Manufacturing method of R-T-B sintered magnet
A technology of R-T-B and sintered magnets, which is applied in the manufacture of inductors/transformers/magnets, electrical components, circuits, etc., which can solve problems such as inability to use multiple times, labor-intensive manufacturing, etc., and achieve the effect of suppressing cracking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
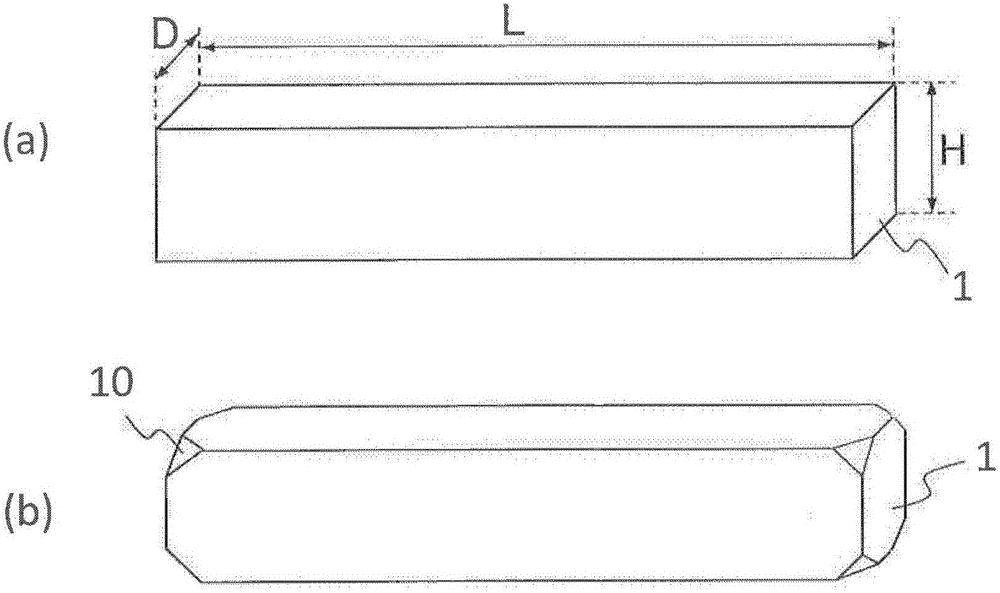
[0111] First, an R-T-B type sintered magnet with a composition ratio of Nd=22.5, Pr=7.0, Dy=0.6, B=1.0, Co=2.0, Al=0.2, Cu=0.1, Ga=0.1, and remainder=Fe (mass %) was produced. Raw material (magnet raw material P). By machining it, a cuboid R-T-B type sintered magnet raw material of 60 mm×4 mm×7 mm elongated in one direction was obtained. After that, chamfers were formed on the eight vertices of the sintered magnet raw material. The magnetic properties of the prepared R-T-B type sintered magnet raw materials were measured by a B-H tracer. As a result, the coercivity H in the properties after heat treatment (500°C) cJ 1100kA / m, residual magnetic flux density B r It is 1.42T.
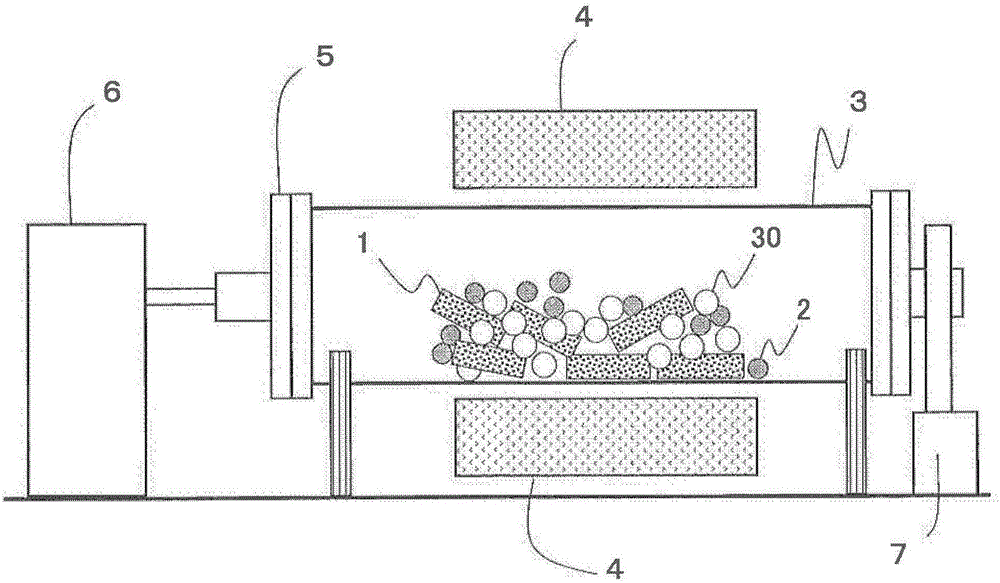
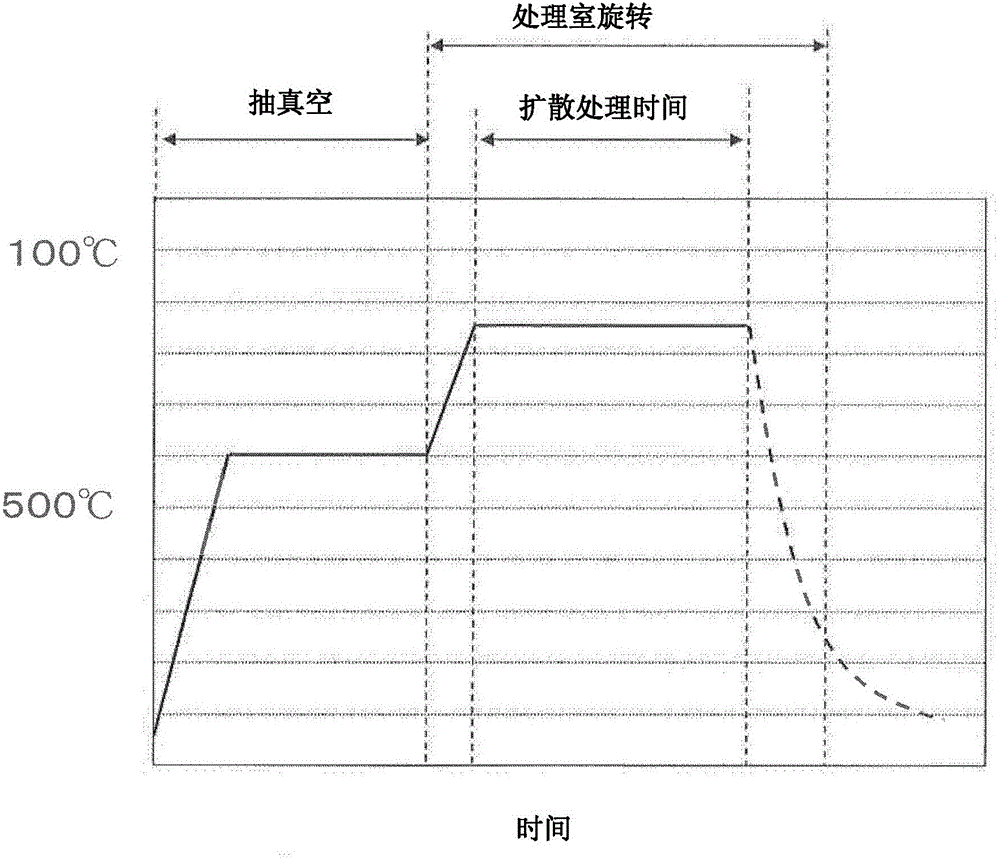
[0112] Next, use figure 2 The device is subjected to RH diffusion treatment. The inner diameter of the cylinder: about 300mm, the length of the cylinder: about 500mm, the input amount of the R-T-B type sintered magnet raw material: 5kg, the input weight of the RH diffusion source: 10kg, and the input...
experiment example 2
[0130]At first, make the R-T-B type sintered magnet raw material (in the table, magnet raw material Q ). By machining it, a cuboid R-T-B type sintered magnet raw material of 60 mm×4 mm×7 mm elongated in one direction was obtained. The magnetic properties of the prepared R-T-B type sintered magnet raw materials were measured by a B-H tracer. As a result, the coercivity H in the properties after heat treatment (500°C) cJ 1000kA / m, residual magnetic flux density B r It is 1.42T.
[0131] Next, diffusion treatment was performed using the same apparatus as in Experimental Example 1. Table 1 shows the conditions related to the type and input amount of the stirring auxiliary parts. The heat treatment conditions such as the heating mode, the atmosphere in the treatment chamber, the rotation speed of the treatment chamber, etc. are the same as those in Experimental Example 1.
[0132] The results of the experiments, the calculated chipping occurrence rates, and the measured magnet...
experiment example 3
[0139] Next, use TbFe as the RH diffusion source 3 (RH diffusion source β in the table) instead of DyFe 2 conduct experiment. The conditions of this example except using TbFe as RH diffusion source 3 instead of DyFe 2 Except for this point, the conditions were the same as those of Experimental Example 1. The detailed conditions are shown in Table 4.
[0140] H after diffusing the RH at 37 from the sample with only φ5 cJ The coercive force H within ±1% of the value of 1966kA / m cJ In the case of "○", the coercive force H will exceed -1% cJ The case of "×". The method of defect determination is the same as that of Experimental Example 1.
[0141] As shown in Table 4 below, the same effects as Experimental Example 1 were obtained in this Experimental Example. Therefore, it can be seen that according to the embodiment of the present invention, the effect is exerted regardless of the composition of the RH diffusion source.
[0142] In addition, it can be seen that the inc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com