A preparation method of anti-droplet polyamide fiber or fabric
A polyamide fiber, anti-droplet technology, applied in fiber type, fiber treatment, physical treatment, etc., can solve the problems of complex synthesis process of flame retardants, no improvement of droplet combustibility, and reduced melt fluidity, etc., to achieve The effect of retaining the original performance, preventing endangering human life, and making the preparation method simple and feasible
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
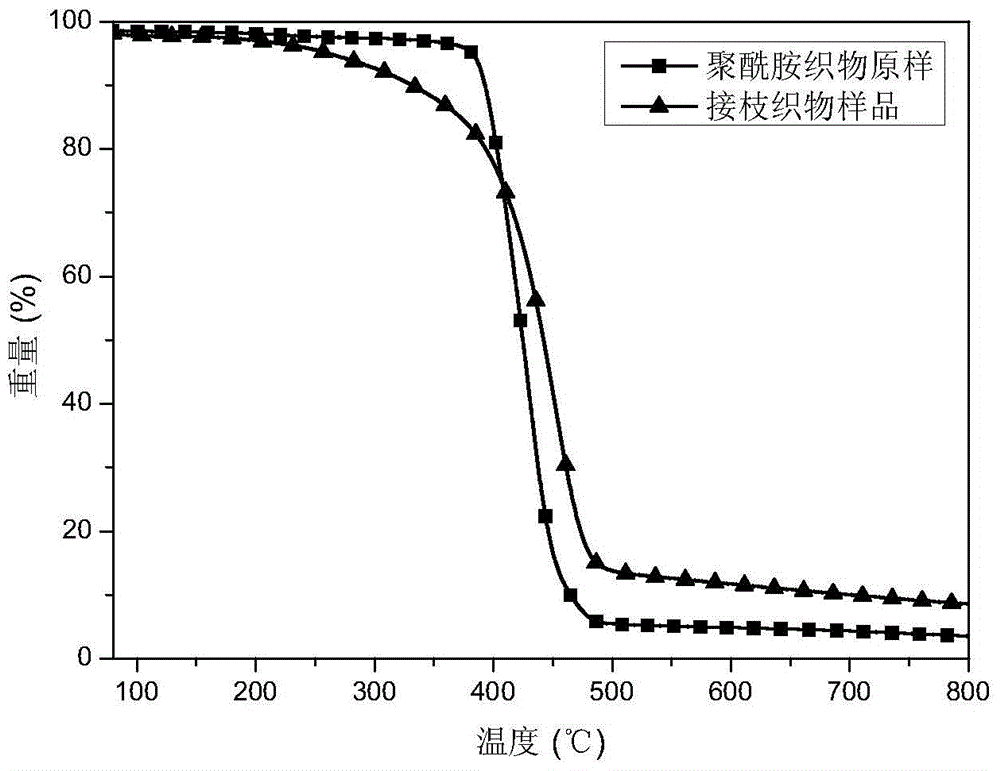
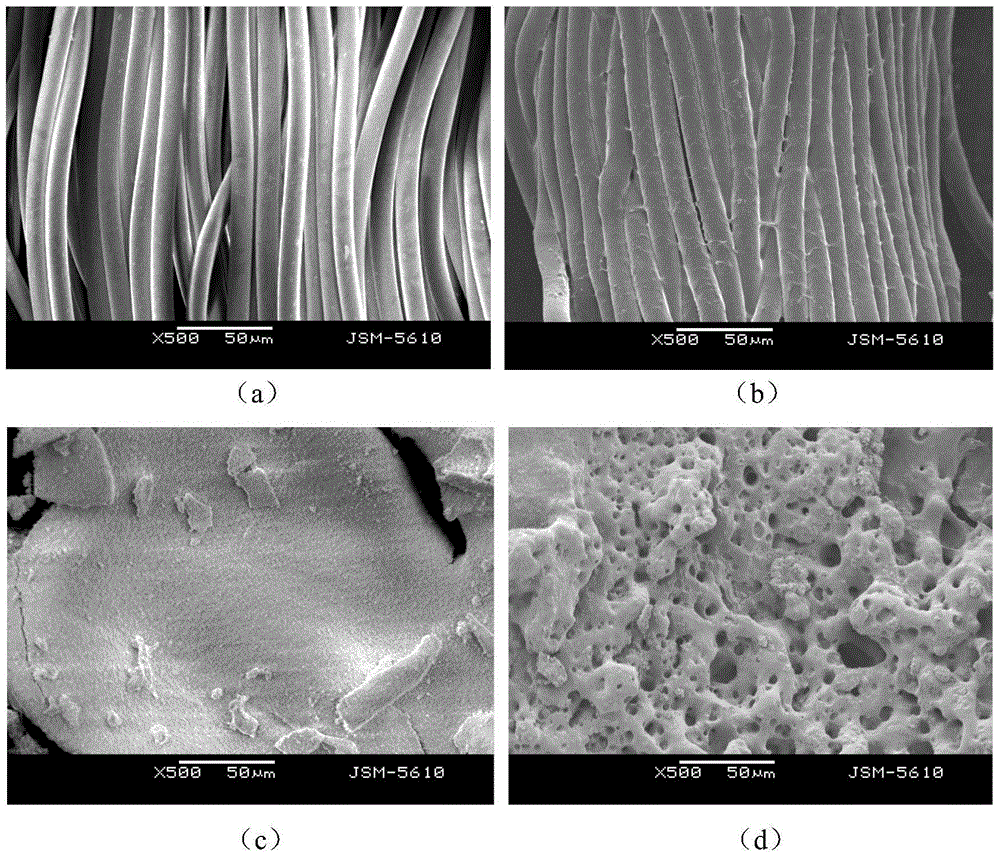
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Under the condition of normal temperature and air, the polyamide fibers are first irradiated with electron beams, so that the dose reaches 80kGy, and the irradiated fibers are immediately placed in 10% acrylic acid aqueous solution, and reacted at 60°C for 1 hour, washed with water after the reaction, and the fibers No significant weight gain, then the polyamide fibers were padded in 10% acrylamide and 5% hydroxyethyl methacrylate and 0.05% Fe 2 SO 4 For a period of time in the mixed aqueous solution, let the fiber pass through the paddle car, the pressure between the two rollers is 0.3Mpa, so that the liquid-carrying rate of the fiber reaches 60%, and then carry out electron beam irradiation grafting, so that the irradiation dose reaches 135kGy, and the irradiation grafting After branching, the fiber was boiled with 1% sodium hydroxide solution for 20 minutes, and then washed with water. The grafting rate was 11.4%.
[0041] The surface of the fiber obtained in this e...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Under the condition of normal temperature and air, the polyamide fibers are first irradiated with electron beams, so that the dose reaches 120kGy, and the irradiated fibers are immediately placed in 10% methacrylic acid aqueous solution, and reacted at 70°C for 1 hour, and washed with water after the reaction. , the fiber has no obvious weight gain, and then the polyamide fiber is padded with 12% acrylamide and 8% hydroxypropyl acrylate and 0.05% Fe 2 SO4 For a period of time in the mixed aqueous solution, let the fiber pass through the paddle car, the pressure between the two rollers is 0.2Mpa, so that the liquid-carrying rate of the fiber reaches 80%, and then carry out electron beam irradiation grafting, so that the irradiation dose reaches 180kGy, and the irradiation grafting After branching, the fibers were boiled with 2% sodium carbonate solution for 20 minutes, and then washed with water. The grafting rate was 15.6%.
[0044] The surface of the fiber obtained in ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Under the condition of normal temperature and air, the polyamide fibers are first irradiated with electron beams, so that the dose reaches 100kGy, and the irradiated fibers are immediately put into 10% itaconic acid aqueous solution, and reacted at 65°C for 1 hour, and washed with water after the reaction , the fiber has no obvious weight gain, and then the polyamide fiber is padded in 20% N-methylolacrylamide and 5% hydroxypropyl acrylate and 0.10% Fe 2 SO 4 For a period of time in the mixed aqueous solution, let the fiber pass through the paddle car, the pressure between the two rollers is 0.3Mpa, so that the liquid-carrying rate of the fiber reaches 60%, and then carry out electron beam irradiation grafting, so that the irradiation dose reaches 90kGy, and the irradiation grafting After branching, the fibers were boiled with 4% sodium bicarbonate solution for 20 minutes, and then washed with water. The grafting rate was 13.4%.
[0047] The surface of the fiber obtain...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| limiting oxygen index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of grafting | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of grafting | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com