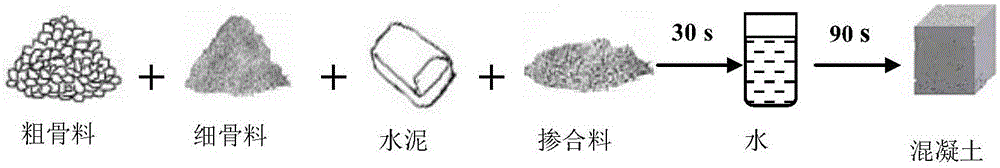
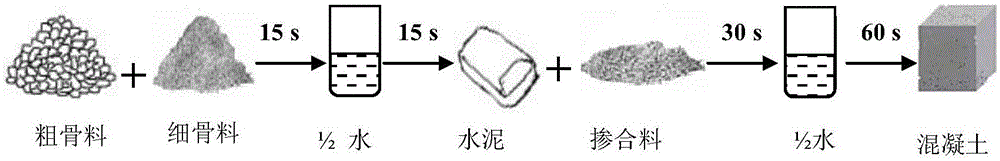
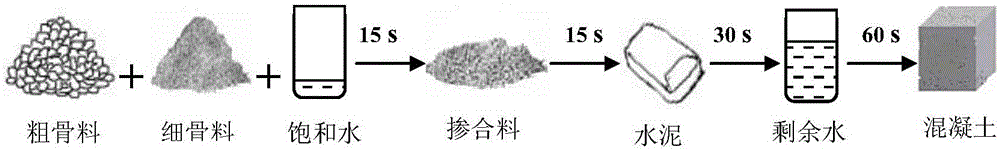
In-situ reinforcement method of recycled aggregate
A recycled aggregate and in-situ strengthening technology, applied in sustainable waste treatment, solid waste management, climate sustainability, etc., can solve equipment investment and production cost increase, non-in-situ strengthening of recycled aggregate, cement slurry Problems such as small water-cement ratio to achieve the effect of improving bond strength, avoiding production costs, and improving compressive strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~8
[0026] Examples 1-8: In-situ strengthening and interface strengthening simulation of recycled aggregates
[0027] (1) Prepare old concrete with a slump of 30-50mm and a design strength grade of C30. After 60 days of natural curing, use a coring machine to drill a cylindrical core sample with a diameter of 100mm and a height of 150mm from the old concrete, and use it as a simulation recycled aggregate.
[0028] (2) Disperse the admixture in water to prepare an admixture dispersion. During preparation, add a water reducer in advance, and the mass ratio of the admixture, water and water reducer is 1:1:0.01. The types of admixtures are detailed in Table 1. The water reducer is a polycarboxylate high performance water reducer.
[0029] (3) After drying the simulated recycled aggregate, soak it in the admixture dispersion for 1min, then place it in the middle of the 150mm×150mm×150mm test mold, pour new concrete around it, and the concrete mix ratio used is the same as that of the...
Embodiment 9~16
[0039] Examples 9-16: Simulation test of in-situ strengthening of recycled aggregates and the effect of in-situ strengthening on the strength of recycled aggregate concrete
[0040] (1) Prepare old concrete with a slump of 30-50mm and a design strength grade of C30. After 60 days of natural curing, use a coring machine to drill a cylindrical core sample with a diameter of 50mm and a height of 100mm from the old concrete, and use it as a simulation recycled aggregate. At the same time, the rest of the old concrete is crushed, screened, and dried to obtain recycled coarse aggregate with a nominal particle size of 5-20mm and recycled fine aggregate with a nominal particle size of less than 5mm.
[0041] (2) The designed new concrete mix ratio is (mass ratio): (cement + admixture): water: fine aggregate: coarse aggregate = 1:0.50:1.71:2.58, and the fine aggregate used is natural medium sand and A mixture of one or two kinds of regenerated fine aggregates in step (1), the coarse a...
Embodiment 17~18
[0064] Examples 17-18: In-situ strengthening of different recycled aggregates
[0065] (1) Cylinder core samples with a diameter of 50mm and a height of 53mm were drilled in the sintered ordinary brick and the autoclaved lime-sand brick, respectively, and used as simulated recycled aggregate. Sintered ordinary bricks and autoclaved lime-sand bricks are crushed, screened and dried to prepare recycled coarse aggregate with a nominal particle size of 5-20mm and recycled fine aggregate with a nominal particle size of <5mm.
[0066] (2) New concrete mix ratio (cement+admixture) designed: water: fine aggregate: coarse aggregate = 1:0.50:1.71:2.58, and the admixture used is 20% fly ash (20% refers to powder The ratio of coal ash to the total mass of all admixtures and cement) and 20% slag micropowder (20% refers to the ratio of slag micropowder to the total mass of all admixtures and cement) are compounded, and the mass of all admixtures ( That is, the mass ratio of fly ash and slag...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shear strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com