A Method for Solving Multi-pass Scheduling Model of Dividable Tasks in Distributed Systems
A distributed system and scheduling model technology, applied in the information field, can solve the problems that the algorithm is difficult to converge to the global optimal solution, the task completion time does not reach the global optimal solution, and the complexity increases.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
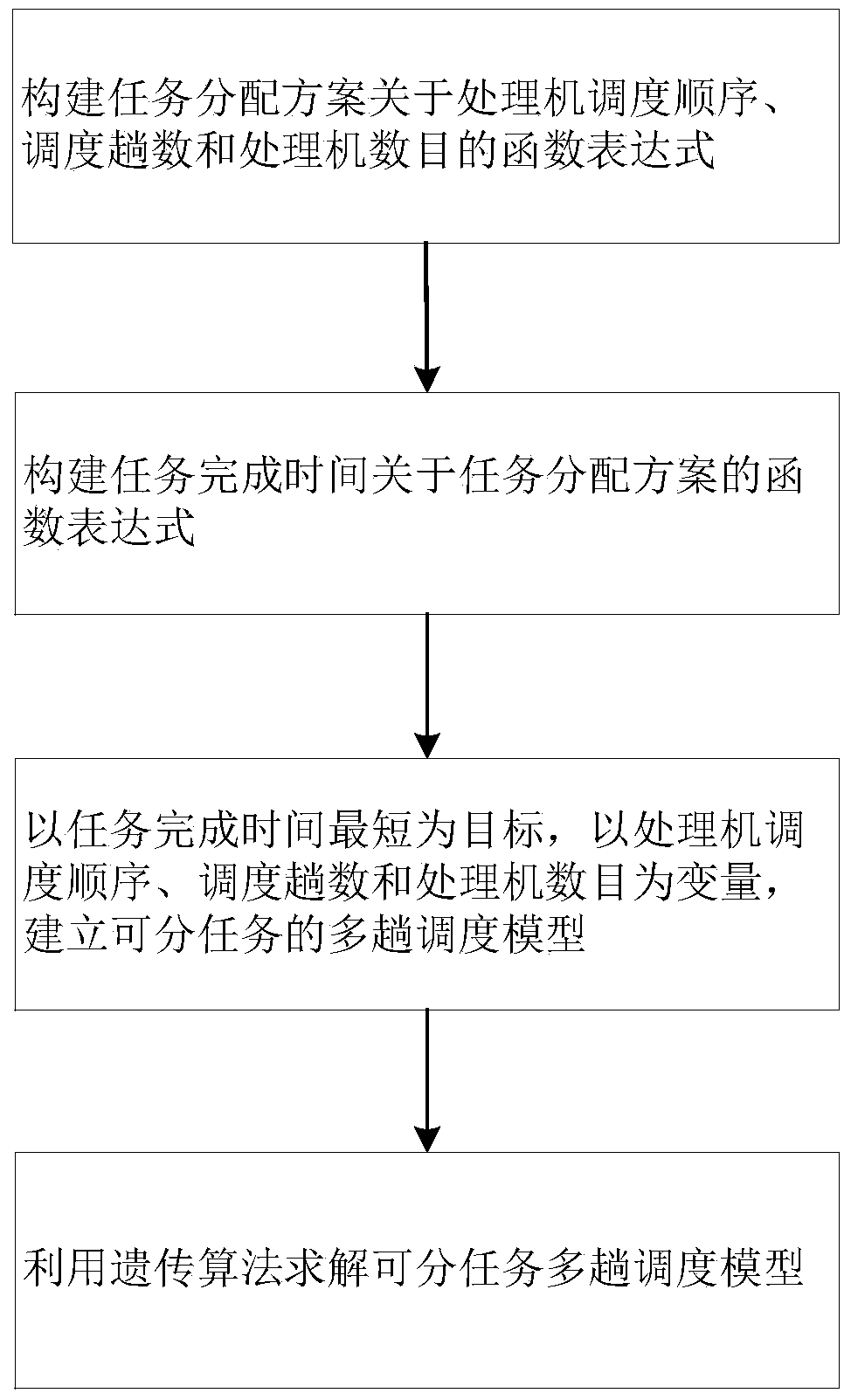
[0092] According to the above-mentioned technical solution, a method of solving the multi-pass scheduling model of divided tasks under the distributed system in this embodiment, see figure 2 , including the following steps:
[0093] Step 1, construct task allocation scheme A=(a ij ) n×m About Processor Scheduling Order The function expression of the scheduling number m and the number n of processors participating in the calculation.
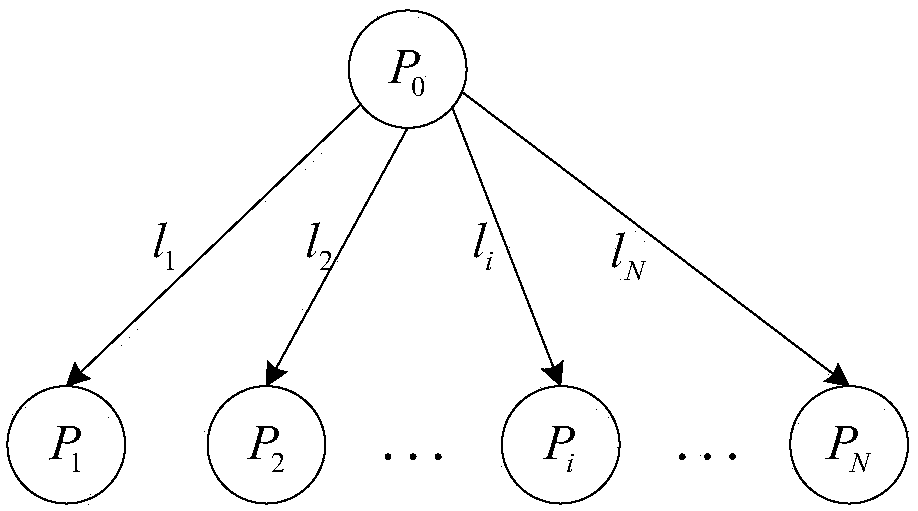
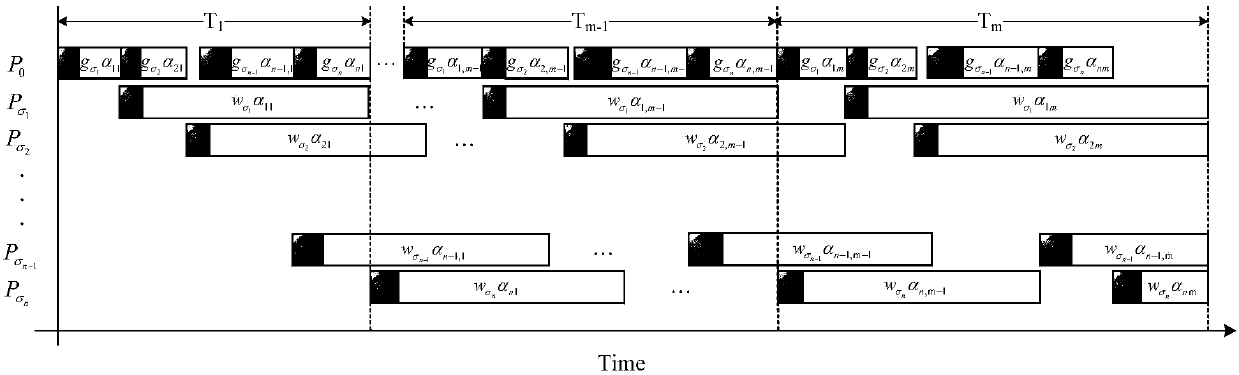
[0094] see figure 1 , N+1 processors are connected to each other in a star topology network, where P 0 main processor, {P i |i∈{1,2,...,N}} is the slave processor. see image 3 , (σ 1 ,σ 2 ,...,σ N ) is the arrangement of 1,2,...N, is the scheduling sequence of processors; α ij main processor P 0 The jth schedule is assigned to the slave processor The task size of , where i=1,2,...,n, j=1,2,...,m. slave processor The computational startup overhead of slave processor The time required for calculating the unit task, the si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com