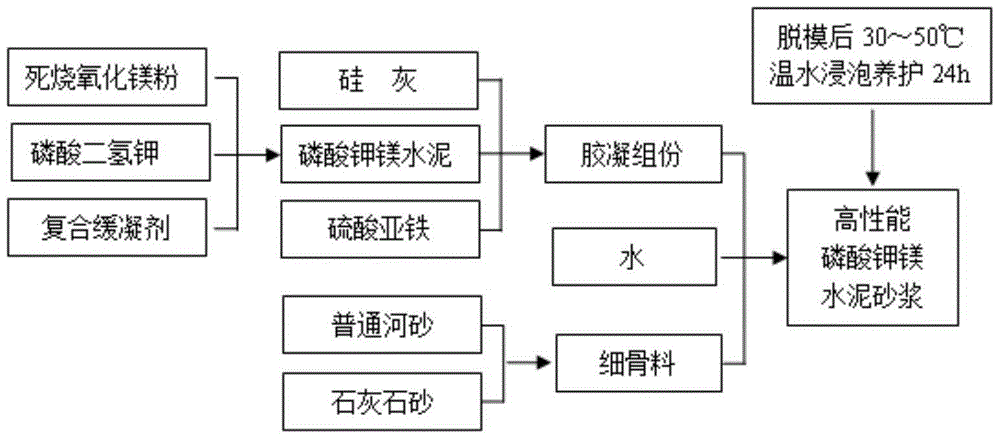
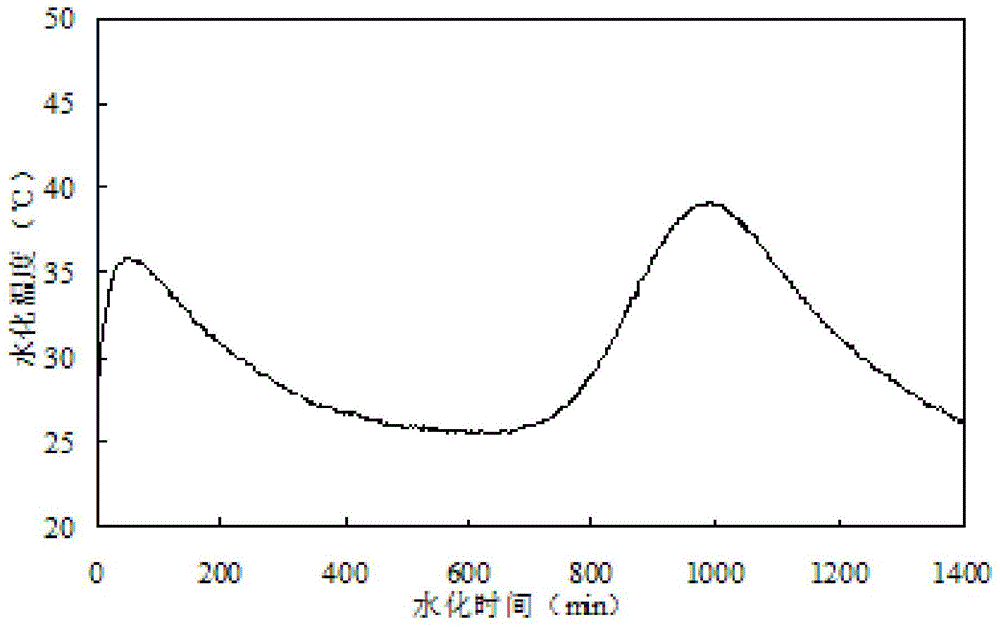
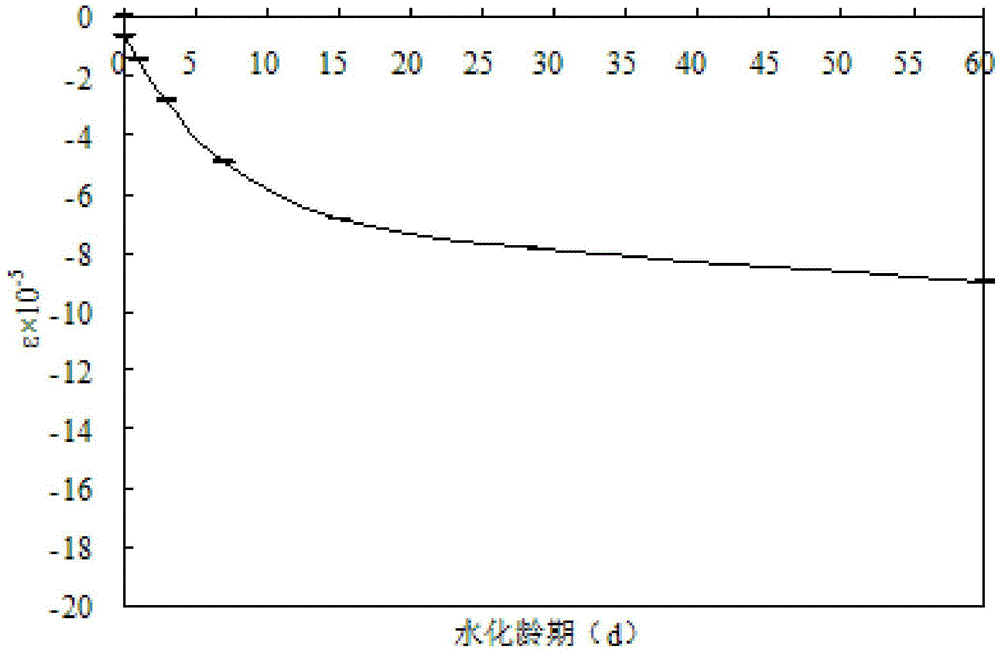
High-performance potassium magnesium phosphate cement mortar and preparation method thereof
A potassium magnesium phosphate cement, high-performance technology, applied in the field of new civil engineering materials, high-performance potassium magnesium phosphate cement mortar and its preparation, can solve the problems of high aggregate quality requirements, poor water stability, low bone-ash ratio, etc., to achieve Effects of improving strength and water stability, increasing flexural strength, and increasing bone-to-cement ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039]Step 1, get 60 mass parts of dead-burned magnesium oxide powder as alkaline component and 40 mass parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate as acidic component, 8 mass parts of composite retarder, prepare potassium magnesium phosphate with coagulation time greater than 0.5 hours cement. The composite retarder is composed of sodium tetraborate, disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate and inorganic chlorine salt, and the mass ratio of each component in the composite retarder is as follows: sodium tetraborate: disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate: inorganic chlorine Salt = 1:3:2.
[0040] It should be noted that, in the first step, the mass ratio of the dead-burned magnesium oxide powder, potassium dihydrogen phosphate and composite retarder is not necessarily 60:40:8. The inventor found through a large number of experiments that in order to achieve the purpose of the present invention, the mass ratio of the dead burnt magnesia powder, potassium dihydrogen phosphate a...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Step 1: Take 64 parts by mass of dead-burned magnesia powder and 36 parts by mass of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, and add 7.5 parts by mass of composite retarder to prepare magnesium potassium phosphate cement with a setting time greater than 0.5 hours. The composite retarder is composed of sodium tetraborate, disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate and inorganic chlorine salt, and the mass ratio of each component in the composite retarder is as follows: sodium tetraborate: disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate: inorganic chlorine Salt = 1:4:3.
[0062] Step 2: Take 90 parts by mass of potassium magnesium phosphate cement, 10 parts by mass of silica fume, and add 0.3 parts by mass of ferrous sulfate, and mix to obtain a gelling component.
[0063] Step 3: Mix 33 parts by mass of ordinary river sand and 67 parts by mass of limestone sand to obtain a two-component fine aggregate with reasonable gradation, whose basic physical parameters are shown in Table 1 above...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Step 1: Take 60 parts by mass of dead-burned magnesia powder and 40 parts by mass of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, and add 7 parts by mass of composite retarder to prepare potassium magnesium phosphate cement with a setting time greater than 0.5 hours. The composite retarder is composed of sodium tetraborate, disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate and inorganic chlorine salt, and the mass ratio of each component in the composite retarder is as follows: sodium tetraborate: disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate: inorganic chlorine Salt = 1:3:2.
[0071] Step 2: Take 90 parts by mass of potassium magnesium phosphate cement, 10 parts by mass of silica fume, and add 0.25 parts by mass of ferrous sulfate, and mix to obtain a gelling component.
[0072] Step 3: Mix 50 parts by mass of ordinary river sand and 50 parts by mass of limestone sand to obtain a two-component fine aggregate with reasonable gradation. The basic physical parameters are shown in Table 4.
[007...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com