Method for separating parenchyma cells from fibers in bamboo wood
A parenchyma cell and fiber separation technology, used in chemical instruments and methods, solid separation, wet separation, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete separation, incompletely pulverized bamboo powder, too fine bamboo powder, etc., to avoid chemical consumption. And the effect of pollution, separation effect is complete, and the effect of avoiding damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] This embodiment provides a method for separating parenchyma cells and fibers, which specifically includes the following steps:
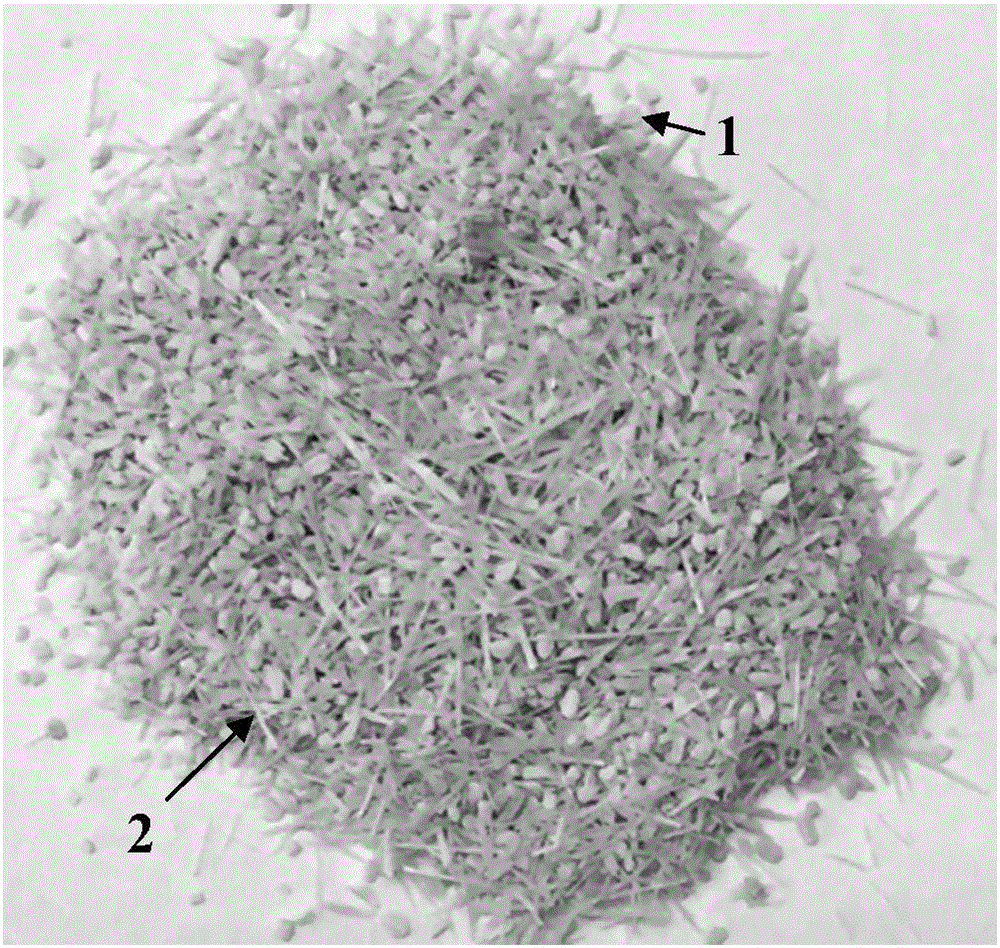
[0043] Step (1) crushing: after removing the bamboo bark and extramedullary tissue of moso bamboo, take the bamboo green part, pre-process it into bamboo stems with a length of 2 cm, a width and a thickness of 0.5 mm, and put the bamboo stems into a small grinder for intermittent crushing 6 minutes (0.5 minutes of work, 1 minute of shutdown), take the powder particles above 30 mesh;
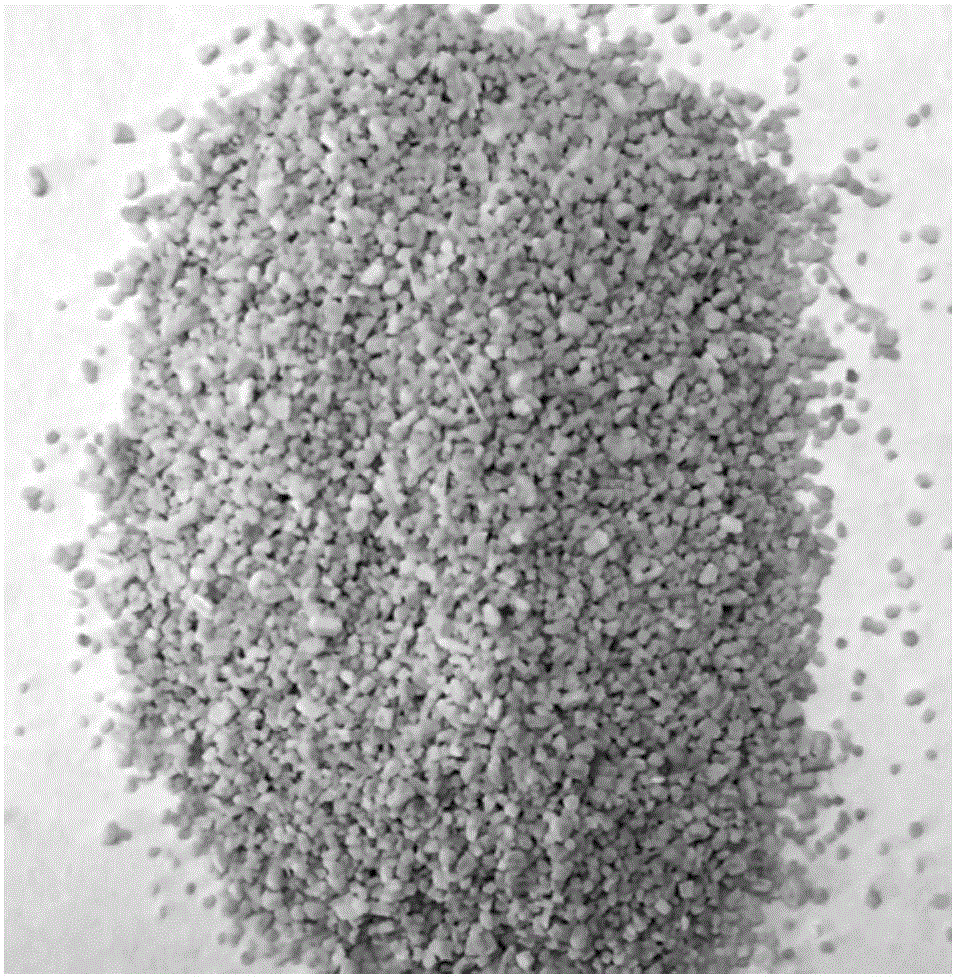
[0044] Step (2) Screening: Sieve the pulverized powder particles through 30, 60, 120, and 200 mesh sieves to obtain 30-60 mesh, 120-200 mesh and larger than 200 mesh powder particles; respectively collect particle sizes of 120-200 mesh powder particles and powder particles larger than 200 mesh to obtain parenchyma cells with different purity;
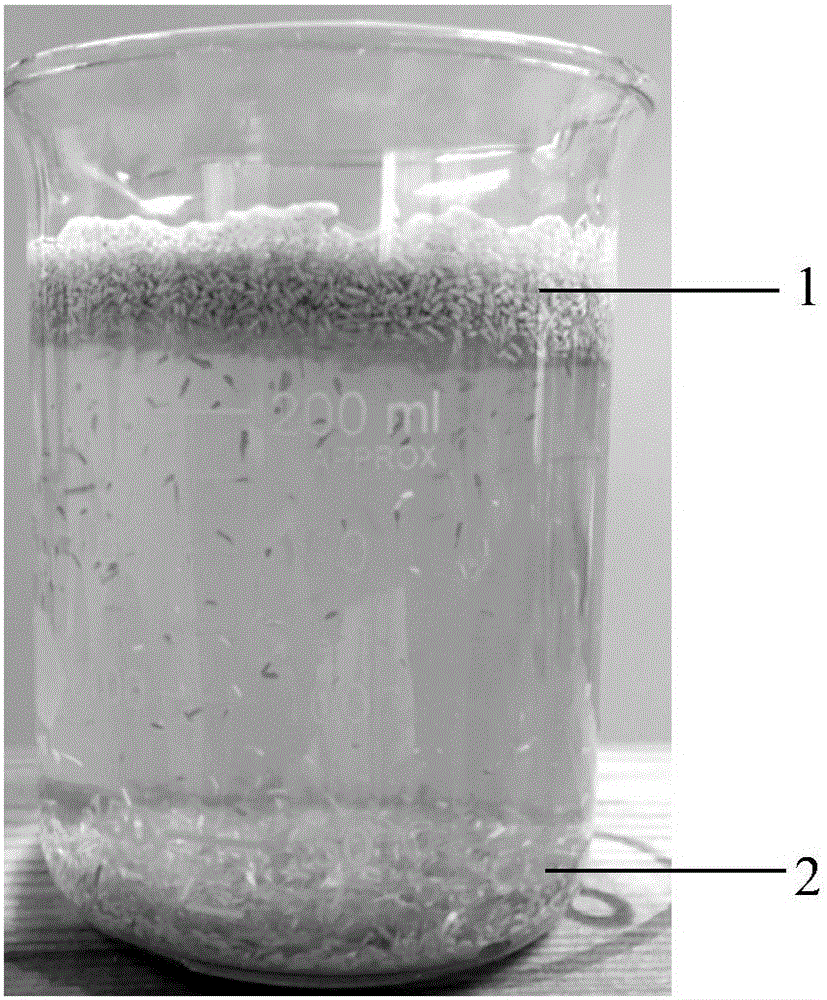
[0045] Step (3) Separation: Take the 30-60 mesh powder particles, add 20 times the volume of water, stir and let stand,...
Embodiment 2
[0053] This embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0054] Step (1) crushing: after removing the bamboo bark and extramedullary tissue of moso bamboo, take the bamboo flesh, and pre-process it into a bamboo stalk with a length of 2.5 cm, a width of 0.5 mm, and a thickness of 0.8 mm. Put the bamboo stalks into a small pulverizer and pulverize them intermittently for 6 minutes (0.5 minutes of work, 1 minute of shutdown), and take powder particles above 30 mesh;
[0055] Step (2) Screening: Sieve the pulverized powder particles through 30, 60, 120, and 200 mesh sieves to obtain 30-60 mesh, 120-200 mesh and larger than 200 mesh powder particles; respectively collect particle sizes of 120-200 mesh powder particles and powder particles larger than 200 mesh to obtain parenchyma cells with different purity;
[0056] Step (3) Separation: Take the powder particles between 30 and 60 meshes, add 15 times the volume of water, stir and let stand, collect the floating matter...
Embodiment 3
[0064] This embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0065] Step (1) crushing: after removing the bark and extramedullary tissue of moso bamboo, take the bamboo yellow part, and pre-process it into a bamboo stalk with a length of 2.5 cm, a width of 0.5 mm, and a thickness of 0.8 mm. Put the bamboo stalks into a small pulverizer and pulverize them intermittently for 6 minutes (0.5 minutes of work, 1 minute of shutdown), and take powder particles above 30 mesh;
[0066] Step (2) Screening: Sieve the pulverized powder particles through 30, 60, 120, and 200 mesh sieves to obtain 30-60 mesh, 120-200 mesh and larger than 200 mesh powder particles; respectively collect particle sizes of 120-200 mesh powder particles and powder particles larger than 200 mesh to obtain parenchyma cells with different purity;
[0067] Step (3) Separation: Take the 30-60 mesh powder particles, add 10 times the volume of water, stir and let stand, collect the upper layer of floating matter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com