Method for preparing difluoro piperonal by utilizing continuous flow microchannel reactor
A technology of difluoropiperonal and channel reactor, which is applied in the direction of organic chemistry, can solve the problems of complex reaction operation process, high energy consumption of the system, and high temperature control requirements, so as to improve reaction efficiency, reduce production energy consumption, and save cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
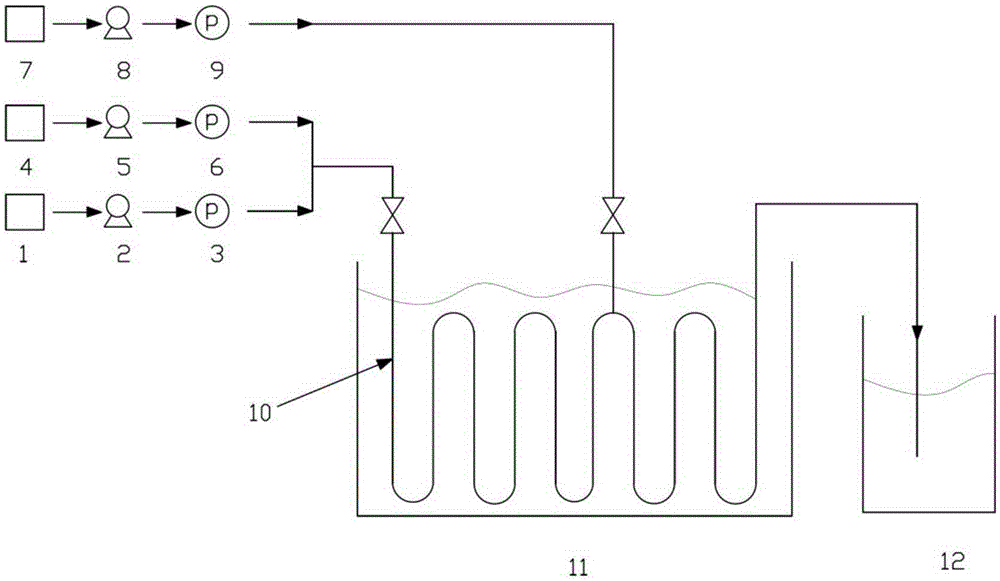
[0027] (1) The device used: a continuous flow microchannel reactor, and the number of reaction modules is determined according to the flow rate and residence time of the reaction solution.
[0028] (2) Raw material storage tanks 1 and 4 are respectively tetrahydrofuran solution (mass fraction 15%) of difluoropipercycline and n-hexane solution (2.7M) of n-butyllithium, and the flow rate of tetrahydrofuran solution of difluoropipercycline is controlled by a metering pump The flow rate of n-butyl lithium in n-hexane is 50mL / min, and the flow rate of n-butyllithium in n-hexane is 18mL / min. It is injected into the precooling module of the microchannel reactor and precooled at -15°C; after precooling, it enters the first mixing module of the microchannel reactor for reaction. Reaction temperature -15°C, residence time 7.1s.
[0029] (3) React the effluent of the first mixing module with N,N-dimethylformamide in the second mixing module, and control the flow rate of N,N-dimethylforma...
Embodiment 2
[0032] (1) The device used: a continuous flow microchannel reactor, and the number of reaction modules is determined according to the flow rate and residence time of the reaction solution.
[0033] (2) Raw material storage tanks 1 and 4 are respectively tetrahydrofuran solution (mass fraction 15%) of difluoropipercycline and n-hexane solution (2.7M) of n-butyllithium, and the flow rate of tetrahydrofuran solution of difluoropipercycline is controlled by a metering pump The flow rate of n-butyllithium n-hexane solution is 33mL / min, and the flow rate of n-butyllithium n-hexane solution is 12mL / min. It is injected into the precooling module of the microchannel reactor and precooled at -15°C; after precooling, it enters the first mixing module of the microchannel reactor for reaction. Reaction temperature -15°C, residence time 10.7s.
[0034] (3) React the effluent of the first mixing module with N,N-dimethylformamide in the second mixing module, and control the flow rate of N,N-d...
Embodiment 3
[0037] (1) The device used: a continuous flow microchannel reactor, and the number of reaction modules is determined according to the flow rate and residence time of the reaction solution.
[0038] (2) Raw material storage tanks 1 and 4 are respectively tetrahydrofuran solution (mass fraction 20%) of difluoropipercycline and n-hexane solution (1.8M) of n-butyllithium, and the flow rate of tetrahydrofuran solution of difluoropipercycline is controlled by a metering pump The flow rate of the n-butyllithium n-hexane solution is 75mL / min, and the flow rate of the n-butyl lithium n-hexane solution is 58mL / min, which is injected into the precooling module of the microchannel reactor and precooled at -15°C; after precooling, it enters the first mixing module of the microchannel reactor for reaction. Reaction temperature -15°C, residence time 3.6s.
[0039] (3) React the effluent of the first mixing module with N,N-dimethylformamide in the second mixing module, and control the flow ra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com