Cobalt-base alloy, as well as thermal processing and thermal treatment methods and application thereof
A heat treatment method and technology of cobalt-based alloy, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve the problem of in-stent restenosis that cannot be effectively suppressed, and achieve the effects of solving in-stent restenosis, reducing or inhibiting in-stent restenosis, and reducing the formation of thrombus.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
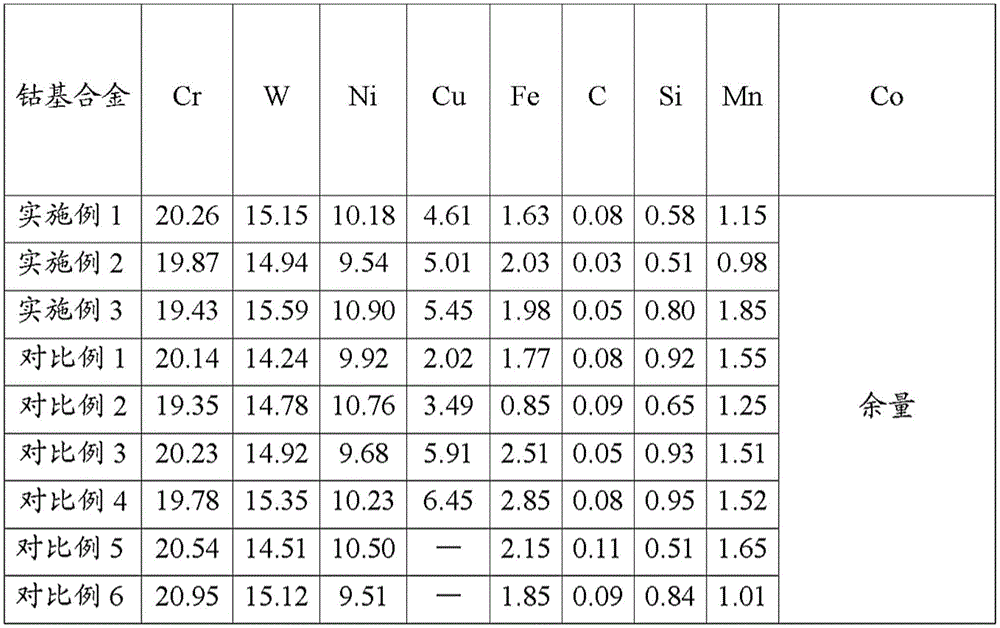
[0059] The content is 20.26 (weight) % of Cr, W: 15.15 (weight) %; Ni: 10.18 (weight) %; Fe: 1.63 %; C: 0.08 (weight) %; Si: 0.58 (weight) %; Mn: 1.15(weight)%; Cu: 4.61(weight)%; the rest is cobalt-based alloy of Co and unavoidable impurities after hot working, specifically:
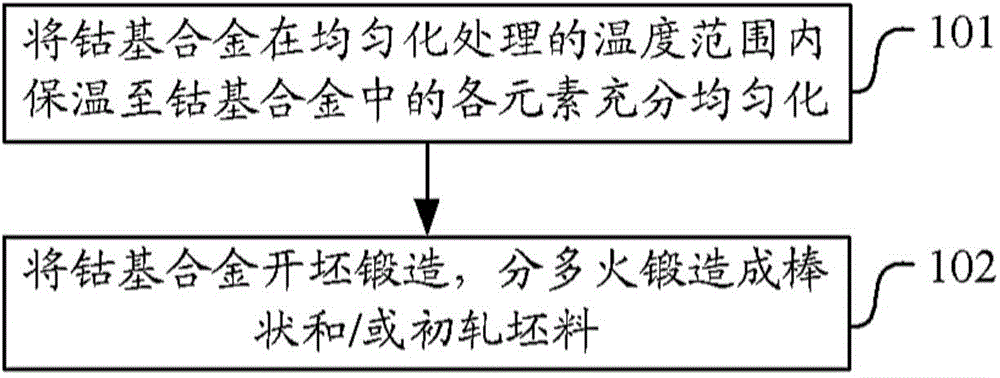
[0060] Homogenize the cobalt-based alloy at 1200-1250°C for 2-4 hours until the elements in the cobalt-based alloy are fully homogenized;
[0061] The cobalt-based alloy is billet-forged and multi-fired forged into rods and / or blooms, and the final forging temperature is not lower than 1000°C.
[0062] After thermal processing and then heat treatment, specifically:
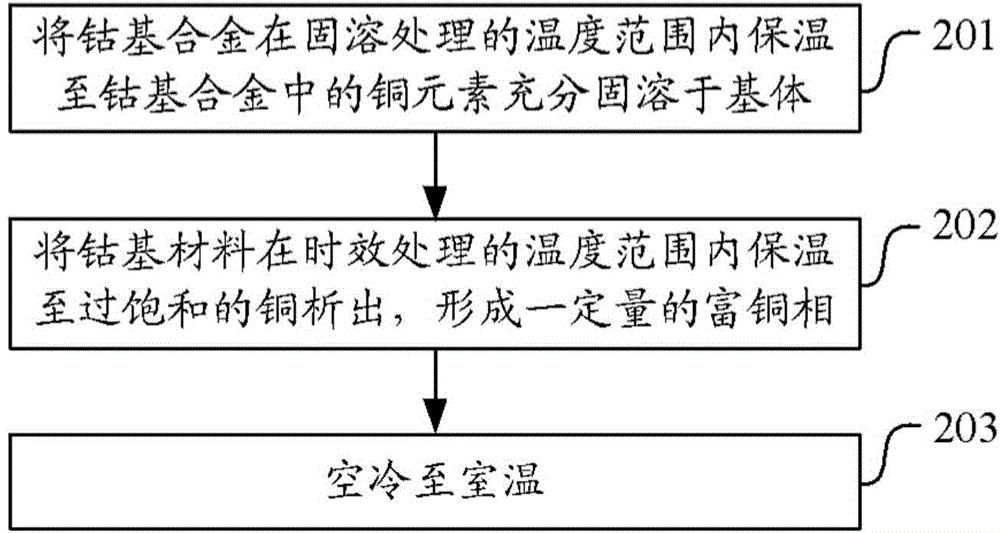
[0063] Solid solution treatment of the cobalt-based alloy at 1100-1200°C for 1-2 hours until the copper element in the cobalt-based alloy is fully dissolved in the matrix;
[0064] Heat the cobalt-based alloy at 700°C for 2-6 hours until the supersaturated copper is precipitated and a certain amount of copper-rich phase is formed;
[006...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Repeat embodiment 1, following difference is arranged: content is that Cr is 19.87 (weight) %, W: 14.94 (weight) %; Ni: 9.54 (weight) %; Fe: 2.03 (weight) %; C: 0.03 (weight) % ) %; Si: 0.51 (weight) %; Mn: 0.98 (weight) %; Cu: 5.01 (weight) %; the rest is Co and unavoidable impurities Cobalt-based alloy after hot working and heat treatment. See Table 1 for the composition content data of the cobalt-based alloy in Example 2 above, and see Table 2 for the cobalt-based alloy after thermal processing and heat treatment.
Embodiment 3
[0070] Repeat embodiment 1, following difference is arranged: content is that Cr is 19.43 (weight) %, W: 15.59 (weight) %; Ni: 10.90 (weight) %; Fe: 1.98 (weight) %; C: 0.05 (weight) % ) %; Si: 0.80 (weight) %; Mn: 1.85 (weight) %; Cu: 5.45 (weight) %; the rest is Co and unavoidable impurities of cobalt-based alloy after hot working and heat treatment. See Table 1 for the composition content data of the cobalt-based alloy in Example 3, and see Table 2 for the cobalt-based alloy after thermal processing and heat treatment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com