrical pipe; the processed cylinder Type pipe, its outer diameter is 2mm, and the pipe wall thickness is 0.5mm;
[0071] 3) Pipe reinforcement and toughening:
[0072] First place the cylindrical pipe in a constant temperature oven at 60°C for 10 hours to promote the orderly formation of the crystal nucleus of the original structure of the material to strengthen and t...
Embodiment 2
[0084] A preparation method for a fully degradable vascular stent for treatment of vascular diseases, comprising the following steps:
[0085] 1) Raw material preparation:
[0086] Put polylactic acid and polylactic acid-trimethylene carbonate copolymer into a twin-screw extruder at a mass ratio of 70:30 for blending and granulation to obtain raw material B; the blending and granulation temperature of the twin-screw extruder is 180℃, the speed is 20rpm;
[0087] Wherein, the number average molar molecular weight of polylactic acid is 400,000, and the number average molar molecular weight of polylactic acid-trimethylene carbonate copolymer is 50,000;
[0088] 2) Processing into pipes:
[0089] Put the raw material B in a plastic extruder, and heat the raw material to a molten state in the plastic extruder. When the internal temperature drops to room temperature, it is processed into a cylindrical pipe; the processed cylindrical pipe has an outer diameter of 2.5mm and a wall ...
Embodiment 3
[0103] A preparation method for a fully degradable vascular stent for treatment of vascular diseases, comprising the following steps:
[0104] 1) Raw material preparation:
[0105] Take polylactic acid as raw material A, and the number average molar molecular weight of polylactic acid is 100,000;
[0106] 2) Processing into pipes:
[0107] Raw material A and polylactic acid-trimethylene carbonate copolymer are respectively placed in two extrusion heads in the extruder, and these two kinds of materials are heated to molten state in these two extrusion heads respectively, its The heating temperature is 180°C; the extruded pipe has two layers, the material of the inner layer is polylactic acid, and the material of the outer layer is polylactic acid-trimethylene carbonate copolymer; finally, it is naturally cooled until the internal temperature of the material drops to room temperature. That is, it is processed into a cylindrical pipe; the processed cylindrical pipe has an outer...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com