Mutated fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 1 and methods of use
A technology of fibroblasts and growth factors, applied in the direction of fibroblast growth factors, growth factors/inducers, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as weight gain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0429] Preparation of mutated FGF1 protein
[0430] Mutant FGF1 proteins can be prepared using known methods (eg, see Xia et al., PLoS One. 7(11):e48210, 2012). Examples are provided below.
[0431]Briefly, a mutant protein encoding FGF1 (e.g., SEQ ID NO: 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 173, 174, 175, 177, 178, 179, 181, 182, 183, 185, 186, 187, 188, 189, 191, 192, 193, 194, 195, 196, 197, 198, 199, 200, 201, 202, 203, 204, 205, 206, 207, 208, 209, 210, 211, 212, 213, 214, Any of 215, 216, 217, 218, 219, 220, 221, 222, 223, 224, 225, 226, 227, 228, 229, 230, 231, 232, 233, 234, 2...
Embodiment 2
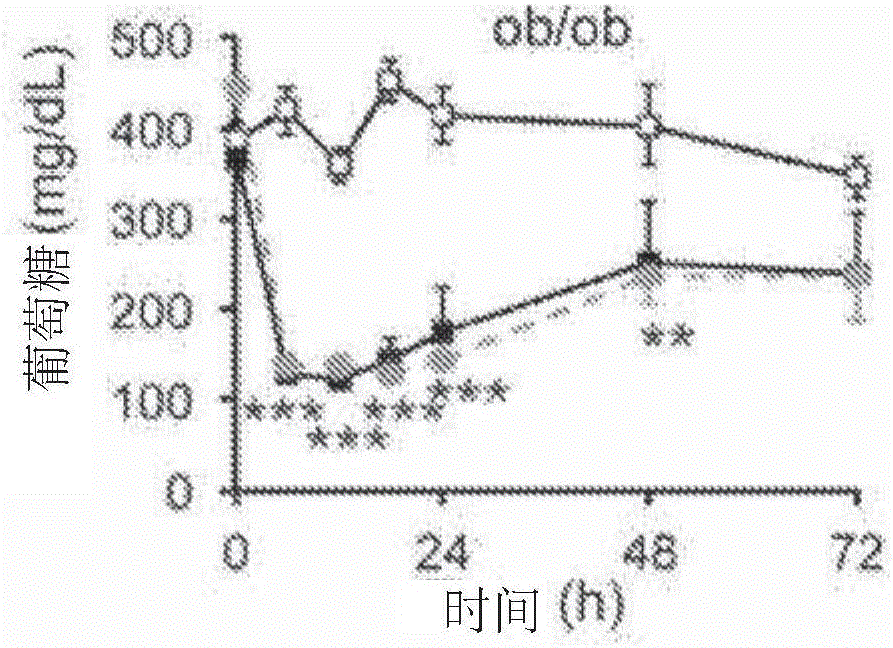
[0436] N-terminal truncated FGF1 reduces blood glucose in ob / ob mice
[0437] The inventors have demonstrated that administration of mature rFGF1 to ob / ob mice lowers blood glucose and reduces adverse effects compared to those observed with thiazolidinediones.
[0438] To separate the mitogenic effect of rFGF1 from its hypoglycemic activity, an FGF1 ligand lacking the first 24 residues at the N-terminus (rFGF1 ΔNT (SEQ ID NO: 7)). Based on the crystal structure of the FGF1-FGFR complex, the truncations are predicted to reduce the binding affinity of FGF1 for selected FGFRs, including FGFR4, and thus reduce the mitogenicity of the ligands.
[0439] animal
[0440] Mice were housed in a temperature-controlled environment with a 12-hour light / 12-hour-dark cycle and used according to regulatory protocols consistent with US law. Male ob / ob mice (B6.V-Lep ob J, Jackson Laboratories) and male C57BL / 6J mice received standard or high-fat diet (MI Laboratories Rodent Diet 5001, Harl...
Embodiment 3
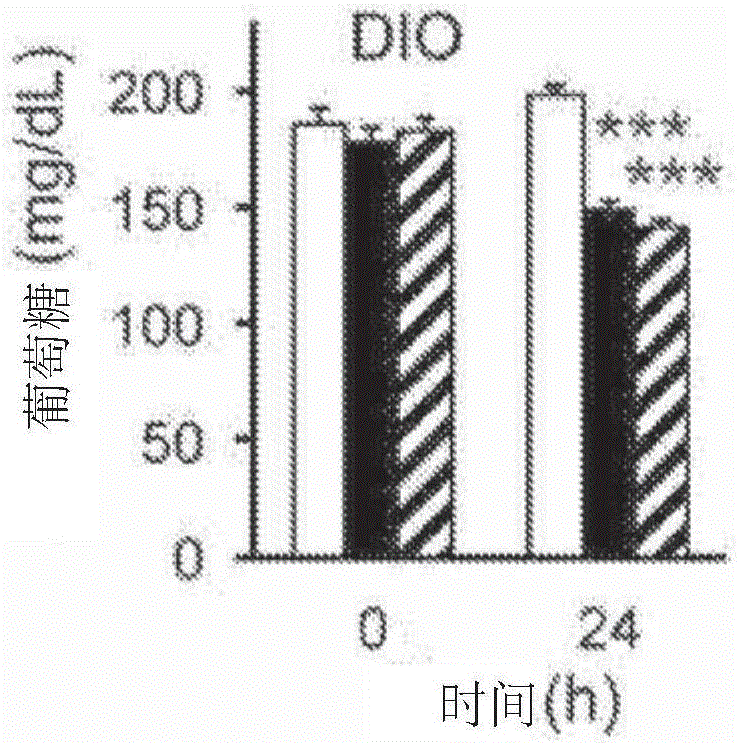
[0450] FGF1 mutant protein reduces blood sugar levels in diabetic mice
[0451] The FGF1 mutants shown in Table 3 were tested as described in Example 2.
[0452] As shown in Table 3, up to 12 N-terminal amino acids could be deleted from FGF1 without significantly affecting activity, whereas FGF1 mutants lacking 14 N-terminal amino acids failed to lower glucose in diabetic mice. Mutations that increase the thermostability of FGF1 are generally well tolerated, but glucose-lowering activity is lost in mutants with high stability. Furthermore, mutations in the putative heparan sulfate-binding site had minimal effects on the glucose-lowering effect of FGF1. Notably, the effects of N-terminal deletions and selected stabilizing mutations appeared additive.
[0453]
[0454]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com