Phosphogypsum treatment method
A treatment method and technology of phosphogypsum, which is applied in the field of phosphogypsum treatment, can solve problems such as ineffective utilization of resources and unstable performance of phosphogypsum, and achieve the effect of reduced content and uniform particles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0008] A method for treating phosphogypsum, comprising the following steps: ① Pretreatment: aging the phosphogypsum until the attached water content is 9% (mass content); ② Compounding reaction: adding a modifier to the aged phosphogypsum , stir until the reaction is complete, the weight ratio of modifier to phosphogypsum is 1:25, the modifier is a mixture of lime and pozzolanic mixed material, and the weight ratio of lime and pozzolanic mixed material is 1:2.5; ③ drying : drying the phosphogypsum after compounding reaction at 400° C. until the attached water content of the phosphogypsum is dried below 2%; ④ calcining; calcining the dried phosphogypsum at 220° C. for 9 minutes.
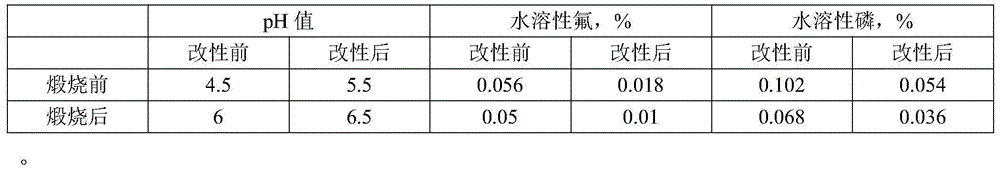
[0009] The performance comparison before and after the phosphogypsum treatment in this embodiment is shown in Table 1.1:
[0010] Table 1.1
[0011]
[0012] The strength comparison before and after treatment of phosphogypsum in this embodiment is shown in Table 1.2:
[0013] Table 1.2
[0014] ...
Embodiment 2
[0017] A method for treating phosphogypsum, comprising the following steps: ① Pretreatment: aging the phosphogypsum until the attached water content is 8% (mass content); ② Compounding reaction: adding a modifier to the aged phosphogypsum , stir until the reaction is complete, the weight ratio of modifier to phosphogypsum is 1:100, the modifier is a mixture of lime and pozzolanic mixed material, and the weight ratio of lime and pozzolanic mixed material is 1:1.5; ③ drying : drying the phosphogypsum after compounding reaction at 360°C until the attached water content of the phosphogypsum is dried below 2%; ④ calcining: calcining the dried phosphogypsum at 200°C for 12 minutes.
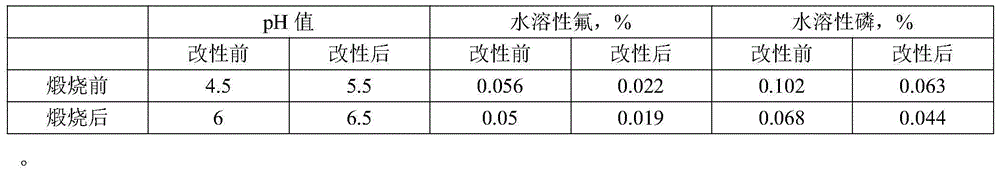
[0018] The performance comparison before and after the phosphogypsum treatment in this embodiment is shown in Table 2.1:
[0019] Table 2.1
[0020]
[0021] The strength comparison before and after treatment of phosphogypsum in this embodiment is shown in Table 2.2:
[0022] Table 2.2
[0023] ...
Embodiment 3
[0026] A method for treating phosphogypsum, comprising the following steps: ① Pretreatment: aging the phosphogypsum until the attached water content is 10% (mass content); ② Compounding reaction: adding a modifier to the aged phosphogypsum , stir until the reaction is complete, the weight ratio of modifier to phosphogypsum is 8:100, the modifier is a mixture of lime and pozzolanic mixed material, and the weight ratio of lime and pozzolanic mixed material is 1:4; ③ drying : drying the phosphogypsum after compounding reaction at 450°C until the attached water content of the phosphogypsum is dried below 2%; ④ calcining: calcining the dried phosphogypsum at 240°C for 6 minutes.
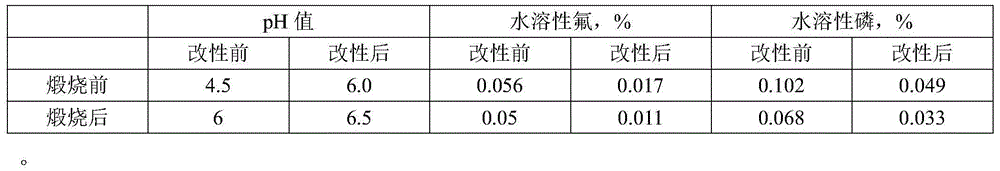
[0027] The performance comparison before and after the phosphogypsum treatment in this embodiment is shown in Table 3.1:
[0028] chart 3.1
[0029]
[0030] The strength comparison before and after treatment of phosphogypsum in this embodiment is shown in Table 3.2:
[0031] Table 3.2
[0032] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com