Method for detecting exosome GPCI protein
An exosome and protein technology, applied in the field of biotechnology detection, can solve the problems of a large number of samples, unsuitability for clinical promotion, and high price of flow cytometry, and achieve the effect of small sample size, low equipment cost, and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
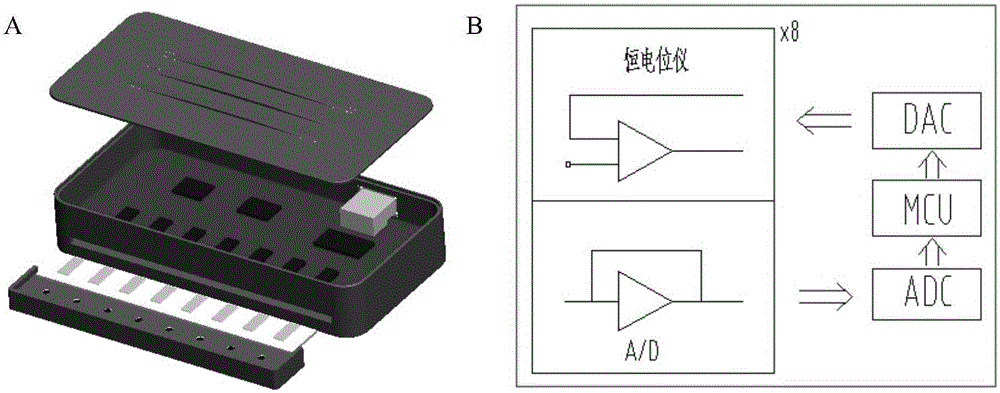
[0039] Embodiment 1 Magnetic force-electrochemical sensor device
[0040] (1) Device introduction
[0041] The device has 8 independent channels ( figure 1 A). Each channel has a potentiostat capable of measuring current in the ±7.5µA range. The input signal is conditioned by a low-pass filter (cutoff frequency 5Hz) to suppress high-frequency noise. Eight potentiostats are connected to a digital-to-analog converter for potential control, an analog-to-digital converter for signal digitization, a multiplexer for channel selection, and a microcontroller unit for system operation ( figure 1 B). The card edge connector is used to connect the electrode box. The whole magnetic frame has eight cylindrical magnets placed under the electrode box. These magnets can enrich the magnetic beads to the sensor surface. The device can quickly read the data from each channel (each channel Time-consuming 50ms), all data can be detected and analyzed by specially designed software.
[0042] (...
Embodiment 2
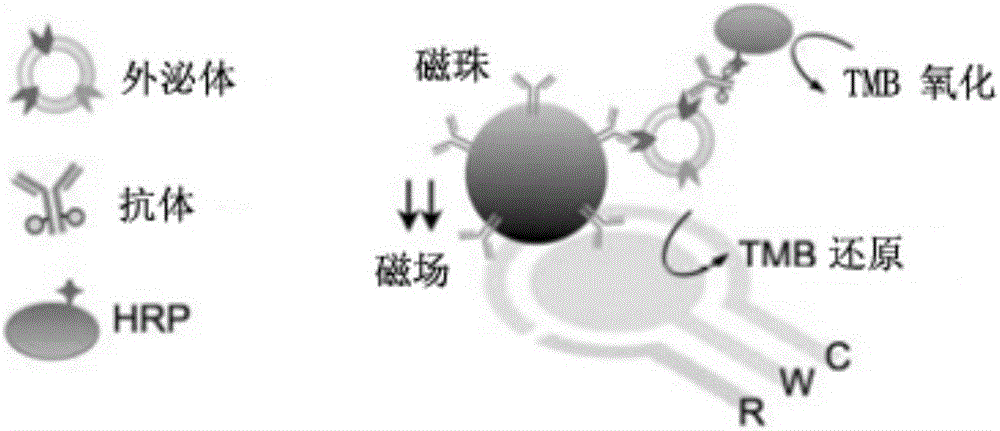
[0044] Example 2 Preparation of Immunomagnetic Beads
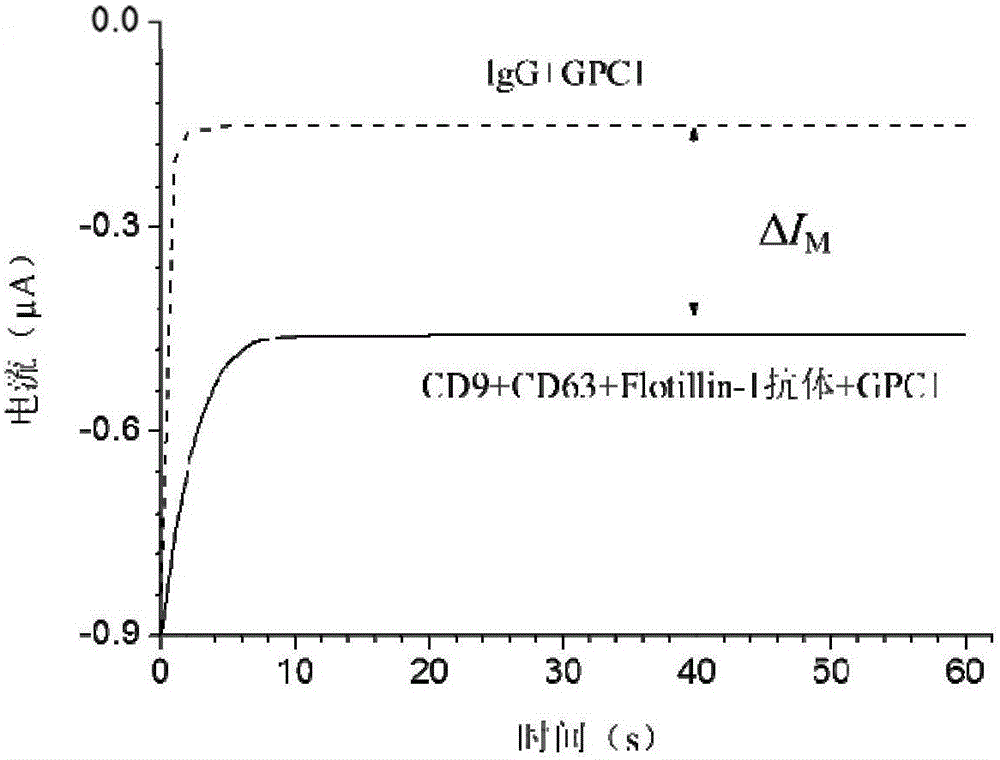
[0045] 5 mg of magnetic beads coated with epoxy groups (M-270 epoxy resin magnetic beads, diameter 2.7 μm, purchased from Invitrogen Company) were added to 1 mL of 0.1 M sodium phosphate solution, and stirred at room temperature for 10 min. Apply an external magnetic field to separate the magnetic beads, discard the solution, then add 100 μL of 0.1 M sodium phosphate solution, add 100 μg of anti-CD9 antibody, anti-CD63 antibody, anti-CD81 antibody or anti-Flotillin-1 antibody (when necessary to prepare double antibody immunomagnetic For beads, add 50 μg of each of the two antibodies; when it is necessary to prepare three-antibody immunomagnetic beads, add 33.3 μg of each of the three antibodies) and mix well (add IgG to the immunomagnetic beads as a negative control and mix well), add 100 μL Ammonium sulfate solution at a concentration of 3M, and the mixture was incubated overnight at 4°C with slow tilting rotation. The m...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3 Biotin Labeling of Anti-GPC1 Antibody
[0047] Take 100 μL of anti-GPC1 antibody with a concentration of 1 mg / mL, dilute it 10 times with PBS, then add 5 μL of sulfo-NHS-biotin solution with a concentration of 10 mM, and incubate at room temperature for 2 h. After the reaction is completed, pass through a Zeba desalting column (7K MWCO (purchased from Thermo Scientific) to remove excess sulfo-NHS-biotin to obtain 80 μg of biotin-labeled anti-GPC1 antibody. The biotin-labeled anti-GPC1 antibody was stored at 4°C for future use.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com