Sodium hydroxide/sodium sulfamate aqueous solution solvent system for dissolving pulp cellulose
A technology of sodium sulfamate and sodium hydroxide, applied in the field of sodium hydroxide/sodium sulfamate aqueous solution solvent system for dissolving pulp cellulose, can solve the limitation of cellulose molecular weight and concentration, unstable cellulose solution and easy gelation and other problems, to achieve the effect of promoting dissolution and increasing viscosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
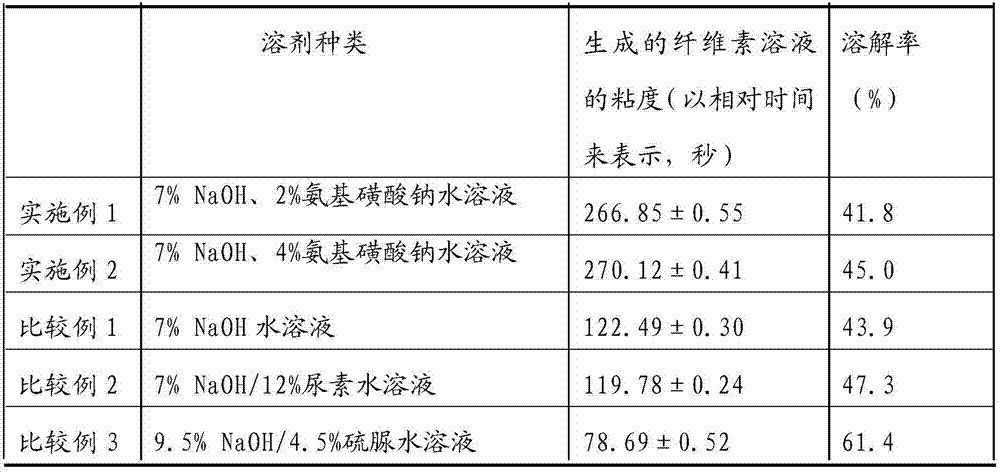
[0014] Example 1: Select sulfite process softwood dissolving pulp with a cellulose content of 97.3% and a degree of polymerization DP of 1520. Taking 2% pulp concentration as an example, add dissolving pulp and 7% NaOH into a transparent sample bottle, and then add 2% (based on the weight percentage of dry pulp) sodium sulfamate. Stir fully, disperse and swell, store in the refrigerator at low temperature (-12°C) for 2 hours, thaw and stir to obtain the dissolving pulp cellulose dissolution system, then centrifuge, extract the upper transparent cellulose solution and measure it with a 0.9-1.0 Ubbelohde viscometer Its viscosity, the size of the viscosity is expressed by the relative time passed. The undissolved part was filtered through an alkali-resistant sand core funnel, washed to neutrality, transferred to a plastic watch glass, and pressed with 2 coverslips in a wet state, and weighed after air-drying at room temperature to calculate the dissolved pulp fiber Solubilizatio...
Embodiment 2
[0015] Example 2: Acidic sulfite processed softwood dissolving pulp with a cellulose content of 97.3% and a degree of polymerization DP of 1520 was selected. Taking 2% pulp concentration as an example, add dissolving pulp and 7% NaOH into a transparent sample bottle, and then add 4% (based on the weight percentage of dry pulp) sodium sulfamate. Others were the same as in Example 1 to observe the dissolving effect of dissolving pulp cellulose.
Embodiment 3
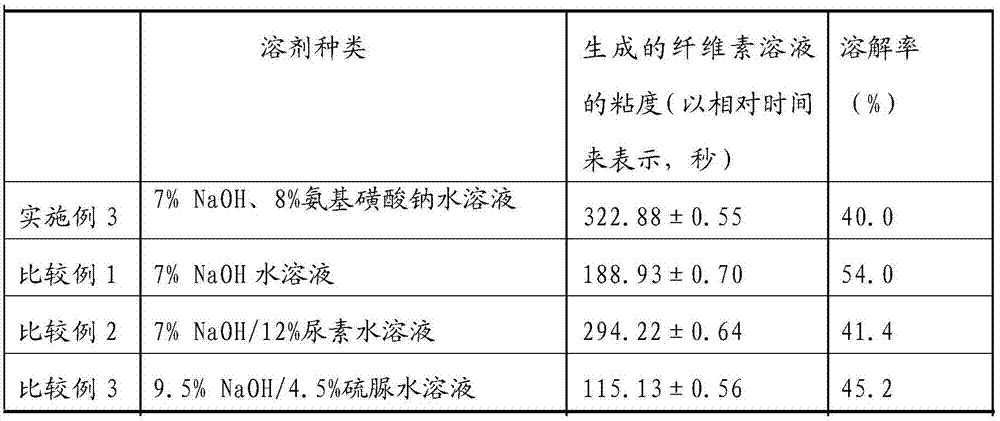
[0022] Example 3: Select pre-hydrolyzed kraft softwood dissolving pulp with a cellulose content greater than or equal to 93.55% and a degree of polymerization DP of 1190. Taking 2% pulp concentration as an example, add dissolving pulp and 7% NaOH into a transparent sample bottle, and then add 8% (based on the weight percentage of dry pulp) sodium sulfamate. Others were the same as in Example 1 to observe the dissolving effect of dissolving pulp cellulose.
[0023] Comparative example 1: only use 7% NaOH aqueous solution, do not add sodium sulfamate, other are carried out the observation of dissolving pulp cellulose dissolving effect identically with embodiment 1.
[0024] As comparative example 2, only with 7%NaOH / 12% urea aqueous solution, do not add sodium sulfamate, other carry out the observation of dissolving pulp cellulose dissolving effect identically with embodiment 1.
[0025] As comparative example 3, 9.5% NaOH / 4.5% thiourea aqueous solution, no sodium sulfamate was...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com