Piston ring and method for manufacturing same
A piston ring and chromium nitride technology, which is applied in the field of piston rings for automobile engines, can solve problems such as insufficient intermediate layers, and achieve the effects of reducing thermal stress, high heat transfer function, and excellent wear resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
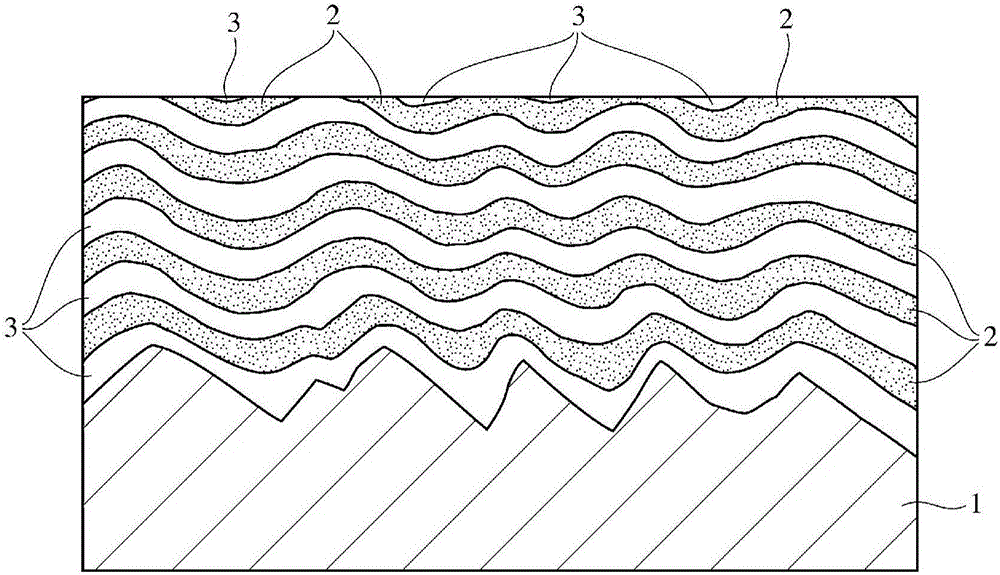
[0059] A piston ring with a rectangular cross-section having a nominal diameter (d) of 96mm, a thickness (a1) of 3.8mm, and a width (h1) of 2.5mm and a barrel-shaped outer peripheral surface is produced from a wire rod of a material equivalent to SWOSC-V. 50 of these piston rings are overlapped, and the outer peripheral surface is adjusted to Rz by sandblasting JIS A surface roughness of 1.6 μm was measured and set into the AIP unit. As the evaporation source, metallic chromium with a purity of 99.9% was used for all relative evaporation source targets. First, in an atmosphere of 1.0 Pa of Ar gas with a purity of 99.99%, a bias voltage of -900V was applied to clean the outer peripheral surface of the piston ring as the base material by bombardment treatment, and then in order to improve the adhesion between the base material and the base layer, Only the metal Cr layer is formed into a film.
[0060] (formation of basal layer)
[0061] As the base layer of embodiment 1, the ...
Embodiment 2~6
[0086] In Examples 2 to 6, as in Example 1, an underlayer including a CrN / Cr laminate film was formed by ion plating under the film formation conditions shown in Table 1. Table 1 also shows the film formation conditions of Example 1 together. In addition, the film-forming conditions not described in Table 1 were set to be the same as Example 1. The formation time of the CrN layer and the Cr layer of setting embodiment 2 is shorter than embodiment 1, and embodiment 3 improves the N when the CrN layer is formed. 2 Divide the pressure and reduce the bias to make a relatively porous CrN layer. In addition, in Examples 4, 5 and 6, the formation time of the CrN layer and the Cr layer is prolonged to make a thicker laminated unit thickness. In Example 4, the formation time of the CrN layer was extended to be longer than the formation time of the Cr layer, and the ratio of the Cr layer was reduced.
[0087] [Table 1]
[0088]
[0089] For the base layer including the CrN / Cr lam...
Embodiment 7
[0100] In Example 7, a base layer including a CrCN / Cr laminate film was formed in the same manner as in Example 1 except that a CrCN layer was used instead of the CrN layer. Here, the process gas used for the formation of the CrCN layer is N 2 Gas 0.87Pa, CH 4 Gas 0.54Pa and Ar gas 0.09Pa. In Example 8, the formation time of the CrCN layer in Example 7 was made longer than that of the Cr layer, that is, the formation time was set to 0.9 minutes and 0.6 minutes, respectively, and the ratio of the Cr layer was reduced. Furthermore, the film-forming time was changed to reduce the thickness of the intermediate layer and the hard amorphous carbon film. The film-forming conditions of the base layer are shown in Table 5, the results of the film thickness measurement and X-ray diffraction measurement of the base layer are shown in Table 6, the film-forming conditions of the intermediate layer and the amorphous hard carbon film are shown in Table 7, Table 8 shows the results of meas...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com