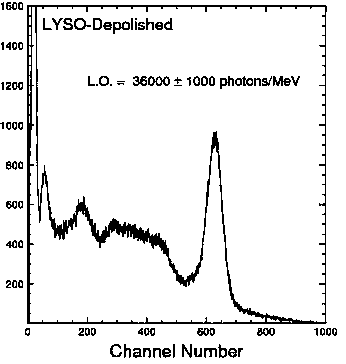
A method for improving scintillation performance of cerium-doped yttrium-lutetium silicate crystal grown by crucible drop method
A technology of crucible drop method and yttrium lutetium silicate, which is applied in the field of improving the scintillation performance of cerium-doped yttrium lutetium silicate crystal grown by crucible drop method, can solve the problems of crystal oxygen deficiency, inability to use, poor light output scintillation performance, etc., to achieve Effects that increase light output, reduce color center absorption, and optimize flicker performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] (1) Put the cerium-doped yttrium-lutetium silicate crystal into a high-temperature atmosphere furnace, first evacuate it to below 10KPa, and then slowly fill it with high-purity nitrogen;
[0022] (2) Heating stage: the crystal sample is heated from room temperature at a rate of 80 °C / h to 400 °C, then at a rate of 100 °C / h to 800 °C, and then at a rate of 60 °C / h to 1250 °C;
[0023] (3) Constant temperature stage: the crystal is kept at the highest temperature for 80 hours, and the color changes from beige to colorless and transparent;
[0024] (4) Cooling stage: After the constant temperature process is over, slowly drop to 900°C at a rate of -60°C / h, then drop to 600°C at a rate of -80°C / h, and finally drop to -100°C / h to room temperature.
[0025] The comparison test before and after shows that the number of channels is 159 before the crystal is processed, and the number of channels increases to 578 after high-temperature heat treatment, and the scintillation perf...
Embodiment 2
[0027] (1) Put the cerium-doped yttrium-lutetium silicate crystal into a high-temperature atmosphere furnace, first evacuate to below 10KPa, and then slowly fill in nitrogen and oxygen respectively, wherein the volume percentage of oxygen is 10%;
[0028] (2) Heating stage: the crystal sample is heated from room temperature at a rate of 80 °C / h to 400 °C, then at a rate of 100 °C / h to 800 °C, and then at a rate of 60 °C / h to 1200 °C;
[0029] (3) Constant temperature stage: the crystal is kept at the highest temperature for 100 hours, and the color changes from slightly yellow to colorless and transparent;
[0030] (4) Cooling stage: After the constant temperature process is over, slowly drop to 900°C at a rate of -60°C / h, then drop to 600°C at a rate of -80°C / h, and finally drop to -100°C / h to room temperature.
[0031] The comparison test before and after shows that the number of channels is 163 before the crystal is processed, but it is increased to 594 after high-temperat...
Embodiment 3
[0033] (1) Put the cerium-doped yttrium-lutetium silicate crystal into a high-temperature atmosphere furnace, first evacuate to below 10KPa, and then slowly fill in nitrogen and oxygen respectively, wherein the volume percentage of oxygen is 25%;
[0034] (2) Heating stage: the crystal sample is heated from room temperature at a rate of 80 °C / h to 400 °C, then at a rate of 100 °C / h to 800 °C, and then at a rate of 60 °C / h to 1300 °C;
[0035] (3) Constant temperature stage: the crystal is kept at the highest temperature for 60 hours, and the color changes from light brown to colorless and transparent;
[0036] (4) Cooling stage: After the constant temperature process is over, slowly drop to 900°C at a rate of -60°C / h, then drop to 600°C at a rate of -80°C / h, and finally drop to -100°C / h to room temperature.
[0037] The comparison test before and after shows that the number of channels is 157 before the crystal is processed, and the number of channels increases to 622 after h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com