Method for anaerobically producing biogas with jerusalem artichoke straw as raw material
A technology for producing biogas from Jerusalem artichoke straw, which is applied in the field of anaerobic biogas production and anaerobic biogas production using Jerusalem artichoke straw as raw material. Transformation and other issues to achieve efficient and stable biogas production, improve biogas production capacity, and effectively utilize waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
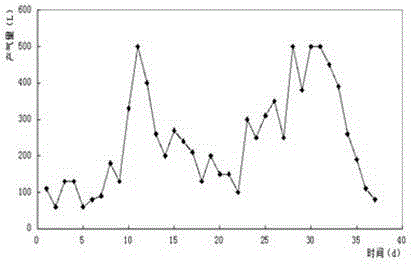
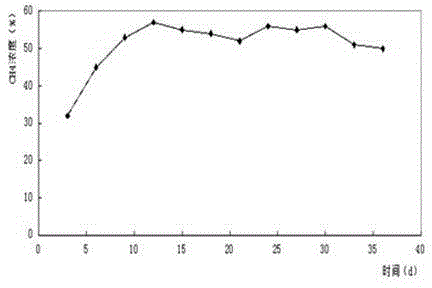
Embodiment 1
[0033] The TS% of the raw material Jerusalem artichoke straw was determined by the oxidative degradation method to be 90.33%, the ash content was 3.6%, the cellulose was 45.6%, the hemicellulose was 16.5%, and the lignin was 24.8%; The amount of decomposing bacteria is 0.2% of the solid-liquid weight, mix well, adjust the water content to 65%, and ferment at constant temperature for 48 hours. Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5%, Aspergillus niger 30%;
[0034] The TS% of fresh cow manure and sheep manure was determined to be 20.56%; take 386g of processed raw materials, add 193g of fresh cow manure and sheep manure and mix well;
[0035] Take the obtained mixture and put it into a 10L anaerobic fermentation device, add 650mL of TS%=10% anaerobic activated sludge, and use biogas slurry to make the volume to 6.5L;
[0036] Medium temperature anaerobic fermentation at 33°C, stirring twice a day, rotating speed 110rpm, 10min / time;
[0037] Anaerobic digestion is defined as the end of an...
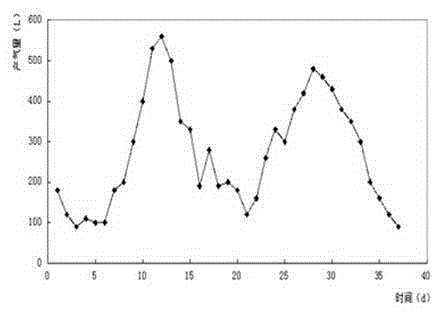
Embodiment 2
[0040] The TS% of the raw material Jerusalem artichoke straw was determined by the oxidative degradation method to be 92.33%, the ash content was 4.3%, the cellulose was 47.6%, the hemicellulose was 13.5%, and the lignin was 25.8%; The amount of decomposing bacteria is 0.3% of the solid-liquid weight, mix well, adjust the water content to 70%, and ferment at constant temperature for 60 hours. Yeast 15%, Aspergillus niger 25%;
[0041] Determination of fresh cow dung TS% is 22.61%; take 354g of raw material after treatment, add 212g of fresh cow dung and mix;
[0042] Take the obtained mixture and put it into a 10L anaerobic fermentation device, add 975mL of TS%=15% anaerobic activated sludge, and use biogas slurry to make the volume to 6.5L;
[0043] Anaerobic fermentation at medium temperature at 35°C, stirring 3 times a day, rotating speed 120rpm, 15min / time;
[0044] Anaerobic digestion is defined as the end of anaerobic digestion when the daily gas production is lower th...
Embodiment 3
[0046] The TS% of the raw material Jerusalem artichoke straw was determined by the oxidative degradation method to be 91.43%, the ash content was 2.97%, the cellulose was 45.36%, the hemicellulose was 12.5%, and the lignin was 24.8%; The amount of decomposing bacteria is 0.5% of solid-liquid weight, mix well, adjust the water content to 70%, and ferment at constant temperature for 72 hours. 5%, Saccharomyces cerevisiae 10%, Aspergillus niger 35%;
[0047] The TS% of fresh cow manure and pig manure was determined to be 25.61%; take 375g of processed raw materials, add 141g of fresh cow manure and pig manure and mix well;
[0048] Take the obtained mixture and put it into a 10L anaerobic fermentation device, add 833mL of TS%=12.5% anaerobic activated sludge, and use biogas slurry to make the volume to 6.8L;
[0049] Anaerobic fermentation at medium temperature at 35°C, stirring 4 times a day, rotating speed 130rpm, 15min / time;
[0050] Anaerobic digestion is defined as the e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com