Biological ink for 3D printing
A bio-ink, 3D printing technology, applied in the field of ink, can solve the problems of difficult to take into account the cytocompatibility, biological activity and mechanical properties, mechanical properties of scaffolds, poor simulation and stability, inability to mix printing, etc., to achieve excellent biological Compatibility, good structural stability, reduced shrinkage or swelling effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
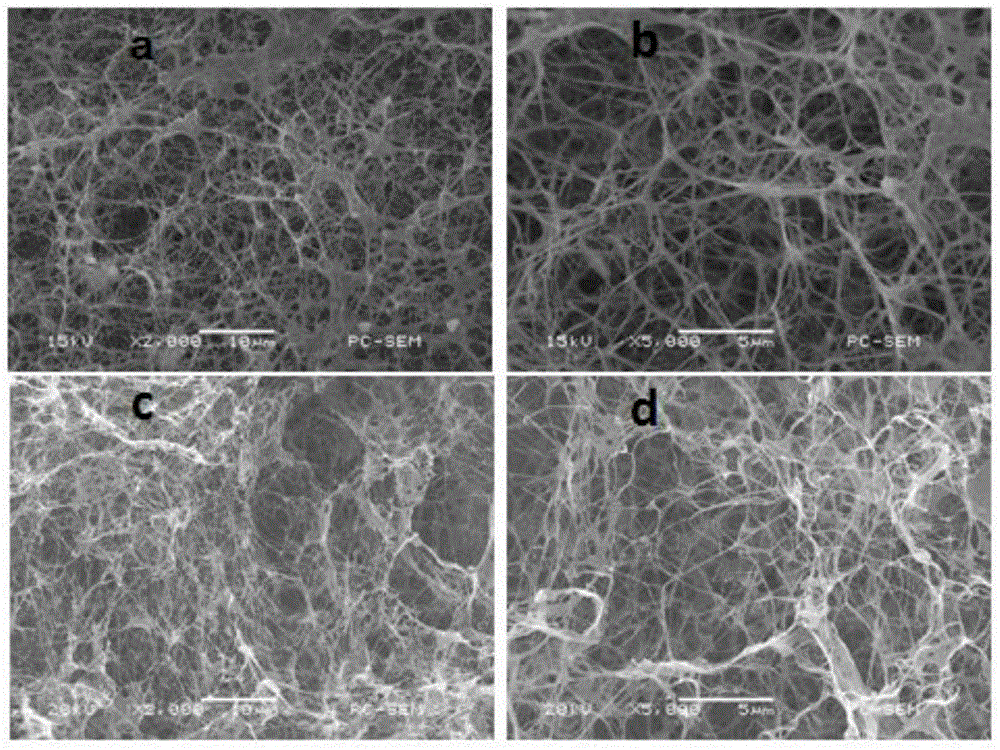
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] A bio-ink for 3D printing is composed of polyether ester, hyaluronic acid, bioactive components, cross-linking initiators and solvents. The bioactive components of this embodiment use acellular matrix, and its preparation method is as follows:
[0027] (1) Use water-soluble PEG to initiate TMC polymerization to obtain PTMC-PEG-PTMC triblock polyether ester copolymer, and modify the end group with double bonds to obtain water-soluble polyether ester PFMC;
[0028] (2) modifying the hydroxyl group of hyaluronic acid with a double bond to obtain a water-soluble natural polymer with a cross-linking function;
[0029] (3) decellularizing the nerve tissue by a decellularization method to obtain decellularized nerve tissue, and pulverizing the decellularized nerve tissue to obtain a water-soluble decellularized nerve matrix material;
[0030] (4) Take 0.5% decellularized matrix powder by mass fraction and digest it with pepsin hydrochloric acid solution (i.e. digestive juice) ...
Embodiment 2
[0033]A bio-ink for 3D printing is composed of polyether ester, hyaluronic acid, bioactive components, cross-linking initiators and solvents. The bioactive components of this embodiment use acellular matrix, and its preparation method is as follows:
[0034] (1) Use water-soluble F127 to initiate TMC polymerization to obtain PTMC-F127-PTMC three-block polyether ester copolymer, and modify the end group with double bonds to obtain water-soluble polyether ester PFMC;
[0035] (2) modifying the hydroxyl group of hyaluronic acid with a double bond to obtain a water-soluble natural polymer with a cross-linking function;
[0036] (3) Decellularize the tendon tissue by a decellularization method to obtain decellularized tendon tissue, and pulverize the decellularized tendon tissue to obtain a water-soluble decellularized nerve matrix material (biologically active component);
[0037] (4) Take 1% acellular matrix powder by mass fraction and digest it with pepsin hydrochloric acid solu...
Embodiment 3
[0042] A bio-ink for 3D printing is composed of polyether ester, hyaluronic acid, bioactive components, cross-linking initiators and deionized water. The bioactive components of this embodiment use short peptides, and the preparation method is as follows:
[0043] (1) Use water-soluble F127 to initiate TMC polymerization to obtain PTMC-F127-PTMC three-block polyether ester copolymer, and modify the end group with double bonds to obtain water-soluble polyether ester PFMC;
[0044] (2) modifying the hydroxyl group of hyaluronic acid with a double bond to obtain a water-soluble natural polymer with a cross-linking function;
[0045] (3) According to the mass fraction, 1% RADARADARADARADA-RGD short peptide, 1% hyaluronic acid, 8% water-soluble polyether ester PEMC, and 0.05% photoinitiator I2959 were dissolved in 100% deionized water to prepare a bioink.
[0046] Take 20ml of the bio-ink and 1ml5×10 5 After the neural stem cells in cells / ml are mixed, they can be photocrosslinked...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com