Quasi-proportional resonance control-based permanent magnet synchronous motor parameter identification system and method
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, quasi-proportional resonance technology, used in control systems, control generators, vector control systems, etc., can solve problems such as voltage injection method overcurrent, reduce current harmonic content, strong versatility, The effect of preventing overcurrent problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
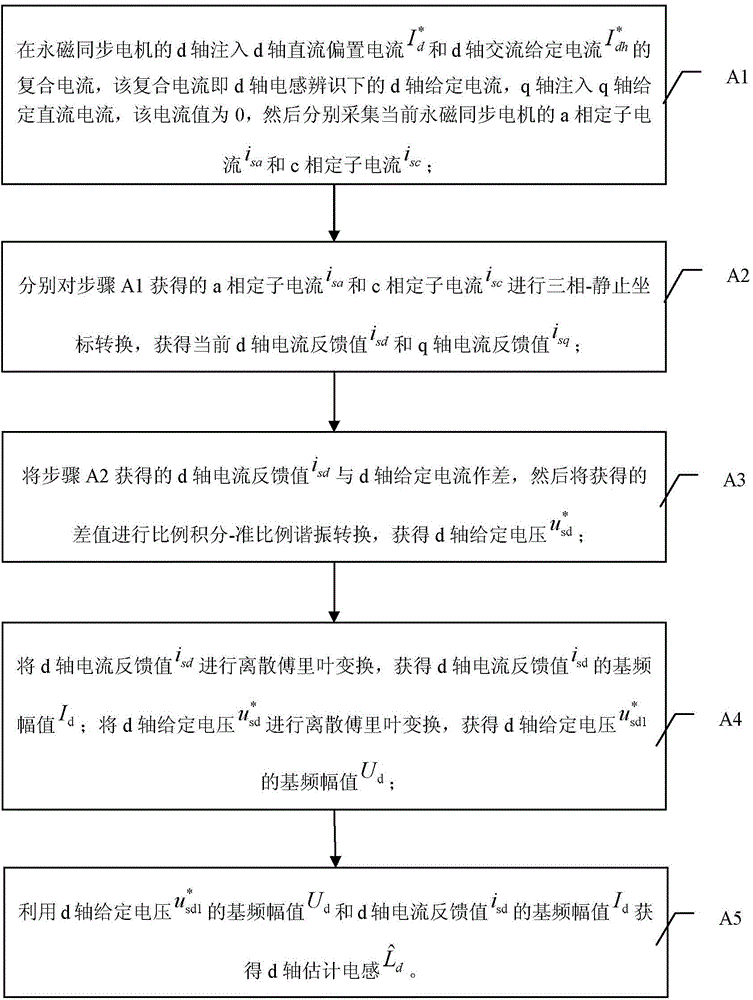
[0043] Specific implementation mode one: refer to figure 1 This embodiment is described in detail. The permanent magnet synchronous motor inductance parameter identification system based on quasi-proportional resonance control described in this embodiment includes: a voltage source inverter 2, a space vector pulse width modulation unit (SVPMW) 3, a three-phase - Stationary coordinate transformation unit 4, rotating-stationary coordinate transformation unit 5, two discrete Fourier analysis (DFT) units 6, inductance identification unit 7, proportional-integral-quasi-proportional resonant (PI-PR) controller 8 and quasi-proportional Resonant (PR) controller 9;
[0044] The current sensor is used to collect the current signal of the input terminal of the permanent magnet synchronous motor 1, the a-phase stator current signal output terminal of the current sensor is connected to the a-phase stator current signal input terminal of the three-phase-stationary coordinate transformation ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0066] Specific embodiment two: This embodiment is a further description of the permanent magnet synchronous motor inductance parameter identification system based on quasi-proportional resonance control described in specific embodiment one. In this embodiment,
[0067] The current fundamental frequency amplitude signal includes: the current fundamental frequency amplitude signal of the q-axis current feedback signal and the current fundamental frequency amplitude signal of the d-axis current feedback signal;
[0068] The voltage fundamental frequency amplitude signal includes: the voltage fundamental frequency amplitude signal of the q-axis voltage given signal and the voltage fundamental frequency amplitude signal of the d-axis voltage given signal;
[0069] The d-axis current feedback signal includes: d-axis DC current feedback signal and d-axis AC current feedback signal;
[0070] d-axis current given signal includes: d-axis dc bias signal and d-axis ac given signal;
[0...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0074] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is to further explain the permanent magnet synchronous motor inductance parameter identification system based on quasi-proportional resonance control described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, it also includes: a current sensor;
[0075] The current sensor is used to collect the a-phase current signal and the c-phase current signal of the permanent magnet synchronous motor 1 , and the current signal output end of the current sensor is connected to the current signal input end of the three-phase-stationary coordinate transformation unit 4 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com