Novel high-temperature resistant alpha-amylase, preparing method of novel high-temperature resistant alpha-amylase and application of novel high-temperature resistant alpha-amylase
A technology of high temperature resistance and amylase, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of reducing economic benefits and increasing the complexity of the process, and achieve the effects of reducing energy consumption, obvious economic and social benefits, and improving stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1: Obtaining of wild-type high temperature resistant α-amylase gene
[0030] (1) Extraction of Bacillus licheniformis genomic DNA:
[0031] ①Cultivate the bacteria at 37°C, 200r / min for 18-24h, and collect the bacteria.
[0032] ②Add 500μL ddH 2 O, resuspend the cells, wash the cells, centrifuge at 5000r / min for 5min, and discard the supernatant.
[0033] ③Add 500μL ddH 2 O, resuspend the bacteria, add lysozyme (15 μg / mL), and digest in a water bath at 37°C for 1 hour.
[0034] ④ Add 50 μL of 10% SDS and 30 μL of proteinase K, and digest in a water bath at 60°C for 2 hours.
[0035] ⑤Add 10% volume of 5mol / L NaCl, transfer the supernatant tube to add an equal volume of phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1), invert the centrifuge tube several times, and centrifuge at 12000r / min for 10min.
[0036] ⑥ Take the supernatant, add an equal volume of phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1), invert the centrifuge tube several times, and centrifuge at 1200r...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: Site-directed mutation of the wild-type high temperature resistant α-amylase gene
[0047] (1) The wild-type thermostable α-amylase gene was ligated into the vector pUC19.
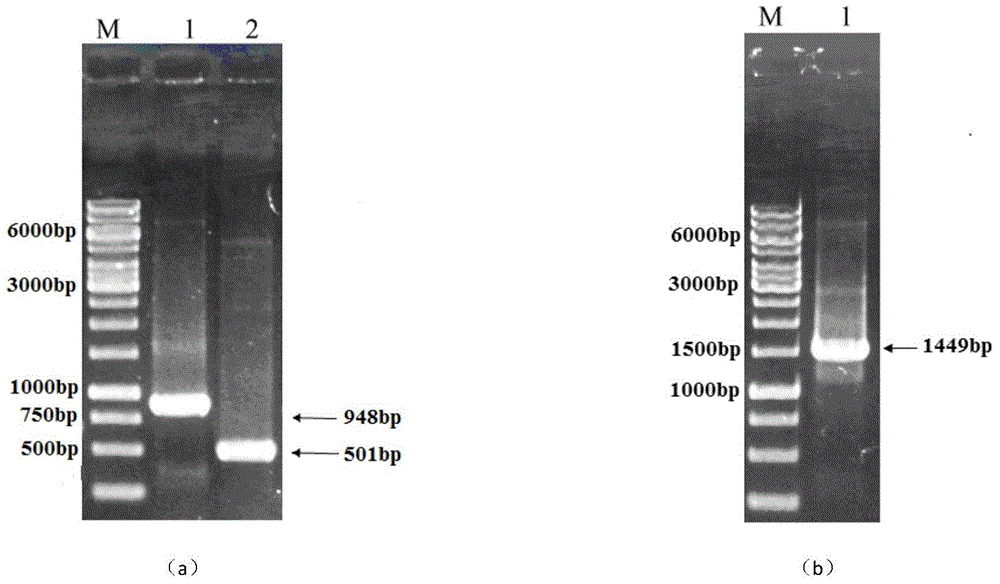
[0048] The target gene amplified by PCR was purified, digested with BamHI and HindIII, and the digested product was purified and detected by agarose gel electrophoresis. At the same time, plasmid pUC19 was double digested with BamHI and HindIII, purified, and finally T 4 DNA ligase was ligated at 12°C for 8 hours to construct the recombinant plasmid pUC19-amy. The recombinant plasmid was transformed into Escherichia coli JM109 by electroporation, and the results of double enzyme digestion and PCR verification showed that the amy gene had been successfully cloned into the vector pUC19.
[0049] Its sequencing shows that it is amplified to the wild-type high temperature resistant α-amylase gene sequence such as SEQ ID NO:5.
[0050] (2) Site-directed mutation
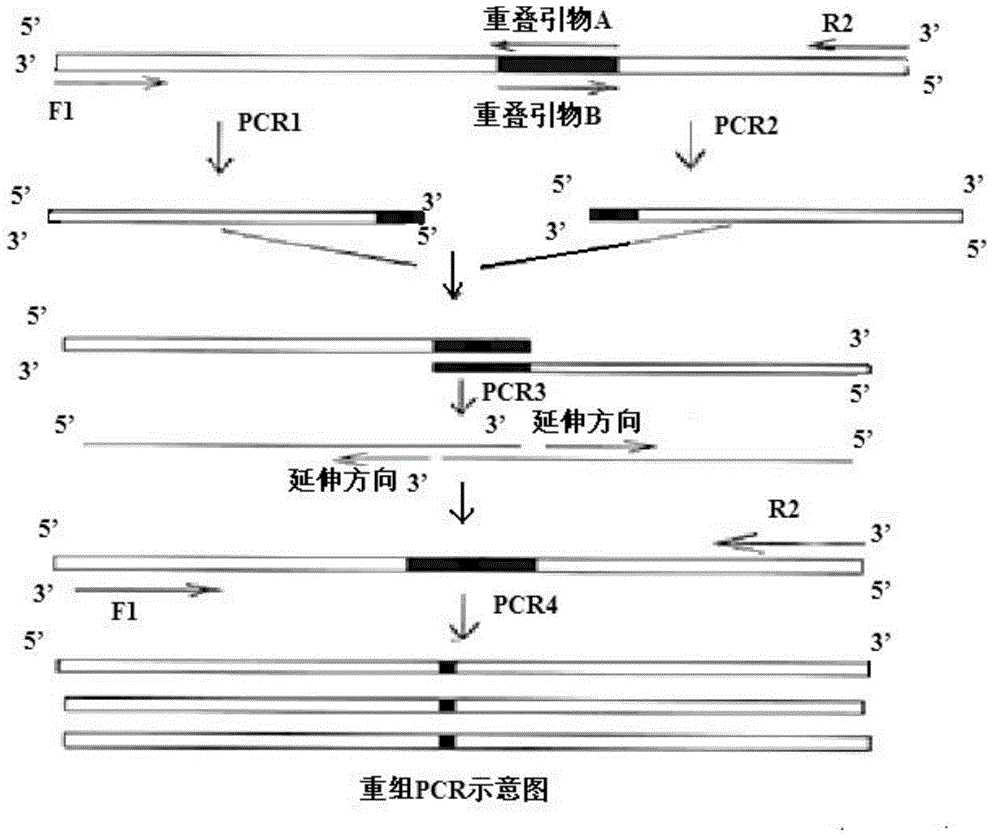
[0051] A new type of high...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Example 3: Construction of a novel high temperature resistant α-amylase expression vector
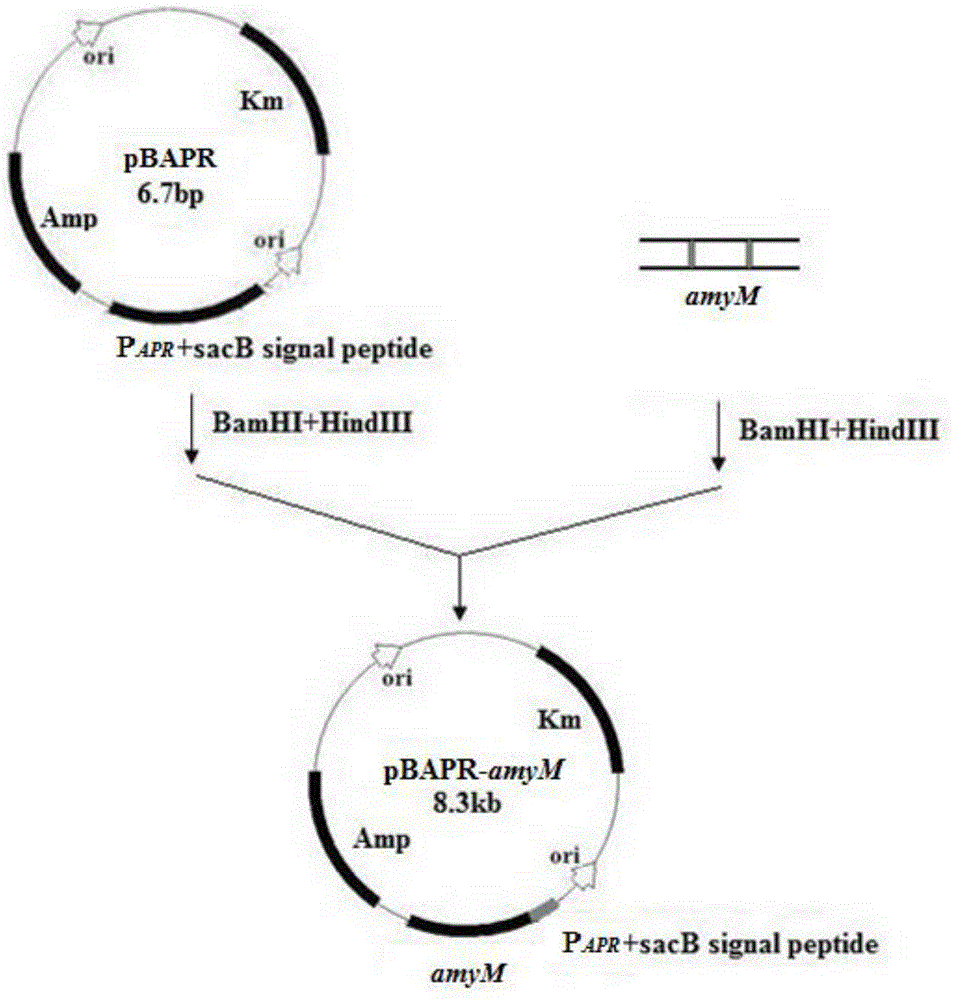
[0065] pBAPR is based on the Escherichia coli-Bacillus subtilis shuttle cloning vector pBE2 as the backbone, cloned into a strong promoter of Bacillus alkalophilus alkaline protease P APR and the fructan sucrase signal sequence sacB that can directly secrete the recombinant protein into the culture medium. It contains both the replicon of the Bacillus subtilis plasmid pUB110 and the replicon of the Escherichia coli plasmid pGEM3, and can autonomously replicate in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis cells. it comes with amp r and Km r Gene, ampicillin resistance can be used as a selection marker in Escherichia coli, and kanamycin resistance can be used as a selection marker in Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis.
[0066] The novel high-temperature-resistant α-amylase gene amyM and pBAPR obtained by overlapping PCR construction were digested ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com