Fundamental transverse mode microcolumn laser based on polymer
A basic transverse mold and polymer technology, applied in the field of lasers, can solve the problems of complex laser production technology, unsuitable for mass production, and high production cost, and achieve the effects of being beneficial to mass production, easy to shape processing, and low processing cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
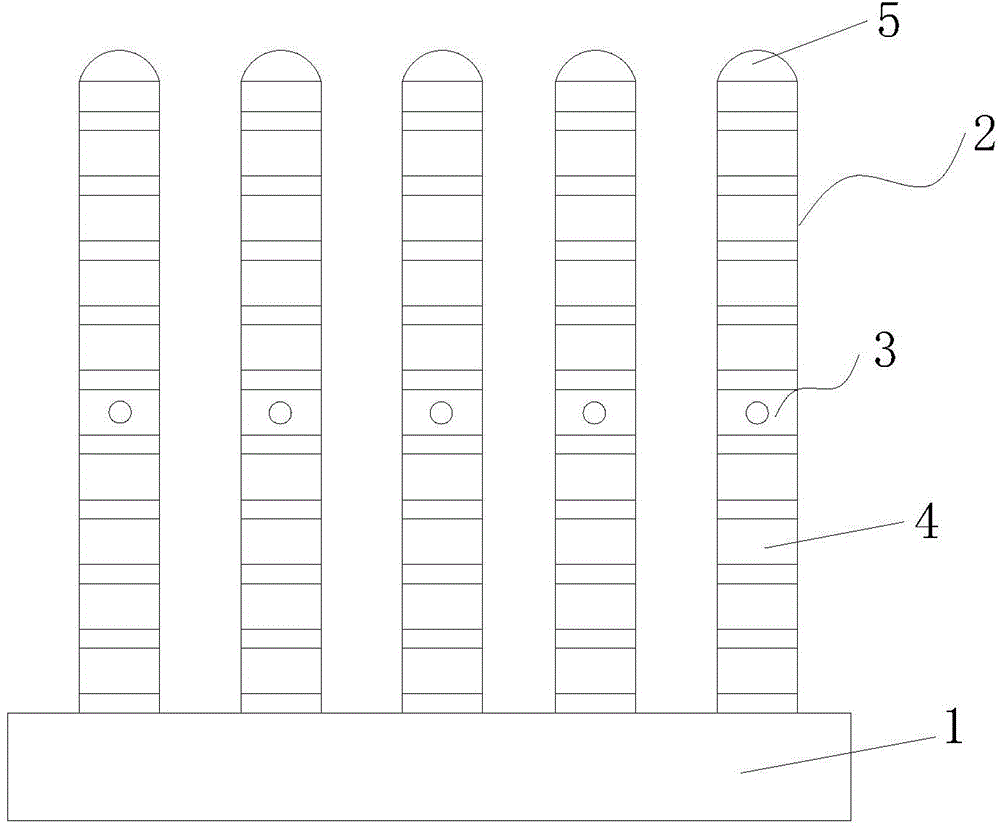
[0030] Such as figure 1 and 2 As shown, a kind of polymer-based fundamental transverse mode micro-cylindrical laser proposed by the present invention includes a base 1 and a plurality of micro-cylindrical optical units 2, wherein:
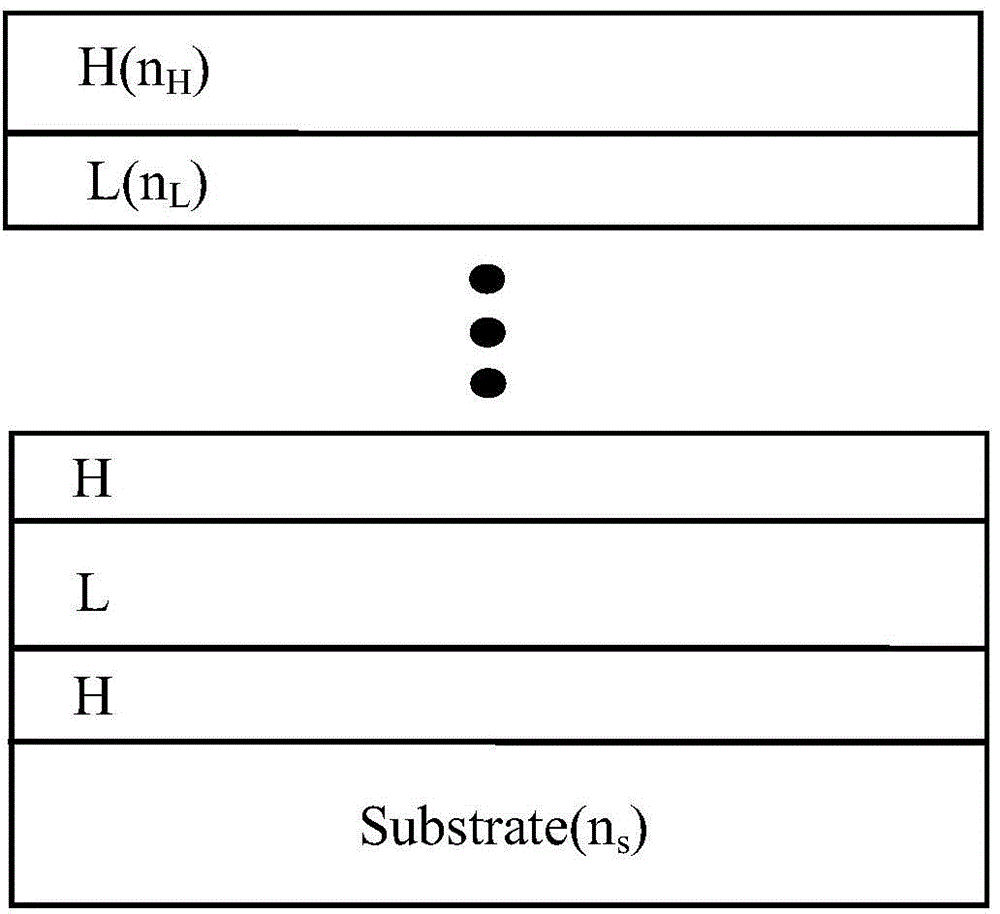
[0031] The optical units 2 are distributed in an array, and can be used in parallel optical transmission systems, optical interconnection networks of parallel processing computer cluster systems, and ultra-small high-performance optical interconnection parallel multiprocessor systems in space-borne free space. The optical unit 2 includes two distributed Bragg reflectors 4, a resonant cavity 3 sandwiched between the two distributed Bragg reflectors 4, and the distributed Bragg reflector 4 has two polymers with different refractive indices A periodic structure formed by alternating thin films; the resonant cavity 3 is made of an organic semiconductor or a single-layer polymer film doped with an active medium, and among the two distributed Bragg refl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com