Wheat stem rust resistance gene
A wheat straw and resistance technology, applied in genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, plant peptides, etc., can solve the problem of wheat stem rust R gene not being cloned
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
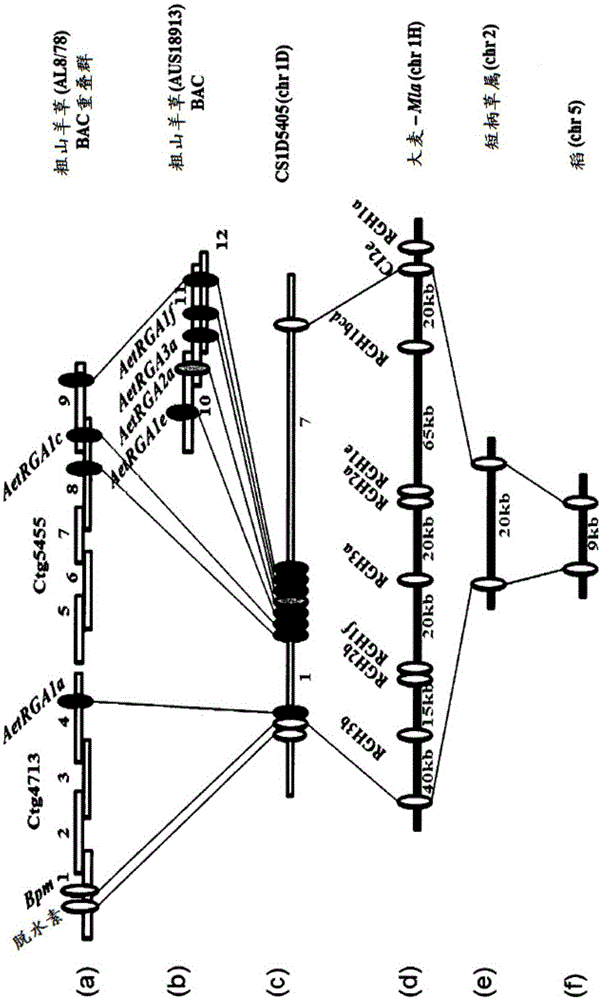
[0285] Example 1. Genetic mapping of Sr33
[0286] Obtained Wheat Variety CS1D5405 Containing the Sr33 Gene - CS1D5405 is Inheritance of a Single Chromosomal Substitution in which Chromosome 1D of the Reference Wheat Genotype China Spring (CS) was replaced by the corresponding Chromosome from the Rattlesnake Grass Variety (RL5288) (donor of Sr33) germplasm line. Wheat leaves were infected with stem rust Puccinia graminearum pathogenic types 34-1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 11 (Plant Breeding Institute culture no. 171, Cobbity, NewSouth Wales, Australia) and histologically examined to determine The Sr33 resistance response was compared to that conferred by the strong response gene Sr45 (also derived from A. tachyphylla and introgressed into hexaploid wheat). In hexaploid wheat leaves collected 5 days post inoculation (dpi), larger infection sites were observed in plants containing Sr33 compared to infected plants containing the Sr45 gene.
[0287] To investigate the potential mode o...
Embodiment 2
[0296] Example 2. Mutagenesis and isolation of Sr33 mutants
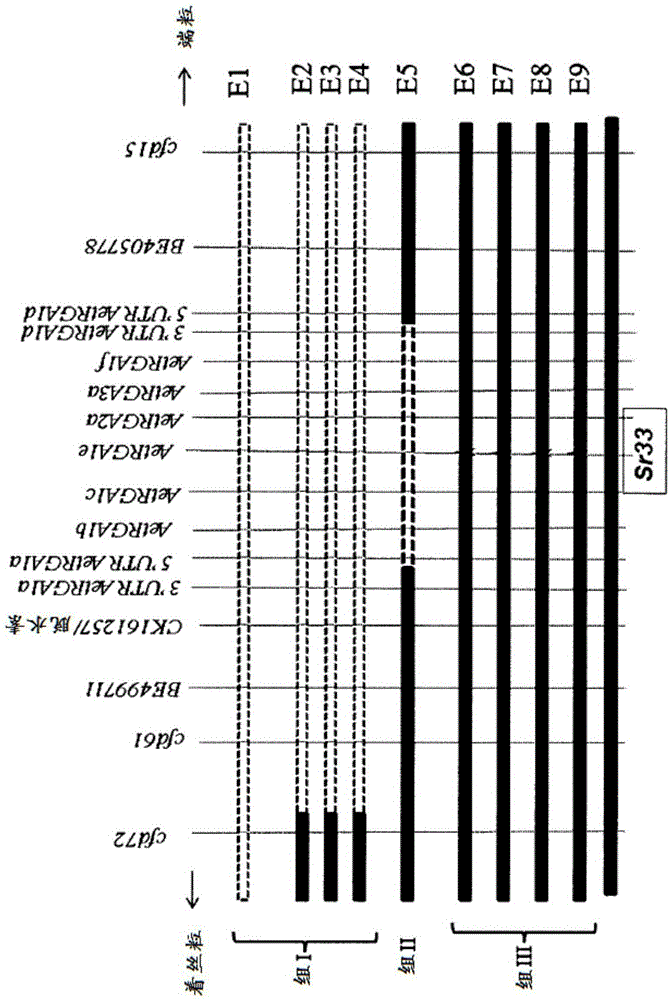
[0297] In order to identify which candidate gene is Sr33, if any of them are indeed Sr33, a mutation method is performed. Mutant lines were generated by treating 2000 seeds of CS1D5405 with ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) (Mago et al., 2005). 850 M2 plants from the mutagenized lines were challenged with rust strains with pathotypes 34-1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 11 to screen them for the Sr33 phenotype. Nine susceptible mutants were identified from the EMS-treated population, which were used to identify gene members responsible for stem rust resistance function as follows.
[0298] Based on chromosome 1D-specific markers, 4 of the mutants (E1 to E4; group I) were identified to carry large deletions in chromosome 1D, while 1 mutant (E5; group II) had loss of AetRGA1b, AetRGA1c, AetRGA1e Short deletions of , AetRGA2a and AetRGA3a genes ( figure 2 ). These 5 mutants were not used to identify the Sr33 gene. In contrast, t...
Embodiment 3
[0303] Embodiment 3. Structure and expression of Sr33 gene and polypeptide
[0304] The genomic sequence of Sr33 has 6 exons and 5 introns, as predicted by RT-PCR and 5' and 3' RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends) reactions. The structure of the gene is schematically shown in Figure 4 , and the gene sequence is provided as SEQ ID NO:5. Exon 1 spans nucleotides 1226 to 1299 of SEQ ID NO: 5, exon 2 spans nucleotides 1389 to 1511, exon 3 spans nucleotides 2238 to 3080, and exon 4 spans nucleotides 4155 to 6157, exon 5 spans nucleotides 6266 to 6344 and exon 6 spans nucleotides 6824 to 7233.
[0305] Pathogen resistant Sr33 polypeptides (SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2) are CC-NB-LRRs containing polypeptides with the following motifs: coiled-coil, EDVID, hhGRExe, WalkerA, WalkerB, RNBS-B, RNBS-C, GLPL, RNBS-D, MHD and LRR. The coiled-coil region generally extends from amino acid residues 1-160 of SEQ ID NO:1. The NB domain generally extends from amino acid residues 161 to 5...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com