Treatment system for removal of COD (chemical oxygen demand) in industrial waste water
A technology for industrial wastewater and treatment systems, applied in multi-stage water treatment, aerobic process treatment, water treatment parameter control, etc., can solve the problems of complex operation, high operating costs, poor adaptability to ambient temperature, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
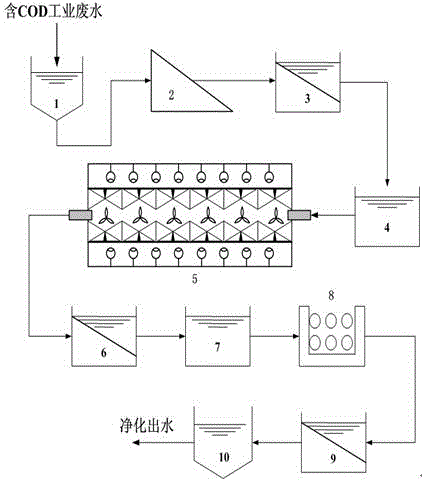
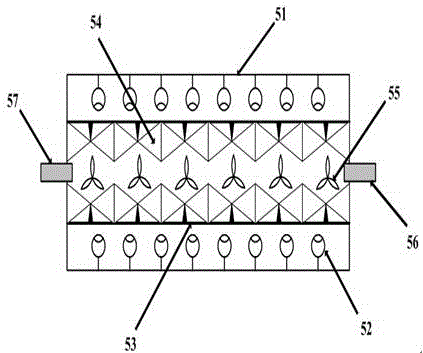
[0021] Such as figure 1 The shown treatment system for removing COD in industrial wastewater includes a water collection well 1, a coarse grid 2, a primary sedimentation tank 3, a pH value adjustment tank 4, a nano-microporous ultrasonic intermittent polymerization reaction tank 5, and a secondary sedimentation tank 6 , aeration nitrification tank 7, biological denitrification tank 8, tertiary sedimentation tank 9, water purification tank 10; wherein the industrial wastewater containing COD enters the water collection well 1 through the waste water pipeline, where centralized collection and preliminary stable adjustment are carried out, and the water collection well 1 The outlet of the coarse grid 2 is connected to the coarse grid 2 through the wastewater pipeline, where the large-diameter solid matter in the industrial wastewater is removed, and the outlet of the coarse grid 2 is connected to the primary sedimentation tank 3 through the wastewater pipeline, where the insoluble...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com