Nucleic acid molecule binding to influenza virus and use therefor
A technology for nucleic acid molecules and influenza viruses, which is applied in the field of nucleic acid molecules combined with influenza viruses and their applications, and can solve the problems of insufficient binding ability of nucleic acid molecules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment A1
[0186] Aptamers capable of binding to influenza virus were prepared, and the ability of each aptamer to bind to influenza virus-derived HA was examined.
[0187] (1) Aptamer
[0188] As aptamers of this example, the following polynucleotides were synthesized.
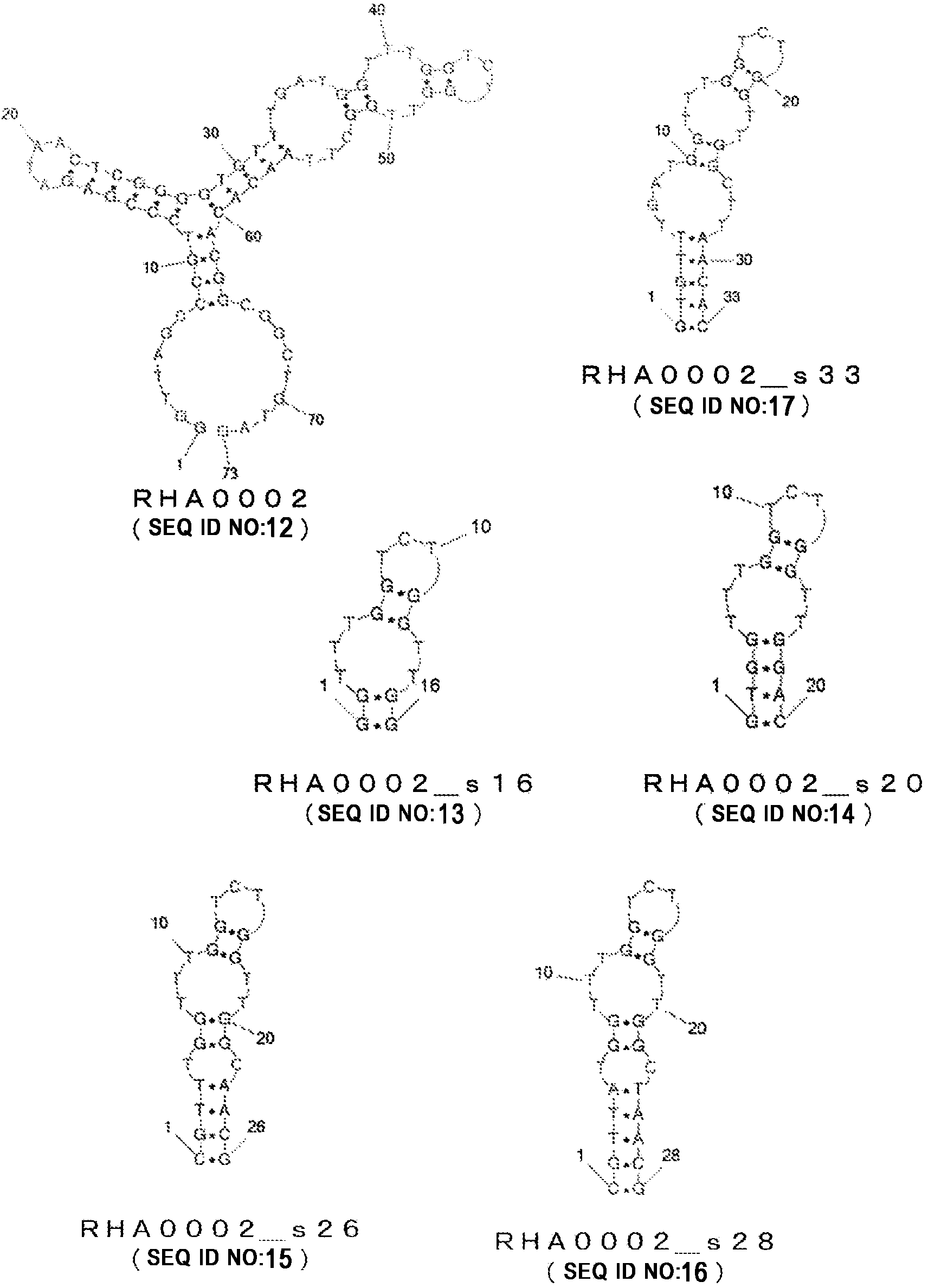
[0189] RHA0002 (SEQ ID NO: 12)
[0190] GGTTAGCCCGTCCCGAGATAACTCGGGGTGTTTGATGGTTTGGTCTGGTTGGCTTAACACACGGCGGCTGTAG
[0191] RHA0006 (SEQ ID NO: 18)
[0192] GGTTAGCCCGTCCCGAGATAACTCGGTGTGTTGGGTTTGGGTTGGGTTGGGTCTTAACACACGGCGGCTGTAG
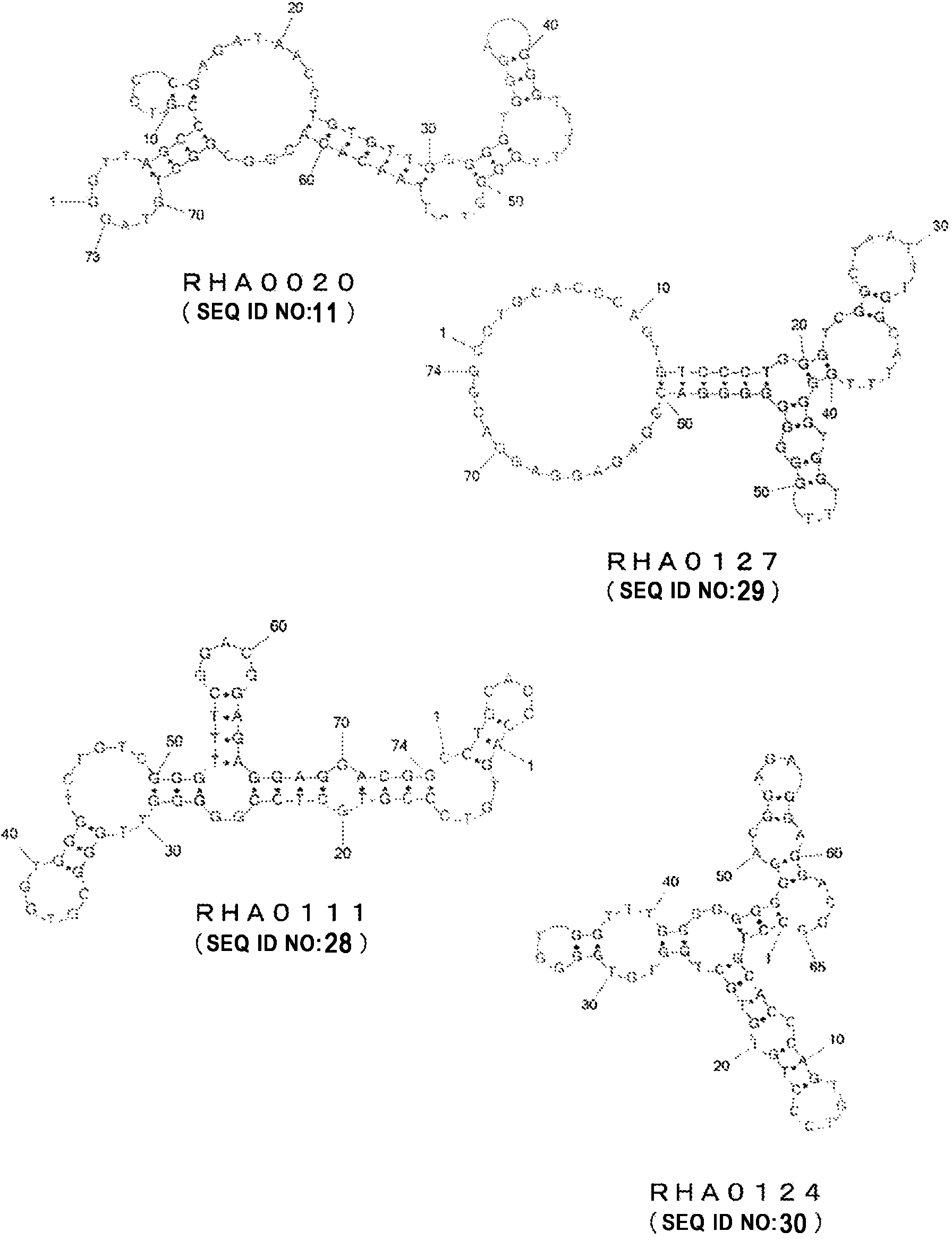
[0193] RHA0111 (SEQ ID NO: 28)
[0194] CCTGCACCCAGTGTCCCGTGCTCCGGGGGTTGGGCGTGGTGGGTCTGTCGGGTTTCGGACGGAGAGGAGGACGG
[0195] RHA0127 (SEQ ID NO: 29)
[0196] CCTGCACCCAGTGTCCCTGGGTCGGCTAATTTGGCATTTGGGGTGGTTTGGGGGGGGGACGGAGAGGAGGACGG
[0197] A DNA library comprising a plurality of DNAs was prepared as Comparative Example N30, each DNA represented by an oligonucleotide of SEQ ID NO: 34 (which includes a random sequence of 30-mers (N) 30 )composition. Moreover, a DNA library comprising ...
Embodiment A2
[0254] This example examines the binding ability of the aptamer obtained by truncating RHA0002 (SEQ ID NO: 12) to HA.
[0255] (1) Aptamer
[0256] RHA0002 (SEQ ID NO: 12) shown below and its truncated aptamer were synthesized.
[0257] RHA0002 (SEQ ID NO: 12)
[0258] GGTTAGCCCGTCCCGAGATAAC TCGGGGTGTTTGATGGTTTGG TCTGGTTGG CTTAACACACGGCGGCTGTAG
[0259] RHA0002_s33 (SEQ ID NO: 17)
[0260] GTGTTTGATGGTTTGGTCTGGTTGGCTTAACAC
[0261] (2) Binding ability analysis by SPR
[0262] Except for using the above aptamers, the binding ability to the target protein was analyzed in the same manner as in Example A1. The results are shown in Table 1 below. In Table 1, relative values were determined in the same manner as in item (3) of Example A1.
[0263] [Table 1]
[0264]
[0265] As can be seen from Table 1, the truncated aptamers showed binding ability to each target protein. In particular, RHA0002_s33 (SEQ ID NO: 17) showed improved binding ability by truncation.
Embodiment A3
[0267] This example examines the binding ability of RHA0006 (SEQ ID NO: 18), a truncated aptamer obtained by truncating RHA0006, and an aptamer including two truncated sequences of the truncated aptamer to HA.
[0268] (1) Aptamer
[0269] RHA0006 (SEQ ID NO: 18)
[0270] GGTTAGCCCGTCCCGAGATAACTCGGTGTGTTGGGTTTGGGTTGGGTTGGGTCTTAACACACGGCGGCTGTAG
[0271] RHA0006_s19 (SEQ ID NO: 19)
[0272] GGGTTTGGGTTGGGTTGGG
[0273] RHA0006_s19_d9 (SEQ ID NO: 32)
[0274] GGGTTTGGGTTGGGTTGGG TTTTTTTTT GGGTTTGGGTTGGGT TGGG
[0275] (2) Binding ability analysis by SPR
[0276] Except for using the above aptamers, the binding ability to the target protein was analyzed in the same manner as in Example A1. The results are shown in Table 2 below. In Table 2, relative values were determined in the same manner as in item (3) of Example A1.
[0277] [Table 2]
[0278]
[0279] As can be seen from Table 2, the truncated aptamers and the aptamers having two truncated sequences each ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com