Production process for biologic mycelium material
A production process and bio-based technology, applied in the field of bio-based mycelium material production, can solve the problems of EPS board not easy to degrade and environmental pollution, and achieve the effect of no pollution and low energy consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
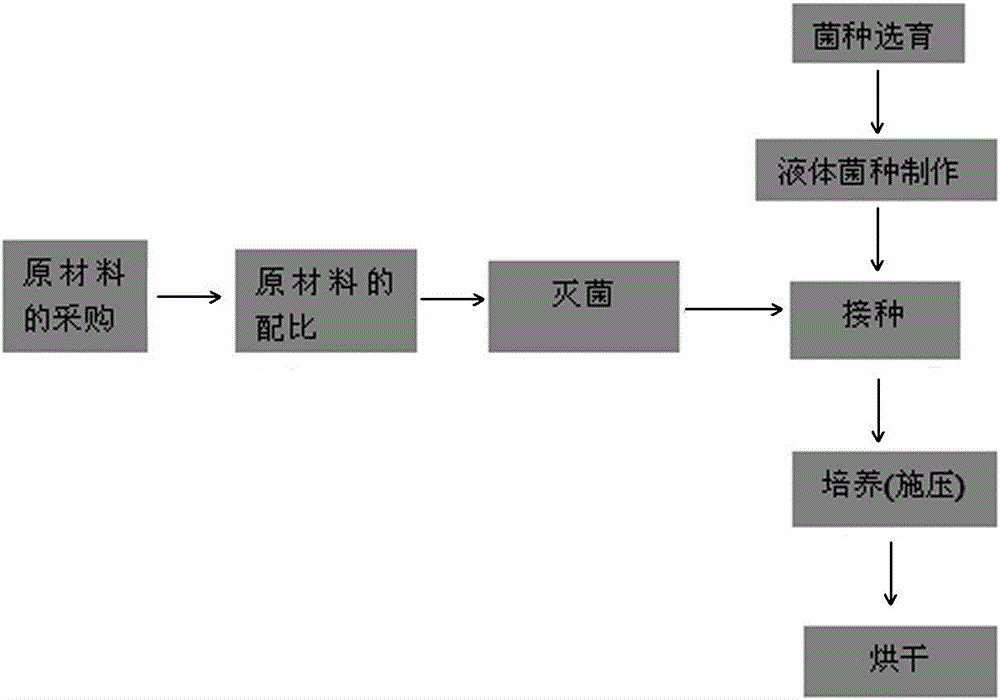
[0026] A production process of a bio-based mycelium material, comprising the following steps:
[0027] (1) Preparation of cultivation substrate: The cultivation substrate is composed of the following components by weight percentage: 92% corn stalks, 4% corn flour, and 4% bran. Corn stalks are crushed to a particle size of 1 cm and mixed with corn flour, Mix the bran, then add water to adjust the water content to 30%, mix well, put the cultivation substrate into a mold with a size of 13.2cm*26cm*3.5cm, sterilize it at high temperature and cool it down to room temperature for use;
[0028] (2) Inoculation: In a sterile environment, insert the oyster mushroom strain into the cultivation medium, and then move it into the cultivation room for cultivation;
[0029] (3) Cultivation: Cultivate for 20 days under the conditions of temperature less than 25 degrees, humidity less than 70%, dark, sterile, and well ventilated.
[0030] (4) Drying: Remove the culture room, take the material...
Embodiment 2
[0032] A production process of a bio-based mycelium material, comprising the following steps:
[0033] (1) Cultivation substrate preparation: 46% corn stalks, 46% hardwood sawdust, 4% corn flour, 4% bran, crush corn stalks and hardwood sawdust to a particle size of 1 cm and mix with corn flour, Mix the bran, then add water to adjust the water content to 30%, mix well, put the cultivation substrate into a mold with a size of 13.2cm*26cm*3.5cm, and cool it down to room temperature for use after high-temperature sterilization;
[0034] (2) Inoculation: In a sterile environment, insert the oyster mushroom strain into the cultivation medium, and then move it into the cultivation room for cultivation;
[0035] (3) Cultivation: Cultivate for 15 days under conditions of temperature less than 25 degrees, humidity less than 70%, dark, sterile, and well ventilated.
[0036] (4) Drying: Remove the culture room, take the material out of the mold and dry it until the moisture content is le...
Embodiment 3
[0038] A production process of a bio-based mycelium material, the steps are the same as in Example 1, the difference is that in step (3) the carbon dioxide is preferably controlled at 8000PPM and the light is less than 50 lux during the cultivation, and the cultivation is carried out for 17 days.
[0039] Conclusion: The bio-based mycelium material produced by the implementation of Case 1-3 has a neat appearance, uniform, dense and pollution-free mycelium growth; the product specifications are uniform, the weight is basically the same, and the specific density and size are respectively: 0.104g / cm 3 ,13.2cm*26cm*3.5cm; 0.142g / cm 3 ,13.2cm*26cm*3.5cm;
[0040] 0.142g / cm 3 ,13.2cm*26cm*3.5cm.
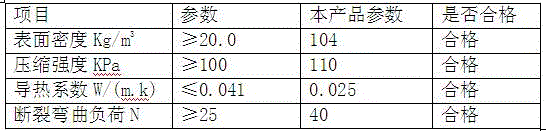
[0041] After testing, the comparison results with "GB / T6343-1995", "GB / T8813-1988" and "GB / T8812-1988" are as follows:
[0042]
[0043] The above comparison results show that the bio-based mycelium material prepared by this process can completely replace EPS foam products.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com