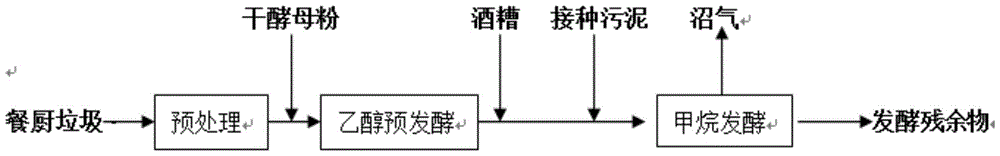
A method for producing biogas by two-phase dry mixed anaerobic fermentation
An anaerobic fermentation and biogas production technology, applied in fermentation, biosynthesis, waste fuel, etc., can solve the problems of harsh conditions for microbial activity, slow industrialization progress, and prone to acidification, so as to alleviate the problem of acid inhibition and enrich the theory , the effect of increasing methane production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
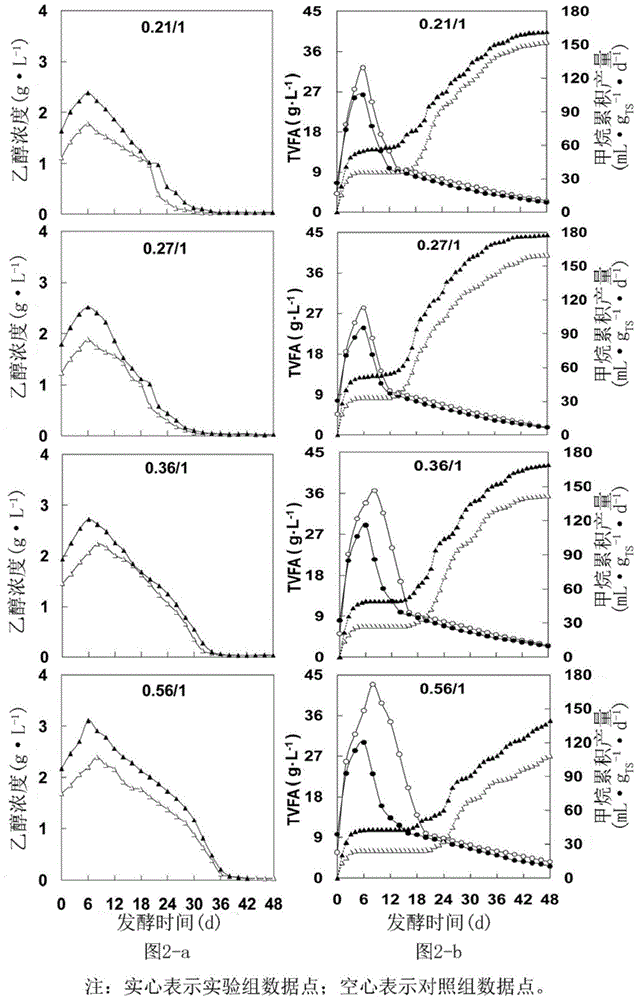
[0029] Put the food waste into an ethanol pre-fermentation tank after being crushed, add dry yeast with a mass of 5‰ of the dry weight of food waste (calculated as VS), and carry out 12 days under the condition of temperature 30±1℃ and anoxic. ~72 hours of ethanol pre-fermentation, and then the food waste and distiller's grains are uniformly mixed at a mass ratio (calculated as VS) of 1:1 to 0.21:1, and the sludge is inoculated and fermented to produce biogas, wherein the inoculation ratio ( Inoculation sludge: Fermentation raw material (food waste + distiller's grains)) is 1:1 (calculated as VS, w / w). 339mL / (d·L). The result is as figure 2 shown, from figure 2 It can be seen that compared with the control group without pre-fermentation, regardless of the mixing ratio of food waste and distiller's grains, the gas production, ethanol concentration, and volatile fatty acid VFA concentration of the ethanol pre-fermentation group were higher , thereby shortening the acid inhi...
Embodiment 2
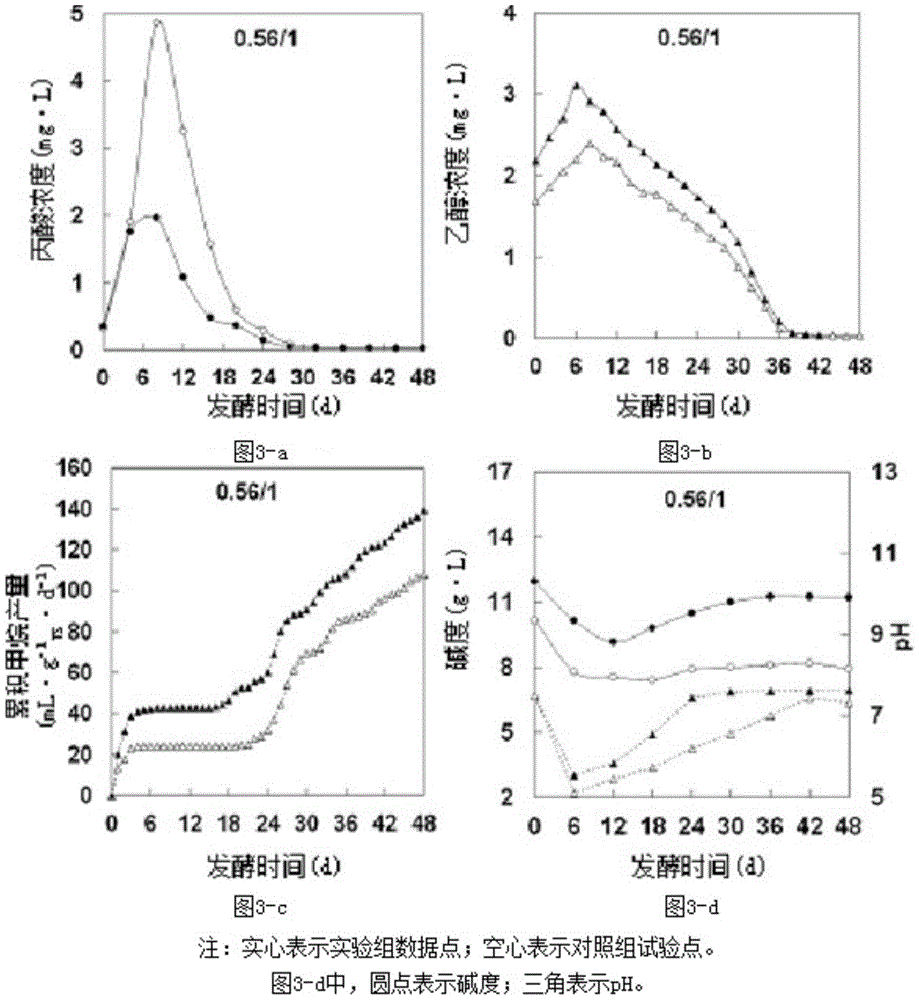
[0031] According to Example 1, after 72 hours of ethanol pre-fermentation of the food waste, the food waste and distiller's grains were evenly mixed at a mass ratio of 0.56:1 (calculated as VS), and the sludge was inoculated and fermented to produce biogas. The ratio (inoculation sludge: fermentation raw material (food waste + distiller's grains)) is 1:1 (in terms of VS, w / w). The result is as image 3 shown, from image 3 It can be seen from the figure that the difference between the experimental group and the control group through ethanol pre-fermentation is obvious by comparison. The concentration of propionic acid in the experimental group after ethanol pre-fermentation is 59% lower than that of the control group, and the ethanol concentration is 24% higher than that of the control group. %, alkalinity increased by 27%, pH increased by 9%, and methane production increased by 29%. The results well indicate that after ethanol pre-fermentation, the buffering capacity of the...
Embodiment 3
[0033] According to Example 1, the food waste was subjected to ethanol pre-fermentation for a period of 72 hours, and the food waste and distiller's grains were evenly mixed at a mass ratio of 0.21:1 (calculated as VS), and the sludge was inoculated and then fermented to produce biogas. The inoculation ratio (inoculation sludge: fermentation raw material (food waste + distiller's grains)) is 1:1 (calculated as VS). The result is as Figure 4 shown, from Figure 4 It can be seen that the concentration of propionic acid in the experimental group after ethanol pre-fermentation decreased by 30.0% compared with the control group, the concentration of ethanol increased by 25.3%, the alkalinity increased by 25.5%, the pH increased by 14.5%, and the methane production increased up 26.7%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com