Method for casting grain structure numerical value prediction
A numerical prediction and organization technology, applied in complex mathematical operations, electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as large amount of calculation and long calculation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0043] A method for numerical prediction of casting grain structure, characterized in that it comprises:
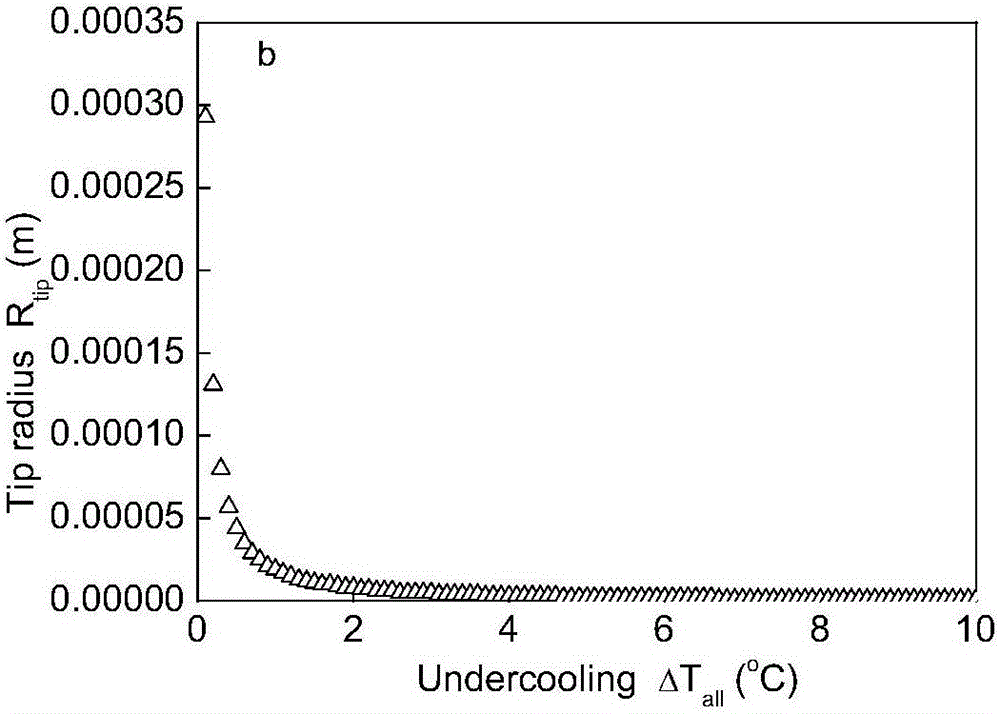
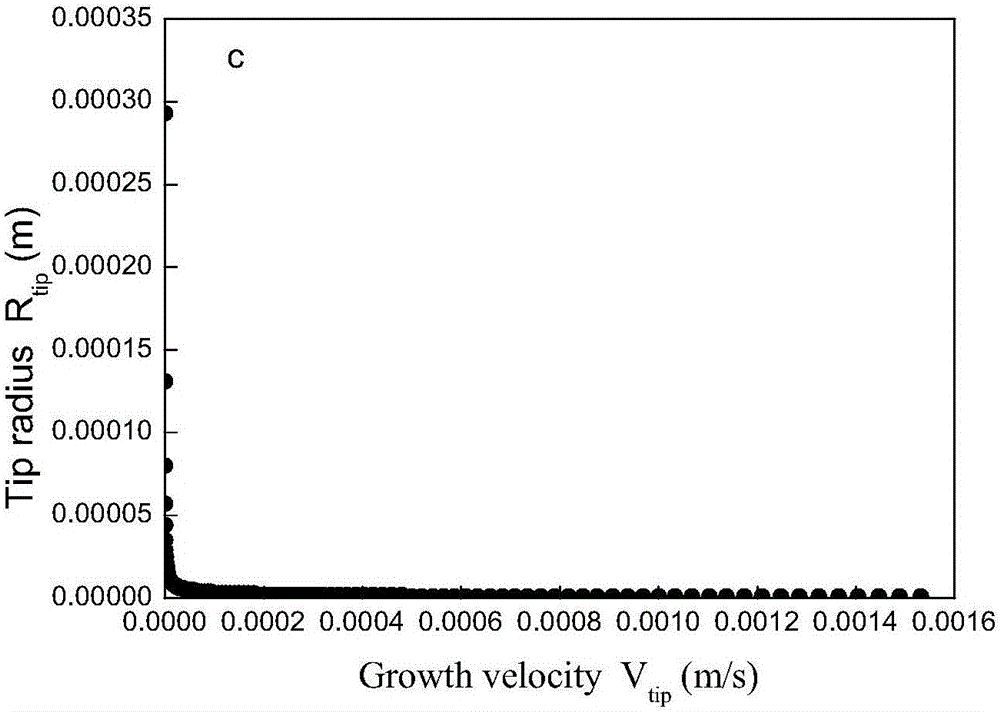
[0044] Step 1. Solve the KGT (Kurz-Giovanole-Trivedi) model of dendrite growth kinetics to obtain the dendrite tip radius-dendrite tip growth rate change curve;
[0045] The KGT model is a nonlinear model, which is solved by an iterative algorithm. The specific process is as follows:
[0046] Step 1 (1), set the change range of the melt supercooling degree, increase from 0°C to 10°C, increase 0.1°C each time, the melt supercooling degree changes 100 times, for the ti-th calculation, the melt supercooling degree is defined as ΔT all [ti], 1≤ti≤100;
[0047] Step 1 (2), when the melt subcooling degree is ΔT all When [ti], set the total number of iterative calculations to NI; set an iterative calculation to ni, and 1≤ni≤NI;
[0048] When performing the iterative calculation of the nith time, the iterative solution order of the equations in the KGT model is:
[0049] ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0070] The specific process of step five described in this embodiment is as follows:
[0071] Step five (1), calculate the energy conservation equation:
[0072] h s =c pL T
[0073] h l =c pL T+ΔH
[0074] [H]=f s h s +(1-f s )h l
[0075] ∂ [ H ] ∂ t + ▿ · ( f l U l h l ) = λ l ▿ · ( ▿ T )
[0076] where: h s and h l Respectively solid phase and liquid phase enthalpy (J / kg), c pL is the specific heat of liquid (J / kgK), λ l is the liquid thermal conductivity (W / m K), ΔH is the latent heat of crystallization (J / kg), f s ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0092] The specific process of step five (four) described in the present embodiment is as follows:
[0093] search computation grid(i, j) chan=0 Left, right, top, and bottom four grids, respectively (i-1, j) chan=0 , (i+1,j) chan=0 , (i, j+1) chan=0 and (i,j-1) chan=0 , examine f s value;
[0094] if 0 s [i,j]s [i+1, j]=0, the label is (i, j) chan=0 It is at the front of solidification, and the solidification direction is from left to right. flag[i,j]=1;
[0095] if 0 s [i,j]s [i-1, j]=0, the label is (i, j) chan=0 At the front of solidification, the solidification direction is from right to left, flag[i,j]=1;
[0096] if 0 s [i,j]s [i, j+1]=0, the label is (i, j) chan=0 It is at the front of solidification, and the solidification direction is from bottom to top. flag[i,j]=1;
[0097] if 0 s [i,j]s [i, j-1]=0, the label is (i, j) chan=0 It is at the front of solidification, and the solidification direction is from top to bottom. flag[i,j]=1;
[0098...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com