Battery negative electrode active material based on quinone structure and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of battery negative electrode and active material, applied in the field of materials, can solve the problems of low Coulombic efficiency, poor cycle performance, hidden safety hazards, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a battery negative electrode material based on a quinone structure, including a quinone compound with a quinone structure as an electrochemical redox reaction site;
[0068] Among them, the quinone compounds include any one of benzoquinone sodium salt derivatives, anthraquinone sodium salt derivatives or naphthoquinone sodium salt derivatives; benzoquinone sodium salt derivatives, anthraquinone sodium salt derivatives or naphthoquinone sodium salt derivatives Derivatives have the following groups -ONa, -SO 3 At least one of Na or -COONa.
[0069] Specifically, the structure of the benzoquinone sodium salt derivative is shown in general formula (I):
[0070]
[0071] General formula (I)
[0072] Among them, the group R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4 At least one group in is -ONa, -SO 3 One of Na or -COONa, other groups include -ONa, -SO 3 Na, -COONa, -H, -CH 3 , -NH 2 、-OCH 3 , -Cl, -Br or -F in one or more.
[0073] The...
Embodiment 2
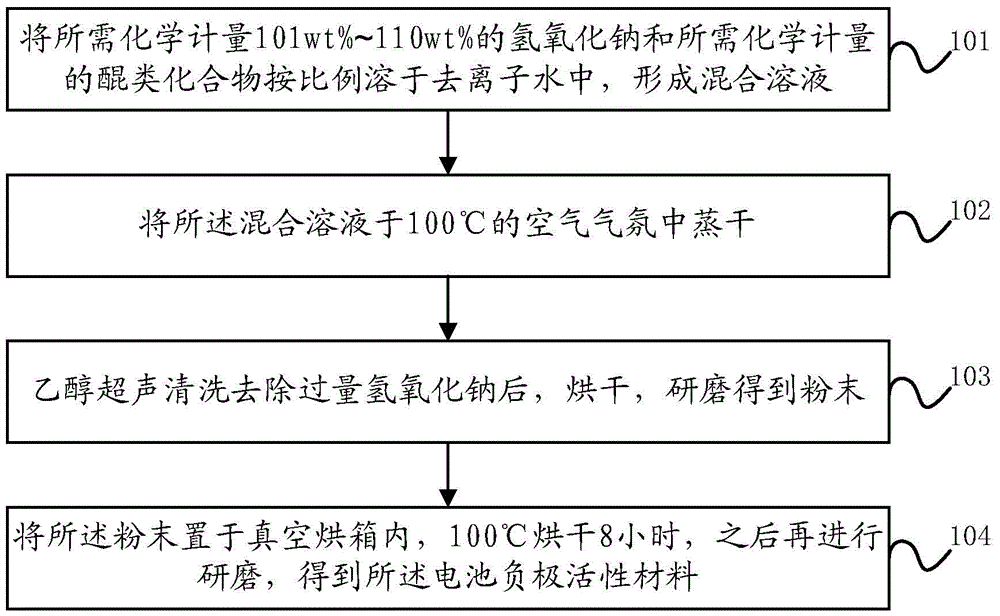
[0083] This embodiment provides a method for preparing a battery negative electrode active material based on a quinone structure, specifically an aqueous solution method, such as figure 1 shown, including:
[0084] Step 101, dissolving the required stoichiometric 101wt% to 110wt% sodium hydroxide and the required stoichiometric quinone compound in deionized water in proportion to form a mixed solution;
[0085] Wherein, the quinone compound is specifically one of hydroxyquinone compounds, carboxylic acid quinone compounds or sulfonic acid quinone compounds.
[0086] Step 102, evaporating the mixed solution to dryness in an air atmosphere at 100°C;
[0087] Step 103, after ultrasonic cleaning with ethanol to remove excess sodium hydroxide, drying and grinding to obtain powder;
[0088] In step 104, the powder is placed in a vacuum oven, dried at 100° C. for 8 hours, and then ground to obtain the negative electrode active material of the battery.
[0089] The preparation meth...
Embodiment 3
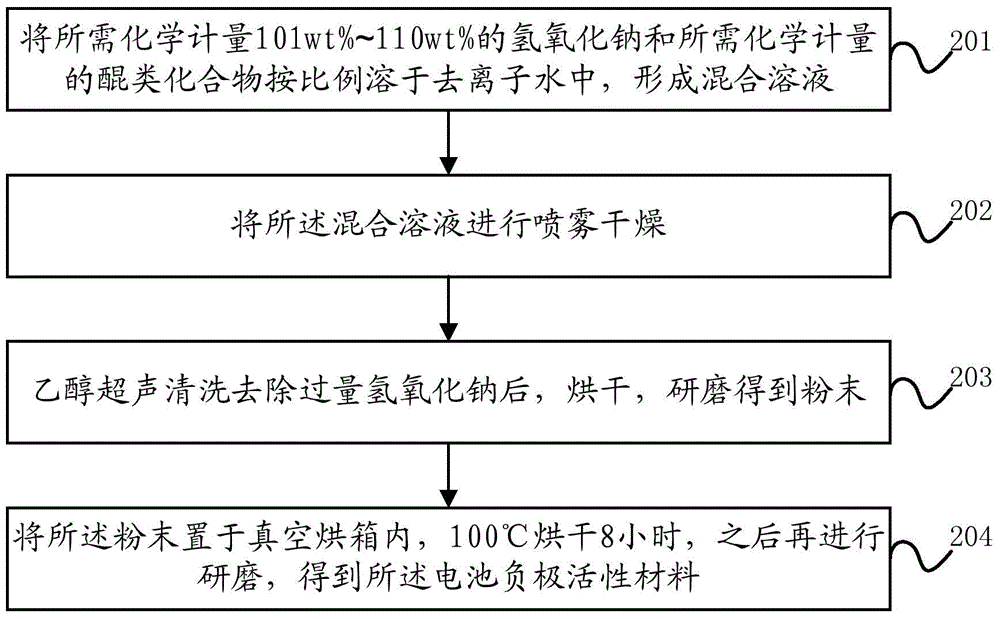
[0091] This embodiment provides a method for preparing battery negative electrode active materials based on quinone structure, specifically spray drying method, such as figure 2 shown, including:
[0092] Step 201, dissolving the required stoichiometric 101wt%-110wt% sodium hydroxide and the required stoichiometric quinone compound in deionized water in proportion to form a mixed solution;
[0093] Wherein, the quinone compound is specifically one of hydroxyquinone compounds, carboxylic acid quinone compounds or sulfonic acid quinone compounds.
[0094] Step 202, spray drying the mixed solution;
[0095] Step 203, after ultrasonic cleaning with ethanol to remove excess sodium hydroxide, drying and grinding to obtain powder;
[0096] In step 204, the powder is placed in a vacuum oven, dried at 100° C. for 8 hours, and then ground to obtain the battery negative electrode active material.
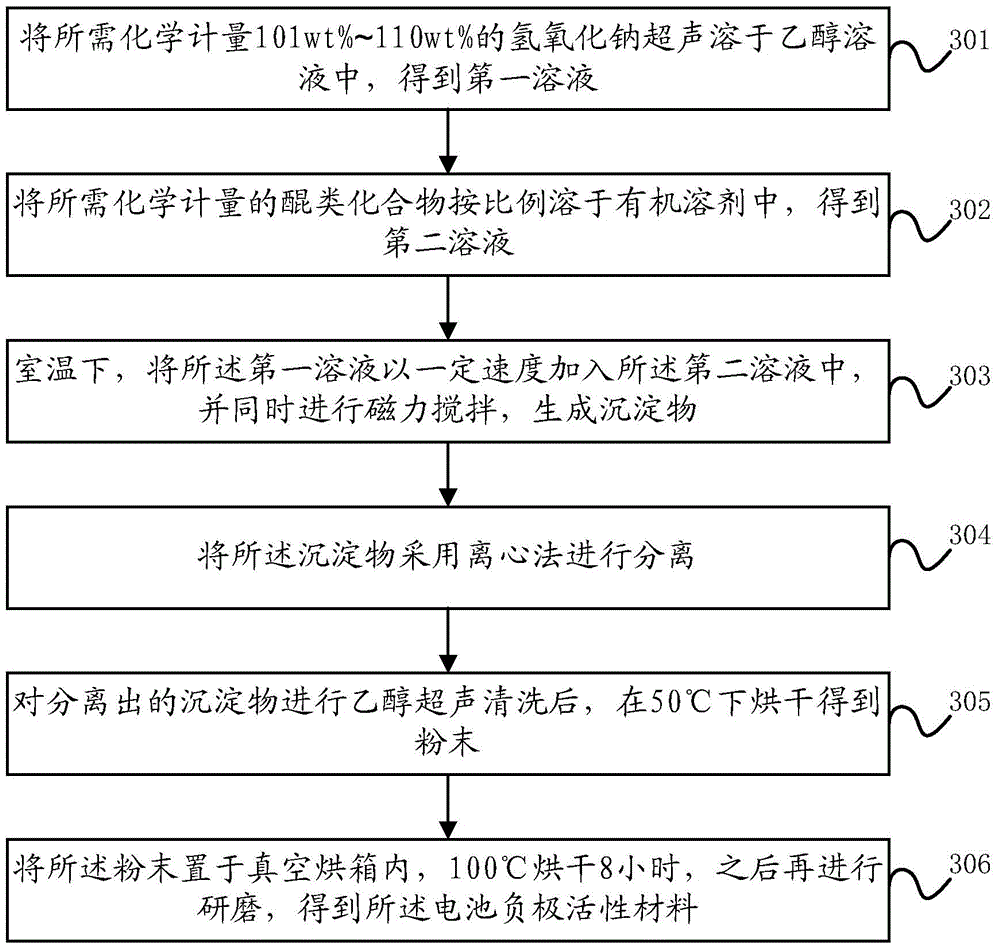
[0097]The preparation method of the negative electrode active material of the battery ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com