Quantum dot ink
A technology of quantum dots and quantum dot materials, applied in the field of quantum dot inks, can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining high-viscosity quantum dot inks and printing difficulties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
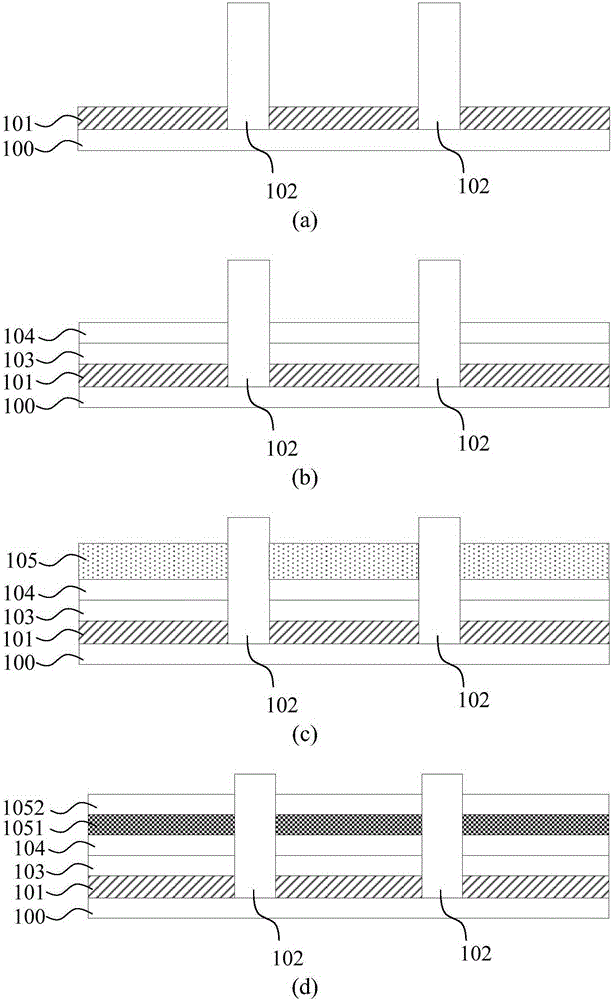
[0049] In a specific embodiment, the quantum dot ink has the following composition: oxadiazole (electron transport material) 5%; Hydrophobic quantum dot material CdSe 2%; Caprylic acid (surface tension regulator) 1%, non-polar organic solvent n-hexane Alkanes 92%.
[0050] When preparing the above quantum dot ink, prepare each component according to the mass ratio, first mix the hydrophobic quantum dot material CdS and the non-polar organic solvent n-hexane; then add the electron transport material oxadiazole, Mix evenly; finally add the surface tension regulator caprylic acid, mix evenly. The above-mentioned mixing methods include electromagnetic stirring, shaking and / or ultrasonic dispersion and the like. The order of mixing is not limited to the above order, as long as a uniformly dispersed mixture of hydrophobic quantum dot materials is finally obtained. After the quantum dot ink is prepared, it is tested that the viscosity of the quantum dot ink is 10 cp (25° C.), and t...
Embodiment 2
[0064] In another specific embodiment, the quantum dot ink has the following composition: CBP (4,4'-N, N'-dicarbazole-biphenyl) (hole transport material) 5%; hydrophobic quantum dot material CdSe2 %; octanoic acid (surface tension regulator) 1% and non-polar organic solvent n-hexane 92%. The same content as in the foregoing embodiments will not be repeated here, and the same below.
[0065] The difference from the previous embodiment is that the electron transport material is replaced by the hole transport material, so the preparation sequence of each layer in the quantum dot light-emitting device needs to be reversed.
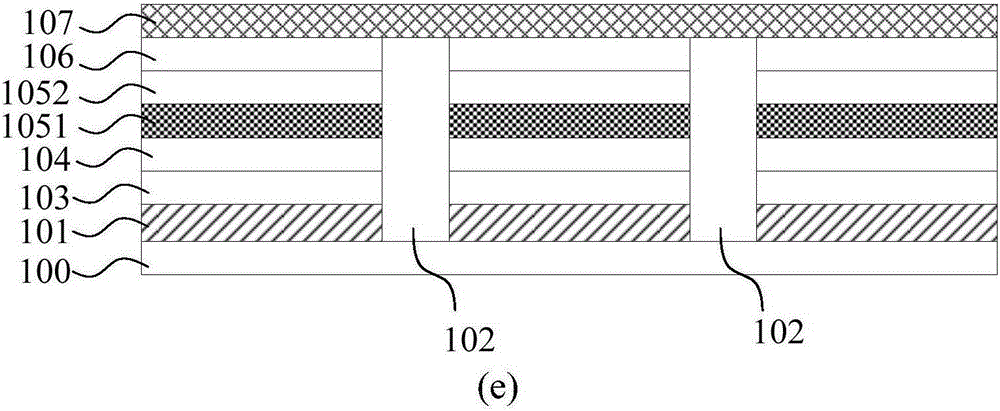
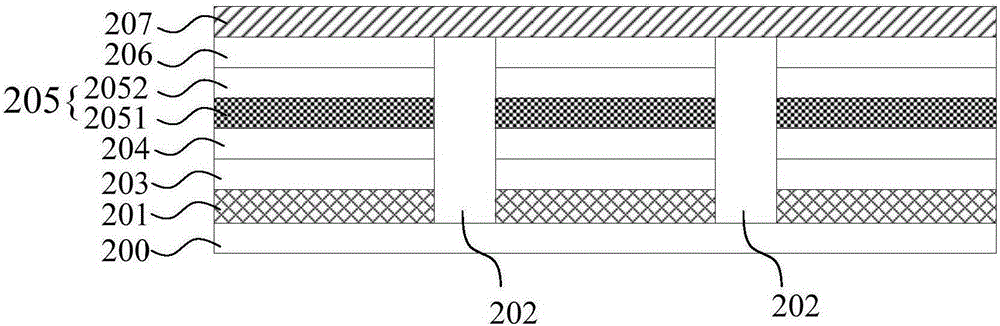
[0066] The following will be combined with figure 2 A method for preparing a quantum dot light-emitting device by printing with the above quantum dot ink is described.
[0067] like figure 2 As shown, a metal cathode 201 and a pixel defining layer 202 are first prepared on a base substrate 200 .
[0068] Then, an electron injection layer 203 and an electro...
Embodiment 3
[0073] In a specific embodiment, the quantum dot ink has the following composition: thiadiazole (electron transport material) 5%; hydrophobic quantum dot material ZnO 20%; octadecylamine (surface tension regulator) 1% and non-polar organic Solvent cyclohexane 74%. The quantum dot ink was configured in the same manner as in Example 1. After testing, the viscosity of the quantum dot ink was 10.5 cp (25° C.), and the surface tension was 33 dynes / cm (25° C.).
[0074] A quantum dot light-emitting device was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 to obtain an electron transport layer with a thickness of 5 nm and a quantum dot material layer with a thickness of 15 nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com