Method for reducing charge and discharge polarization of lithium air battery with nonaqueous electrolytic solution
A lithium-air battery and electrolyte technology, applied in secondary battery charging/discharging, fuel cell-type half-cells and secondary battery-type half-cells, secondary battery repair/maintenance, etc., can solve battery cost, energy Adverse impact of density, high charge and discharge polarization, restricting development and application, etc., to improve bulk charge transport capability and reduce charge and discharge polarization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
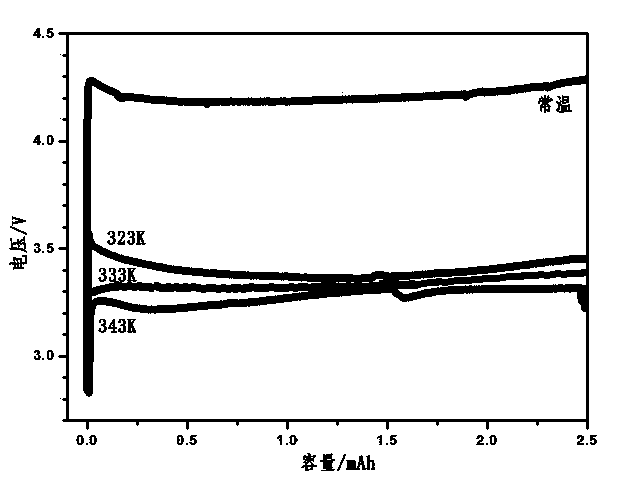
[0032] A discharged battery is charged at 70°C, 60°C, and 50°C, and compared with a battery charged at room temperature.
[0033] The positive electrode of the discharged battery adopts Li 2 O 2 It is mixed with the binder PVDF according to the mass ratio of 80:20. After thorough grinding and mixing, an appropriate amount of NMP is added dropwise. After ultrasonic dispersion, the above-mentioned slurry is coated on the foamed nickel current collector, and vacuum dried at 100 ℃ for 2 h After cooling to room temperature, the desired positive electrode is obtained.
[0034] The battery assembly is carried out in a glove box filled with argon protection. The electrolyte is 0.65 M LiTFSI DME / DOL mixed solvent (volume ratio 1:1), and the injection volume is about 800 μL. The positive electrode of the battery is the discharged positive electrode prepared above, the negative electrode is a metal lithium sheet, and the separator is Celgard 2350. When assembling, first put in the negative ...
Embodiment 2
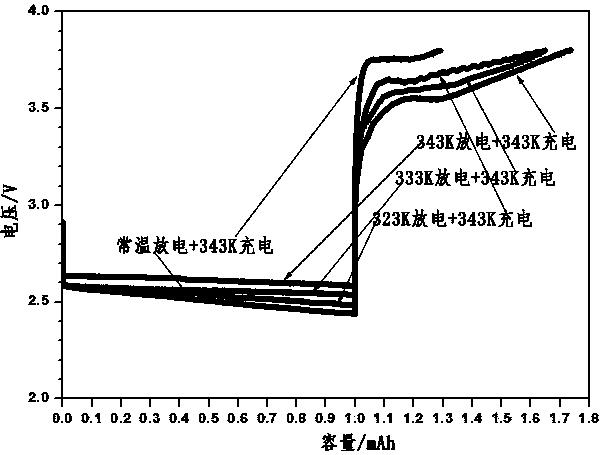
[0037] After discharging the charged battery at 70℃, 60℃, and 50℃, compare it with the battery discharged at normal temperature. The cut-off capacity for discharge at 70°C, 60°C, 50°C and normal temperature is 1 mAh to ensure the same amount of discharge products when used for subsequent charging. Subsequently, considering that the state of the discharged products at different temperatures may be inconsistent, the four batteries in the discharged state were charged at the same charging temperature (70°C).
[0038] The positive electrode of the rechargeable battery adopts a carbon electrode. By adding a 60% PTFE solution to an appropriate amount of deionized water, while ultrasonically dispersing, add an appropriate amount of isopropanol and superconducting carbon black Super P (Super P and PTFE mass ratio 7:3) and continue Ultrasonic dispersion. Subsequently, the slurry was coated on a stainless steel mesh current collector, vacuum dried at 200°C for 12 h, and the desired positi...
Embodiment 3
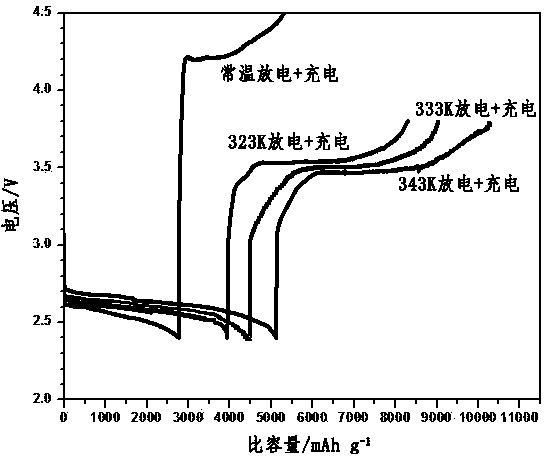
[0042] Use rechargeable batteries to discharge and charge at 70°C, 60°C, and 50°C, and compare with batteries that are discharged and charged at room temperature. The charge and discharge current is 0.05 mA cm -2 , The charge cut-off voltage is 3.8V, the charge reaction can reach more than 90%, when the discharge voltage is 2.4V, the discharge reaction can reach more than 90%, the charged battery is discharged at 70℃, 60℃, 50℃, and the discharge cut-off The voltage 2.4V completes the discharge reaction, and then the battery in the discharged state is charged at 70°C, 60°C, and 50°C until it reaches the charge cut-off voltage of 3.8V to complete the charging reaction. The battery experiment at room temperature is the same as above.
[0043] The positive electrode of the rechargeable battery adopts a carbon electrode. By adding a 60% PTFE solution to an appropriate amount of deionized water, while ultrasonically dispersing, add an appropriate amount of isopropanol and superconductin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com