Polyvinyl wood-plastic composite and preparation method thereof
A wood-plastic composite material and polyethylene-based technology, applied in the field of composite materials, can solve the problems of poor antibacterial performance and inapplicability, and achieve the effects of improving antibacterial performance, improving compatibility, and improving mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
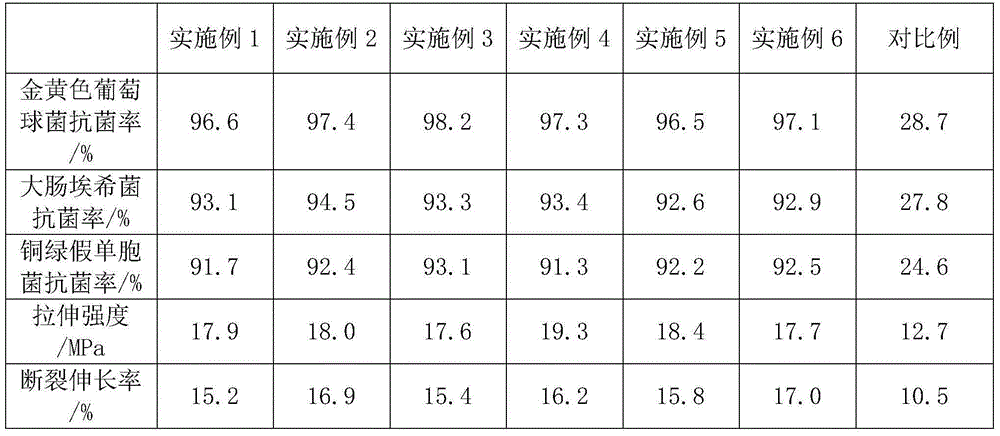
Embodiment 1
[0027] A polyethylene-based wood-plastic composite material is made of the following components in parts by weight: 44 parts of HDPE, 36 parts of hazelnut shell powder, 4.5 parts of PE-g-MAH, 2 parts of PE wax, and 0.8 parts of calcium stearate 12 parts of guava leaf extract, 10240.3 parts of antioxidant, 6 parts of antimony trioxide, 15 parts of light calcium carbonate, 0.5 part of p-benzoylphenol; the hazelnut shell powder, guava leaf extract The particle size is 200 mesh.
[0028] The steps of its preparation method are as follows:
[0029] (1) Wash the guava leaves and dry them at room temperature for 20 hours, pulverize them with a pulverizer and add them into an ethanol solution with a mass fraction of 65%, ultrasonically extract them at 45°C for 90 minutes, filter and reduce the extract at 45°C Concentrate under pressure, freeze-dry the concentrated solution to constant weight, and pass through a 200-mesh sieve to obtain the guava leaf extract for subsequent use;
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0032] A polyethylene-based wood-plastic composite material, made of the following components in parts by weight: 45 parts of HDPE, 35 parts of hazelnut shell powder, 7 parts of PE-g-MAH, 1.8 parts of PE wax, 0.6 parts of calcium stearate Parts, 10 parts of guava leaf extract, 10240.4 parts of antioxidant, 7.5 parts of antimony trioxide, 12 parts of calcined kaolin, 0.7 part of p-benzoylphenol; the particle diameter of the hazelnut shell powder and guava leaf extract Both are 200 mesh.
[0033] Its preparation method is the same as Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0035] A polyethylene-based wood-plastic composite material, made of the following components in parts by weight: 40 parts of HDPE, 40 parts of hazelnut shell powder, 6.5 parts of PE-g-MAH, 1.5 parts of PE wax, 0.9 parts of calcium stearate Parts, 11 parts of guava leaf extract, 10240.4 parts of antioxidant, 8 parts of antimony trioxide, 14 parts of calcined kaolin, 0.9 part of p-benzoylphenol; the particle diameter of the hazelnut shell powder and guava leaf extract Both are 200 mesh.
[0036] Its preparation method is the same as Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com