Experimental method for simulating stress corrosion of metal material under working conditions
A technology of stress corrosion and experimental methods, applied in the fields of weather resistance/light resistance/corrosion resistance, analysis materials, measuring devices, etc. Provide reliable basis for service life prediction, etc., to achieve the effect of good stress stability of the sample and high precision of strain value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
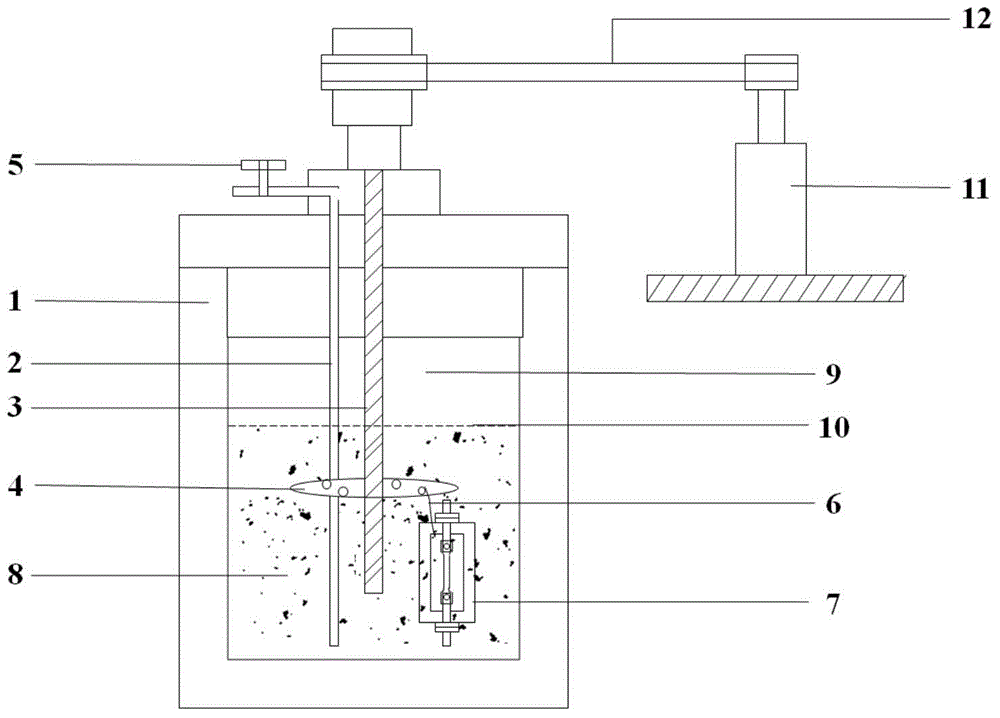
[0055] To test the stress corrosion resistance of a certain metal composite pipe, first process 4 pieces of metal specimen A, the specific dimensions are shown in Table 1. Calculate the force on the specimen according to the actual working conditions, use the strain gauge to load, and set parameters such as temperature, pressure, and flow rate according to the working conditions. The specific parameters are shown in Table 2.
[0056] In order to verify the force stability and reliability of the metal test piece under tensile stress, the stress of the test piece was measured and the test data was recorded in real time. The results are as follows: Figure 6 As shown, the force of the test piece fluctuates around the set value, within the error range, which verifies the stability of the force of the test piece and the rationality of the design of the loading fixture.
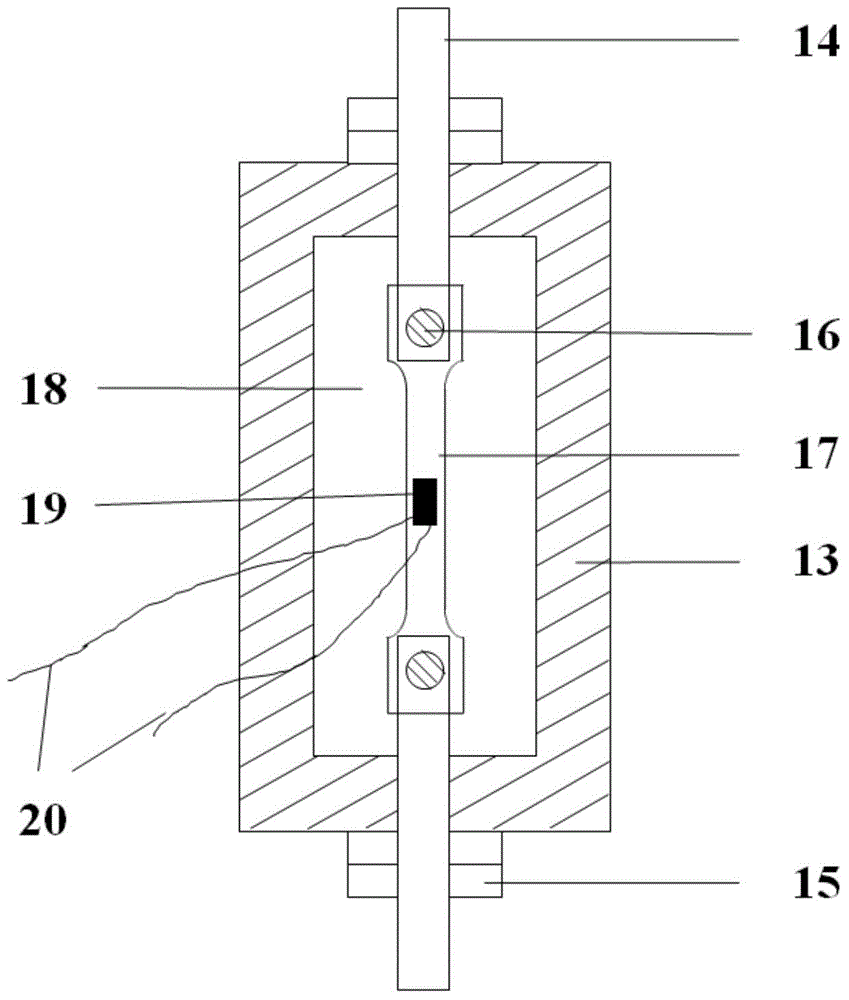
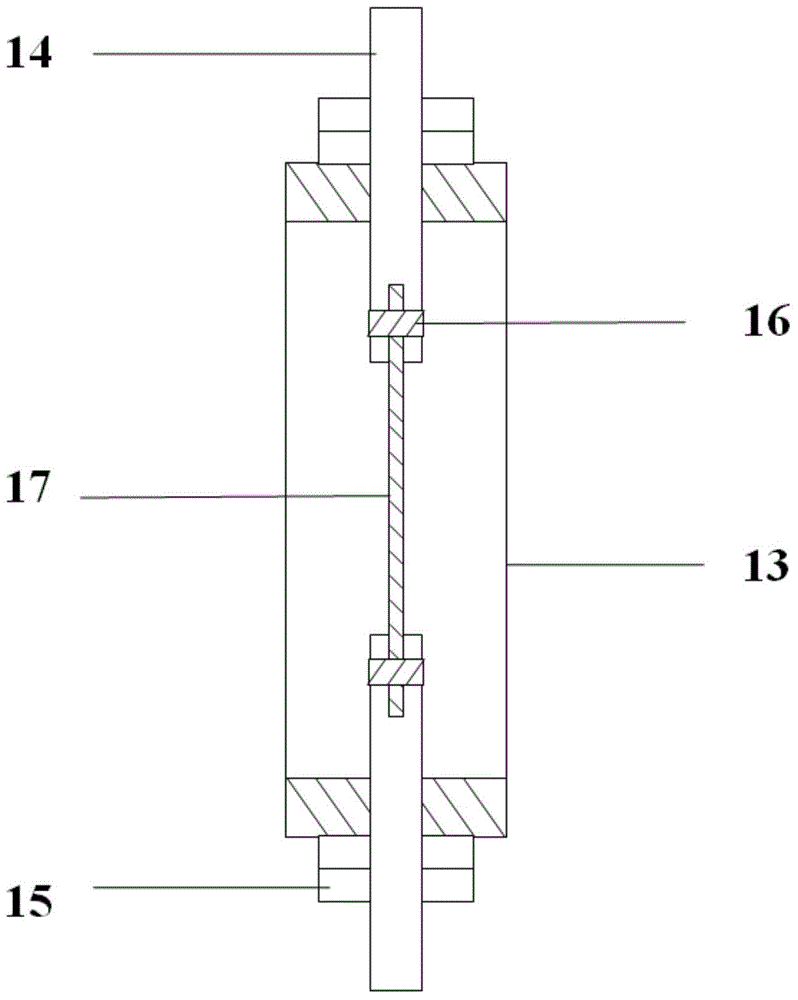
[0057] According to the present invention, each test piece is installed on the loading fixture, and the strain g...
Embodiment 2
[0063] The difference from Example 1 is that the flow velocity in the environmental parameters is 1.0m / s. Reprocess 4 pieces of A metal material test pieces, the dimensions are shown in Table 3, the environmental parameters are shown in Table 4, and the average value of the obtained corrosion rate is shown in Table 3. Figure 7 As shown, the tensile strength loss rate is as Figure 8 As shown, compared with Example 1, it can be known that the increase of the flow rate increases the corrosion rate of the metal material, and its tensile performance also loses more.
[0064] table 3
[0065]
[0066] Table 4
[0067] Stress (KN)
Embodiment 3
[0069] The difference from Example 1 is that: B metal material is selected for the experiment, and the size of the test piece is as follows: Figure 5 and Table 5, the resulting corrosion rate averages are Figure 7 As shown, the tensile strength loss rate is as Figure 8 As shown, compared with Example 1, it can be known that metal B is more corrosion-resistant in the same corrosive environment, and the loss of tensile properties is less.
[0070] table 5
[0071]
[0072] The corrosion test method of the present invention can measure the corrosion of metal materials under the action of specific temperature (30°C-300°C), pressure (0MPa-30MPa), flow velocity (0m / s-4.0m / s) and load (0KN-3KN) According to the experimental results, the applicability of metal materials in specific working conditions can be evaluated and their service life can be estimated.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com