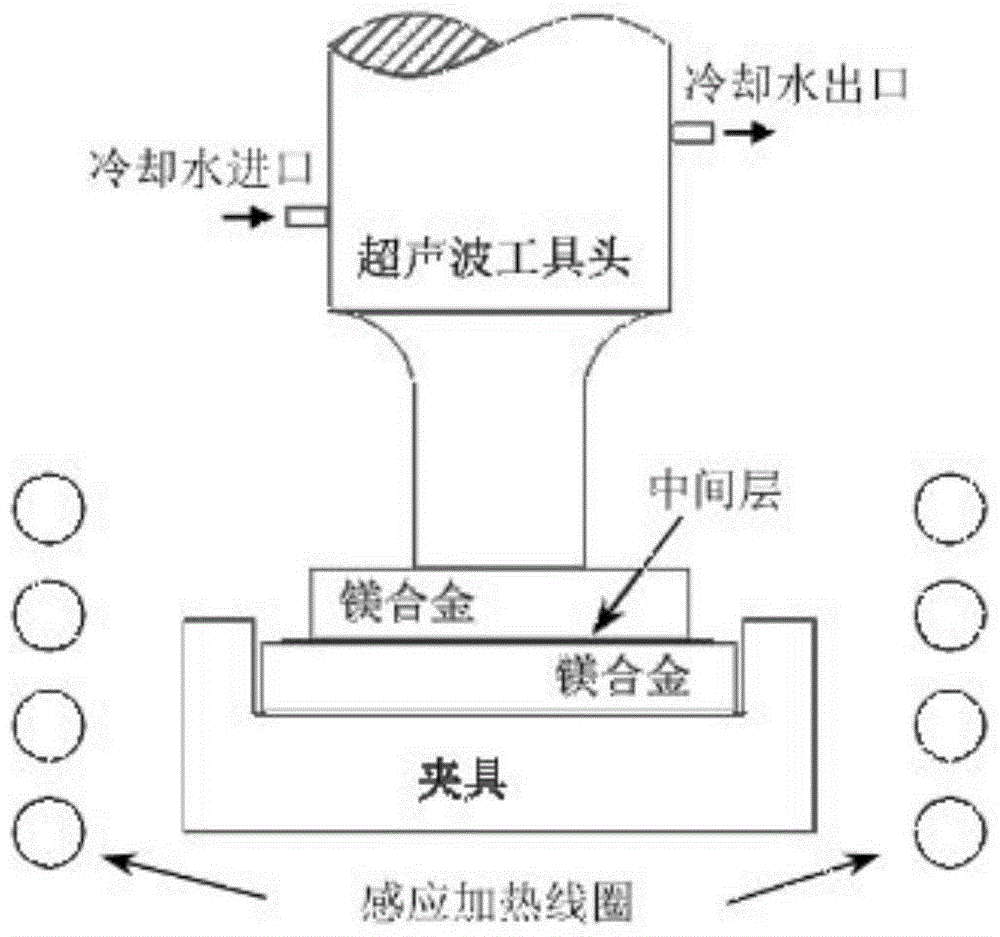
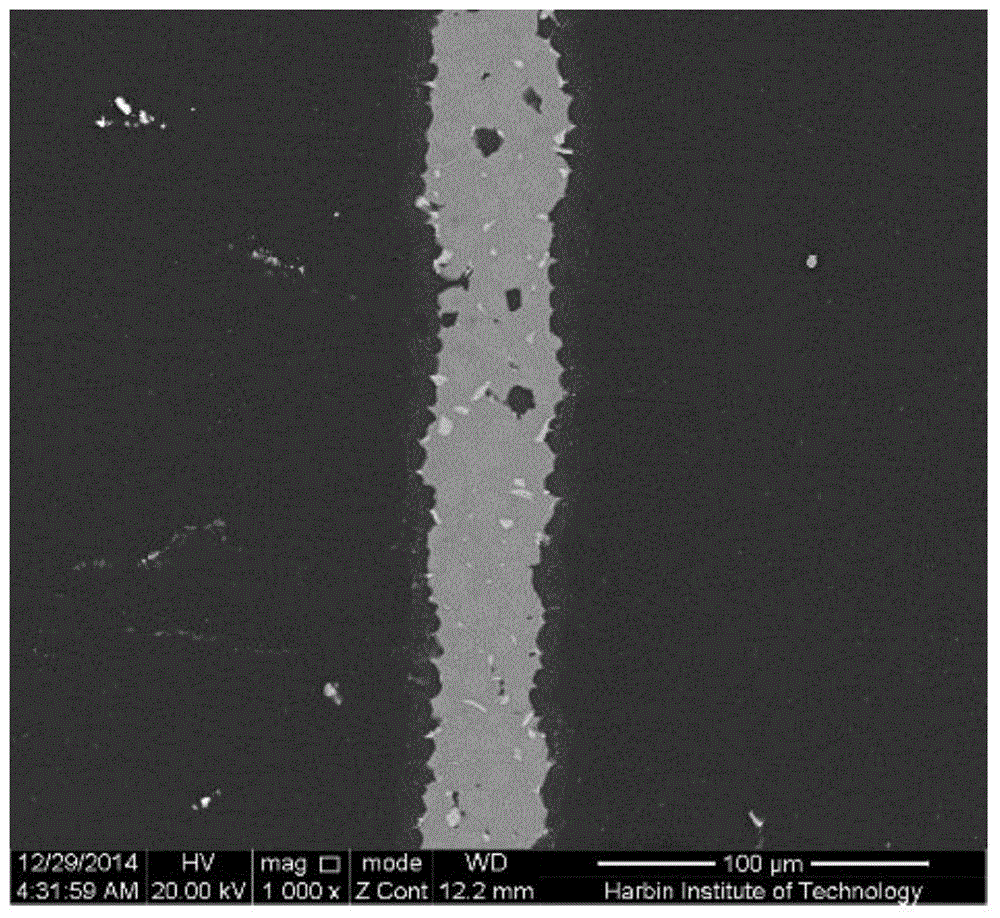
Ultrasonic-assisted transitional liquid phase bonding method
A technology of ultrasonic wave and transition fluid, applied in welding equipment, non-electric welding equipment, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problem of long time consumption and achieve the effect of shortening welding time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0011] Specific Embodiment 1: In this embodiment, an ultrasonic-assisted transitional liquid-phase joining method is as follows: 1. Mechanically grind and clean the base material to be welded, and then follow the sequence of "base material to be welded - intermediate material - base material to be welded" Assemble to obtain the components to be welded, in which the base material to be welded and the intermediate layer material have eutectic; 2. Apply the ultrasonic tool head vertically to the components to be welded, apply a pressure of 0.02 ~ 5kN, then heat, and then apply ultrasonic vibration 1s ~ 10min to complete isothermal solidification; 3: If the isothermal solidification time is longer than 10min, continue to heat up, and then apply ultrasonic vibration for 1s ~ 10min to complete isothermal solidification; 4. After the isothermal solidification is completed in step 2 or step 3, cool with the furnace to room temperature and done.
[0012] The ultrasonic-assisted transit...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0013] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: if the base material to be welded is a magnesium alloy or a magnesium-based composite material, the material of the intermediate layer is Zn, Cu, Al, Ag or silver-copper alloy; If the welding base material is aluminum alloy or aluminum-based composite material, the intermediate layer material is Zn, Cu, Mg, Ag or silver-copper alloy; if the base material to be welded is copper alloy or copper-based composite material, the intermediate layer material is Zn, Al, Mg or Ag. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0014] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the intermediate base material described in step 1 is pre-placed on the surface of the base material to be welded by evaporation or sputtering. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| shear strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shear strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com