ATRP (Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization) method for constructing high-transfection niosomes cation gene carrier
A gene carrier and cationic technology, which is applied in the field of non-viral gene carrier preparation, can solve the problems of low effective toxicity, high toxicity, and inequalities, and achieve good transfection efficiency and increase transfection efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Take 0.2g of cholesterol initiator CHO-Br completely dissolved in 5mL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), then 1.73mL of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) and 135μL of pentamethyldiethylenetriamine (PMDETA) Dissolve it in the solution, and quickly add 54 mg of cuprous bromide (CuBr) after bubbling nitrogen gas for 5 minutes, and immediately seal it with a rubber stopper. The system was reacted at 27-30°C under an oxygen-free nitrogen protection environment for 30 minutes, opened the cork and stood still for 2-3 minutes, then precipitated with methanol, and washed twice with methanol to remove PDMETA, CuBr, unreacted GMA and large Part of the solvent DMSO. After centrifugation, the supernatant was removed, and the residual methanol in the lower precipitate was dried, then dissolved with 1-2mL DMSO, precipitated with deionized water and washed twice. After centrifugation, the supernatant was removed, and a small amount of pure water was added to lyophilize. The freeze-dried product...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Take 0.2 g of cholesterol initiator, the reaction steps and post-treatment are as in Example 1, except that the volume of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) added is 3.46 mL. The polymer obtained in this way is designated as CHO-PGMA2. The number average molecular weight (Mn) of the polymer (CHO-PGMA2) was 9365, and the molecular weight distribution index (Mw / Mn) was 1.23.
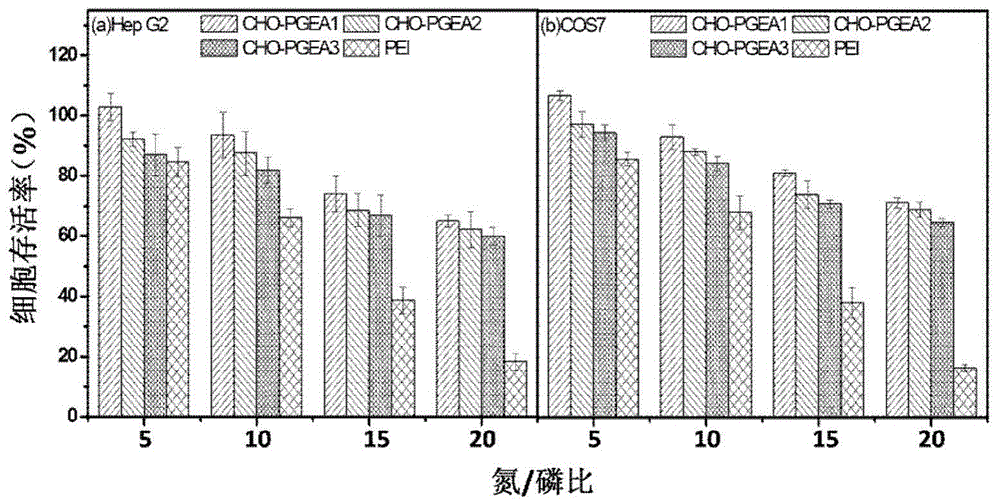
[0038] Take 0.15 g of the obtained CHO-PGMA2 and dissolve it in 4 mL of DMSO. The reaction steps and post-treatment methods are as in Example 1. The obtained flocculent polymer is the cationic gene carrier of the cholesterol matrix we need, which is recorded as CHO-PGEA2.
[0039] The number average molecular weight (Mn) of the polymer (CHO-PGEA2) was 15000, and the molecular weight distribution index (Mw / Mn) was 1.85.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Take 0.2 g of cholesterol initiator, the reaction steps and post-treatment are as in Example 1, except that the volume of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) added is 5.19 mL. The polymer obtained in this way is designated as CHO-PGMA3. The number average molecular weight (Mn) of the polymer (CHO-PGMA3) was 13500, and the molecular weight distribution index (Mw / Mn) was 1.30.
[0042] Take 0.15 g of the obtained CHO-PGMA3 and dissolve it in 4 mL of DMSO. The reaction steps and post-treatment methods are as in Example 1. The obtained flocculent polymer is the cationic gene carrier of the cholesterol matrix we need, which is recorded as CHO-PGEA3.
[0043] The number average molecular weight (Mn) of the polymer (CHO-PGEA3) was 18000, and the molecular weight distribution index (Mw / Mn) was 1.80.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| distribution coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distribution coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com