Frameworks and viruses encoding bispecific molecules secreted to mediate effector cell killing of target cells
A bispecific, mediated technology, applied to viruses/bacteriophages, medical preparations containing active ingredients, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as high preparation costs, short half-life, complex expression and purification of fusion proteins, and achieve titer High, low toxicity, and the effect of reducing the number of treatments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
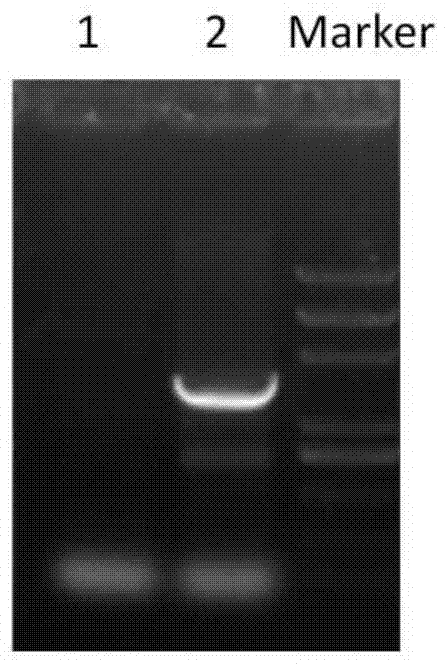
[0035] Example 1. Construction and identification of recombinant adenovirus
[0036] 1. Preparation of recombinant adenovirus
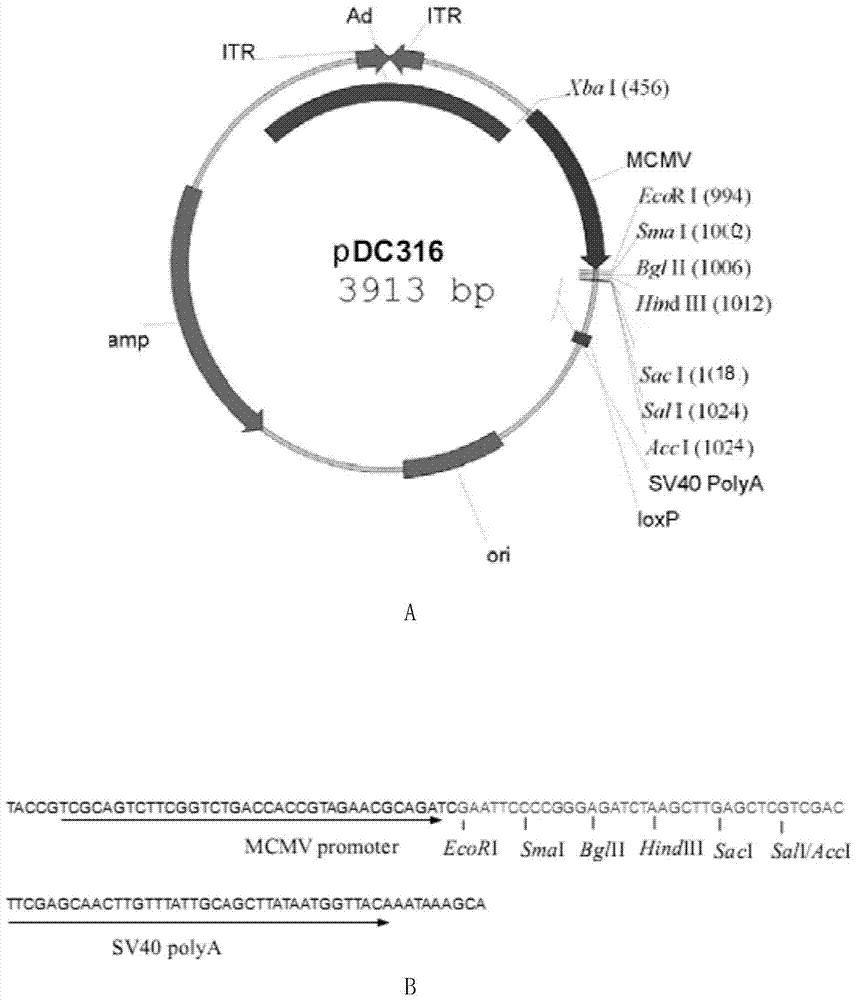
[0037] 1. Insert the double-stranded DNA molecule shown in Sequence 1 of the sequence table between the EcoRI and SalI restriction sites of plasmid PDC316 to obtain a recombinant plasmid.
[0038] The double-stranded DNA molecule shown in Sequence 1 of the Sequence Listing encodes the protein shown in Sequence 2 of the Sequence Listing (in Sequence 1, nucleotides 1 to 51 encode a signal peptide, which will eventually be excised). The protein shown in Sequence 2 of the sequence listing is named F3 protein, also known as Fcab-anti-CD3 protein. In sequence 2, positions 1-243 are anti-CD3 fragments (anti-CD3 fragments target T cells), positions 246-483 are Fcab fragments (Fcab fragments target HER2 antigen on the surface of tumor cells), and positions 484-493 Bits are myc tags.
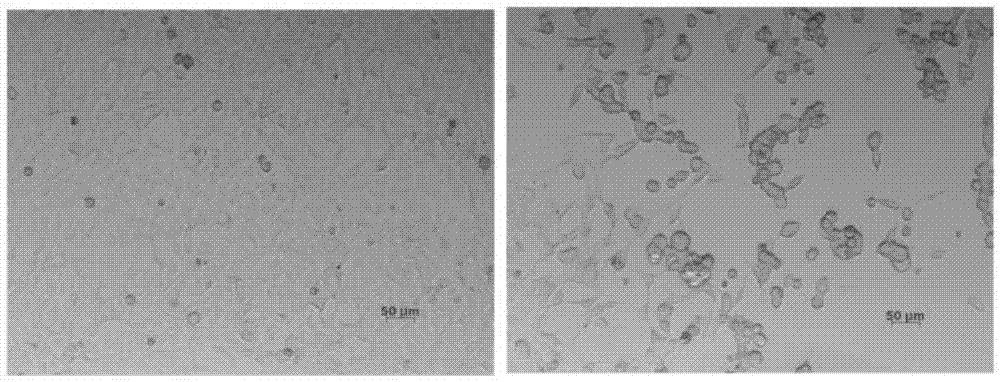
[0039] 2. Spread 293A cells in a six-well plate (about 6 × 10 per well). ...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Example 2. Construction of recombinant adenovirus
[0080] 1. Insert the double-stranded DNA molecule shown in sequence 3 of the sequence table between the EcoRI and SalI restriction sites of plasmid PDC316 to obtain a recombinant plasmid.
[0081] The double-stranded DNA molecule shown in Sequence 3 of the Sequence Listing encodes the protein shown in Sequence 4 of the Sequence Listing (in Sequence 3, the 1-51 nucleotides encode a signal peptide, which will eventually be excised). The protein shown in SEQ ID NO: 4 of the sequence listing is named H3 protein, also known as HER2-anti-CD3 protein. In sequence 4, positions 1-242 are HER2 fragments (HER2 fragments target the HER2 antigen on the surface of tumor cells), positions 260-502 are anti-CD3 fragments (anti-CD3 fragments target T cells), and positions 505-514 Bits are myc tags, bits 516-520 are His tags.
[0082] Other steps are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0083] Example 3. Construction of recombinant adenovirus
[0084] 1. Insert the double-stranded DNA molecule shown in Sequence 5 of the sequence table between the EcoRI and SalI restriction sites of plasmid PDC316 to obtain a recombinant plasmid.
[0085] The double-stranded DNA molecule shown in Sequence 5 of the Sequence Listing encodes the protein shown in Sequence 6 of the Sequence Listing (in Sequence 5, nucleotides 1 to 51 encode a signal peptide, which will eventually be excised). The protein shown in SEQ ID NO: 6 of the sequence listing is named M3 protein, also known as Mart1-anti-CD3 protein. In sequence 6, positions 1-117 are Mart1 fragments (Mart1 fragments target the HLA-A2-MART1 polypeptide complex on the surface of tumor cells), and positions 137-379 are anti-CD3 fragments (anti-CD3 fragments target T cells) , positions 382-391 are myc tags, and positions 393-397 are His tags.
[0086] Other steps are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com