Salt stress-induced specific promoter of plant leaf and application thereof
A technology of plant leaves and promoters, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve problems such as death, plant metabolic imbalance, hindering normal growth and development of plants, etc., achieve wide application value and improve salt tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
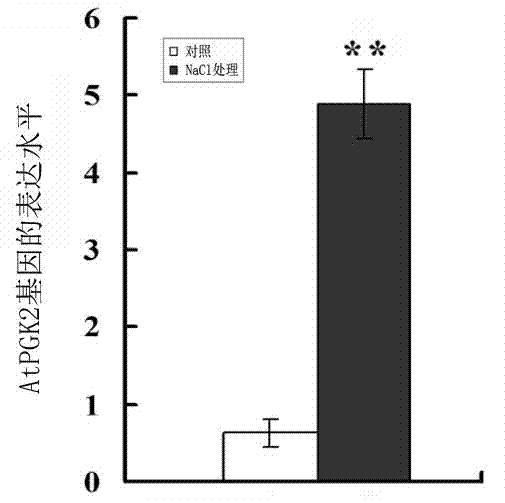
[0032] Example 1: Cloning of a leaf-specific promoter induced by salt stress in Arabidopsis
[0033] First, using Arabidopsis genomic DNA as a template, the 1444 bp salt stress-induced Arabidopsis leaf-specific promoter was amplified by PCR method, and the amplified product was recovered and TA cloned.
[0034] (1) PCR amplification of the target fragment:
[0035] ①According to known Arabidopsis AtPGK2 Design specific primers for the sequence of the gene promoter region, and introduce in the upstream primer Bam H I restriction site, introduced in the downstream primer Nco I restriction site:
[0036] Upstream primer: 5'-CGC GGATCC AATATCACACCACGGATTGGG-3'
[0037] Downstream primer: 5'-CATG CCATGG GTGAAGTCAACAGATAGTGA-3'
[0038] ② Extract Arabidopsis thaliana genomic DNA according to a conventional method, use the genomic DNA as a template, and use the above primers to perform PCR amplification to prepare the Arabidopsis leaf-specific promoter fragment ind...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: Using the pCAMBIA1301 vector (containing GUS reporter gene) to construct the "salt stress-induced plant leaf-specific promoter-GUS" fusion gene
[0058] (1) Extract vector pCAMBIA 1301 plasmid (purchased from CAMBIA Company) from Escherichia coli, use Bam H I / Nco Recover the large carrier fragment (which contains GUS reporter gene sequence).
[0059] (2) Extract the plasmid from the TA clone prepared in Example 1, and use Bam H I / Nco I double-enzyme digestion, and recovered (same as Example 1) plant leaf-specific promoter fragments induced by salt stress by agarose gel electrophoresis.
[0060] (3) Ligate the above two fragments under the catalysis of ligase overnight at 16°C to complete the construction of the "salt stress-induced plant leaf-specific promoter-GUS" fusion gene on the pCAMBIA 1301 vector.
[0061] Connection system:
[0062] Reagent Amount added (μl) Salt stress-induced plant leaf-specific promoter fragme...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3: Preparation of transgenic Arabidopsis plants
[0070] (1) Transform Arabidopsis thaliana with the "salt stress-induced plant leaf-specific promoter-GUS" fusion gene constructed in Example 2. The specific transformation method uses the Agrobacterium-mediated Floral dip method (Clough and Bent, 1998) , the obtained seeds were subjected to 50 mg l -1 For hygromycin resistance screening, normal growing plants were transferred to soil for culture.
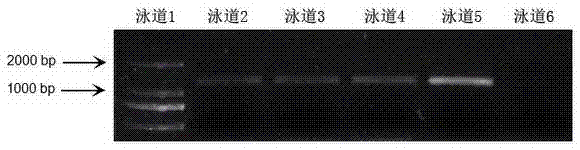
[0071] (2) PCR detection of transgenic plants: Cut the leaves of transgenic plants and wild-type plants respectively, refer to the method of "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide (Third Edition)" (Huang Peitang et al., 2002) to extract genomic DNA from leaves, and use the following primers for PCR Reaction, reaction system is as embodiment 1:
[0072] Upstream primer: 5'-CGCGGATCCAATATCACACCACGGATTGGG-3'
[0073] Downstream primer: 5'-TACAGTCTTGCGCGACATGCG-3'
[0074] The PCR products were subjected to agarose gel ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com