Ginseng leaf extractive manufacturing method and cosmetic composition comprising ginseng leaf extractive serving as effective ingredient
A manufacturing method and technology of ginseng leaves, applied in the direction of medical preparations containing active ingredients, cosmetics, drug combinations, etc., can solve the problems of wrinkles, decreased skin elasticity, etc., and achieve the improvement of skin fine lines, high extraction rate, excellent anti-aging The effect of the aging effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1: the manufacture of sand-fried ginseng leaf extract
[0037] Mix 600 g of ginseng leaves that have been dried in the shade and remove impurities, and clean sea sand (SeaSand) with a similar volume ratio that can fully bury the ginseng leaves, and heat at 100-160°C while stirring. At this time, when the surface of the original yellow-green medicinal material turns brown, stop heating, cool at room temperature, and make sand-fried ginseng leaves. Shake off the sea sand, select only processed ginseng leaves, put in 10L alcohol ethanol as solvent, reflux extraction at 70°C for 3-6 hours, filter under reduced pressure, concentrate the filtrate under reduced pressure in a water tank at 40°C to obtain concentrated Ethanol sand fried ginseng leaf extract.
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2: Manufacture of vinegar-baked ginseng leaf extract
[0039] After fully absorbing 600 g of ginseng leaves dried in the shade and removing impurities, an acetic acid aqueous solution containing 4 to 6% of acetic acid (acetic acid) having an acid ratio similar to vinegar, was heated at 100 to 160° C. while stirring. At this time, when the surface of the original yellow-green medicinal material turns brown, stop heating, cool at room temperature, and make vinegar to roast ginseng leaves. The manufactured processed product is put into 10L alcohol ethanol as a solvent, refluxed at 70°C for 3-6 hours, filtered under reduced pressure, and the filtrate is concentrated under reduced pressure in a water tank at 40°C to obtain concentrated ethanol-vinegar roasted ginseng leaf extract.
experiment example 1
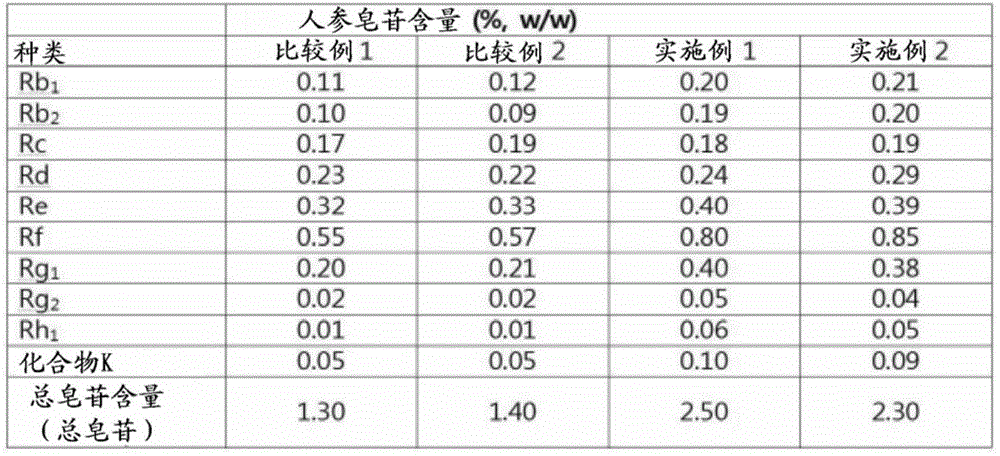
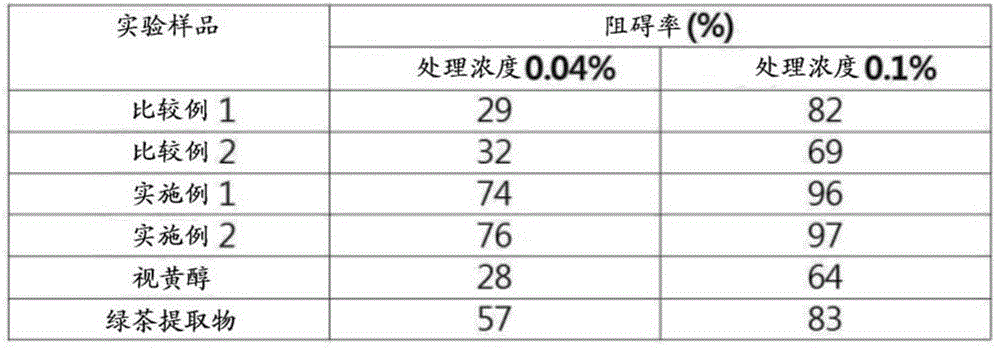
[0044] [Experimental Example 1: Composition confirmation and content experiment of sand-fried ginseng leaf extract (Example 1) and vinegar-roasted ginseng leaf extract (Example 2)]
[0045] In order to confirm the main properties of the sand-fried ginseng leaf extract of Example 1, the vinegar-roasted ginseng leaf extract of Example 2, the ginseng leaf raw product extract and the ginseng leaf carbon extract obtained in Comparative Example 1 and Comparative Example 2 for comparison, Quantitative analysis of phenolic substances in the ingredients and changes in total phenolic content and ginsenoside content were performed as follows.
[0046] (1) Quantitative analysis of phenolic substances
[0047] Add 1-2 drops of 2.5% FeCl to the solution obtained by dissolving each extract in ethanol 3 Place it in the ethanol solution, and observe whether the color is dark green or a precipitate is formed.
[0048] (2) Analysis of total phenol content
[0049] 10 ml of distilled water was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com