Amifostine slow-release microspheres for subcutaneous injection and preparation method thereof
A technology of using amifostine and slow-release microspheres, which is applied in the directions of non-active ingredient medical preparations, medical preparations containing active ingredients, and pharmaceutical formulas, can solve the problem that the advantages of sustained-release preparations are discounted, amifostine Rapid gushing and other problems, to overcome the uneven release of subcutaneous injection, solve unfavorable factors, and achieve the effect of long-acting drug release
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0026] The invention provides a method for preparing amifostine sustained-release microspheres for subcutaneous injection, comprising the following steps:
[0027] Step 1, dissolving amifostine in dimethyl sulfoxide to obtain amifostine solution S;
[0028] Step 2, dissolving the biodegradable polymer material in an organic solvent to obtain an oil phase O;
[0029] Step 3, preparing 1-4% polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution as the water phase W;
[0030] Step 4, transfer the amifostine solution S obtained in the step 1 into the oil phase O obtained in the step 2, and emulsify with a ultrasonic emulsifier to obtain an S / O type primary emulsion;
[0031] Step 5, inject the primary emulsion S / O obtained in step 4 into the water phase W prepared in step 3, and emulsify with an ultrasonic emulsifier to obtain a S / O / W type secondary emulsion;
[0032] Step 6, centrifuge the S / O / W type secondary emulsion obtained in step 5 at a speed of 300-900rpm for 1-10 hours; then centrifuge at ...
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Preparation of amifostine sustained-release microspheres for subcutaneous injection
[0035]In this embodiment, the degradable polymer material is poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA), and the organic solvent is dichloromethane. Dissolve 20 mg of amifostine in 0.5 ml of dimethyl sulfoxide to obtain amifostine solution S; dissolve 100 mg of PLGA in 3 ml of dichloromethane to form oil phase O; dilute and prepare 2% polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution as the water phase W; transfer the obtained amifostine solution S into the oil phase O obtained in step 2, emulsify with a ultrasonic emulsifier to obtain an S / O primary emulsion, then inject it into the water phase W with a glass syringe, and perform ultrasonic emulsification Emulsified with a device to obtain S / O / W type secondary emulsion; then the S / O / W type secondary emulsion was centrifuged at a speed of 500rpm for 4 hours; then centrifuged at a speed of 4000rpm for 15 minutes to obtain precipitated microspheres...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2 Morphological determination of amifostine sustained-release microspheres for subcutaneous injection
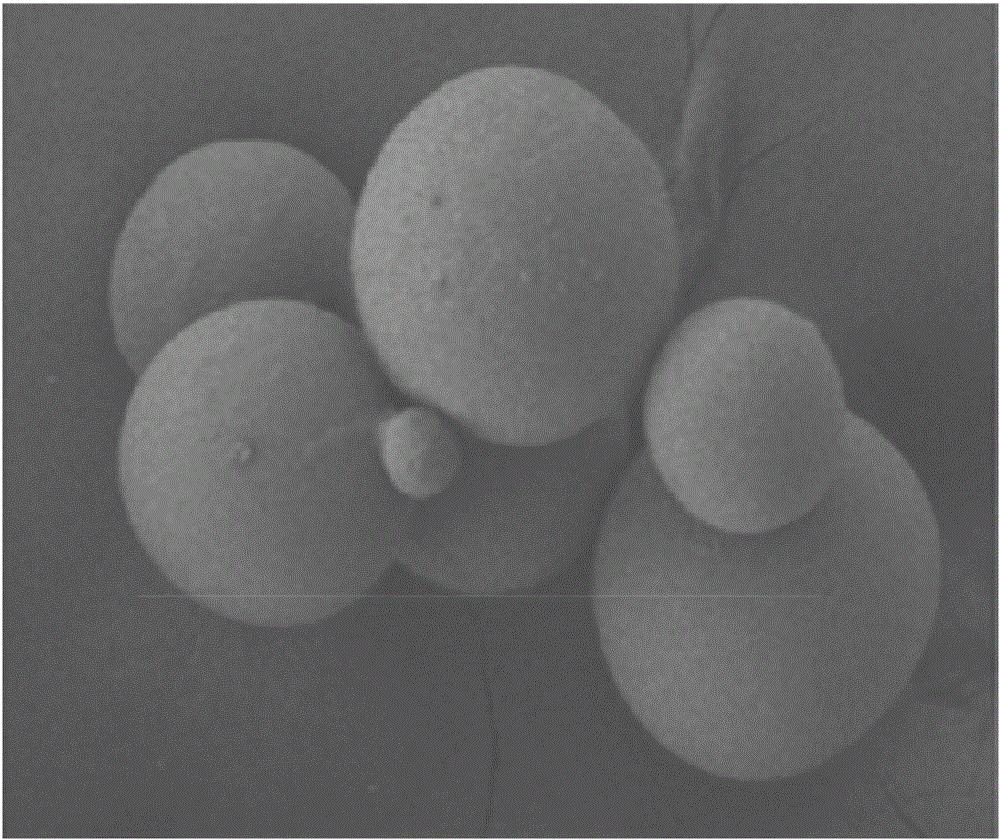
[0037] The surface morphology of the sustained-release microspheres prepared in Example 1 was observed with a scanning electron microscope. like figure 1 As shown, the surface of the amifostine sustained-release microspheres prepared in Example 1 is quite smooth, with only some small depressions (related to the evaporated organic solvent during the drying process).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com