Solar cell, method for producing solar cell, and solar cell module
A technology of solar cells and manufacturing methods, applied in the direction of electrical components, final product manufacturing, sustainable manufacturing/processing, etc., can solve problems such as complicated processes, and achieve the effect of easy electrode formation and excellent photoelectric conversion characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
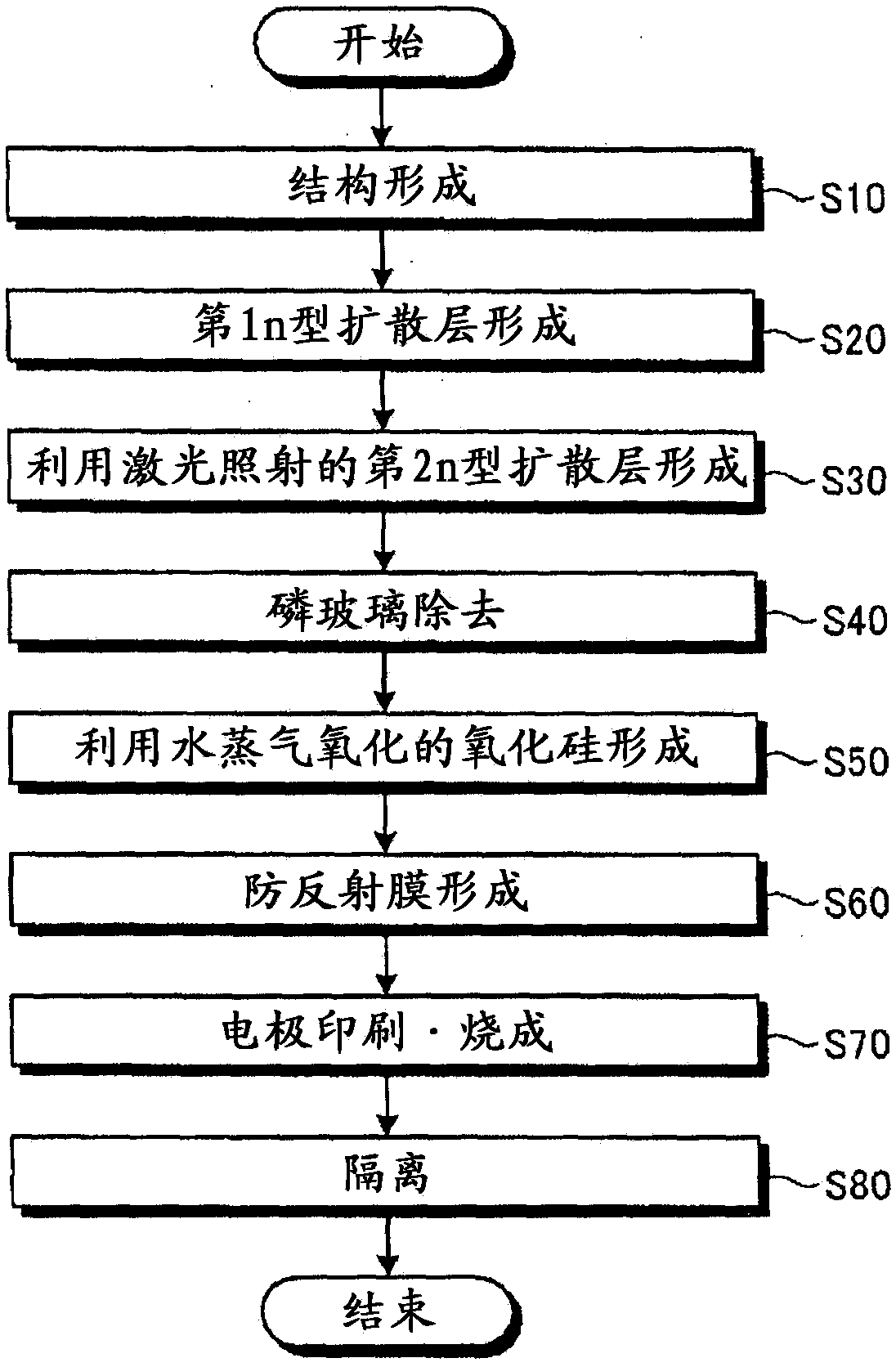
[0038] figure 1 It is a flowchart for explaining an example of the manufacturing process of the solar battery cell concerning Embodiment 1 of this invention. Figure 2-1 to Figure 2-9 It is a cross-sectional view of main parts for explaining an example of the manufacturing process of the solar cell according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. image 3 It is a main part perspective view which shows the schematic structure of the solar battery cell concerning Embodiment 1 produced by the manufacturing method of the solar battery cell concerning Embodiment 1. FIG. be explained, although in figure 1It is not described in the following descriptions, but immersion treatment in hydrofluoric acid and water washing treatment for the purpose of wafer cleaning treatment and natural oxide film removal are performed as necessary between each process.
[0039] First, as a semiconductor substrate, for example, a p-type monocrystalline silicon substrate (hereinafter referred to as a ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0092] Figure 8 It is a flowchart for explaining an example of the manufacturing process of the solar battery cell concerning Embodiment 2 of this invention. Although the case of removing the phosphorous glass after laser irradiation was described in Embodiment 1, the sequence of laser irradiation and phosphorous glass removal is not limited to this. The order of laser irradiation and phosphorous glass removal may be reversed, that is, laser irradiation is performed after phosphorous glass is removed.
[0093] When using phosphorus oxychloride (POCl 3 ) after thermal diffusion of the gas, phosphorus (P) that has not been electrically activated (inactive) exists on the surface of the silicon substrate. When laser irradiation is performed in this state, inactive phosphorus (P) is activated by laser irradiation, and the activated phosphorus (P) diffuses into a deeper region of the silicon substrate to form an SE structure. Thereafter, when the silicon substrate is subjected t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com