Enzymatic acidolysis-based method for synthesizing structured lipids from palmitic acid triglycerides
A technology of palmitic acid triglyceride and structural lipids, applied in the direction of edible oil/fat, food science, application, etc., can solve the problems of waste of resources, unreachable preparation process effect, cumbersome preparation process, etc., to extend the industrial chain , Improve the effect of resource utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] This example illustrates the process of extracting free fatty acids from different raw oils and fats, and the obtained free fatty acids are used in subsequent examples.
[0037] Alkaline hydrolysis is adopted; the free fatty acid extraction method is: dissolve the oil in 95vt.% ethanol of 0.006g / mL NaOH, the oil concentration is 0.25g / mL, saponify and reflux in nitrogen (65°C, 6h), and recover by rotary evaporation Ethanol, add 50mL of distilled water and adjust the pH to 3~4 with HCl, let it stand for 1h, add 50mL of petroleum ether after removing water, then add 50mL of distilled water and wash until the oil phase is neutral, take the petroleum ether layer and dehydrate with anhydrous magnesium sulfate After filtration and rotary evaporation, free fatty acids were obtained. After methyl esterification, the types and contents of fatty acids in each component were detected by gas chromatography. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0038] Table 1. Types and contents of...
Embodiment 2
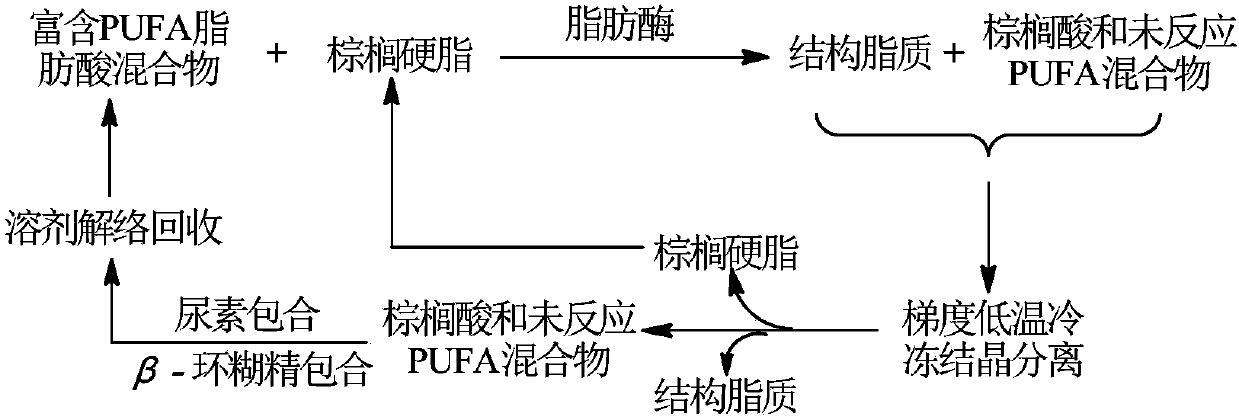
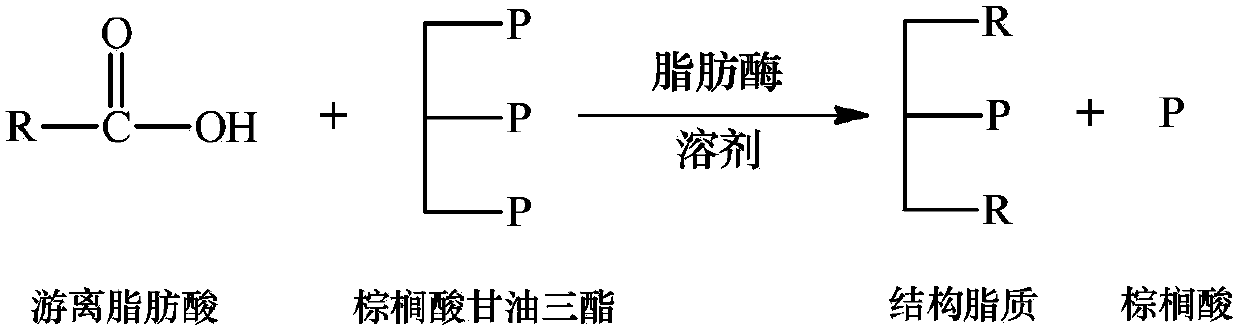
[0041] This example illustrates the reaction process of enzymatic acid hydrolysis of free fatty acid and palmitic acid triglyceride.
[0042] Silkworm chrysalis oil was hydrolyzed with alkali to obtain free fatty acids, and enzymatic acid hydrolysis of silkworm chrysalis oil free fatty acids and palmitic acid triglycerides prepared sn-2 structural lipids rich in palmitic acid. Among them, the content of unsaturated fatty acid in silkworm chrysalis oil is more than 80%, and the content of oleic acid, linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid is more than 80%. Reaction conditions: substrate ratio is silkworm chrysalis oil free fatty acid (mol): palmitic acid triglyceride (mol)=12:1; Lipozyme RM IM enzyme amount: 10% (by substrate weight, wt%); Temperature: 60 ℃ ;Reaction time: 24h. After the reaction, samples were collected, and after methyl esterification, gas chromatography was used to determine the fatty acid species, content and distribution of the product triglyceride. As de...
Embodiment 3
[0046] This example illustrates the reaction process of enzymatic acid hydrolysis of free fatty acid and palmitic acid triglyceride.
[0047] Silkworm chrysalis oil was hydrolyzed with alkali to obtain free fatty acids, and enzymatic acid hydrolysis of silkworm chrysalis oil free fatty acids and palmitic acid triglycerides prepared sn-2 structural lipids rich in palmitic acid. Among them, the content of unsaturated fatty acid in silkworm chrysalis oil is more than 80%, and the content of oleic acid, linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid is more than 80%. Reaction conditions: substrate ratio is silkworm chrysalis oil free fatty acid (mol): palmitic acid triglyceride (mol)=7: 1; Lipozyme RM IM enzyme amount: 7% (by substrate weight, wt%); Temperature: 40 ℃ ; Reaction time: 48h. After the reaction, samples were collected, and after methyl esterification, gas chromatography was used to determine the fatty acid species, content and distribution of the product triglyceride. As de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com