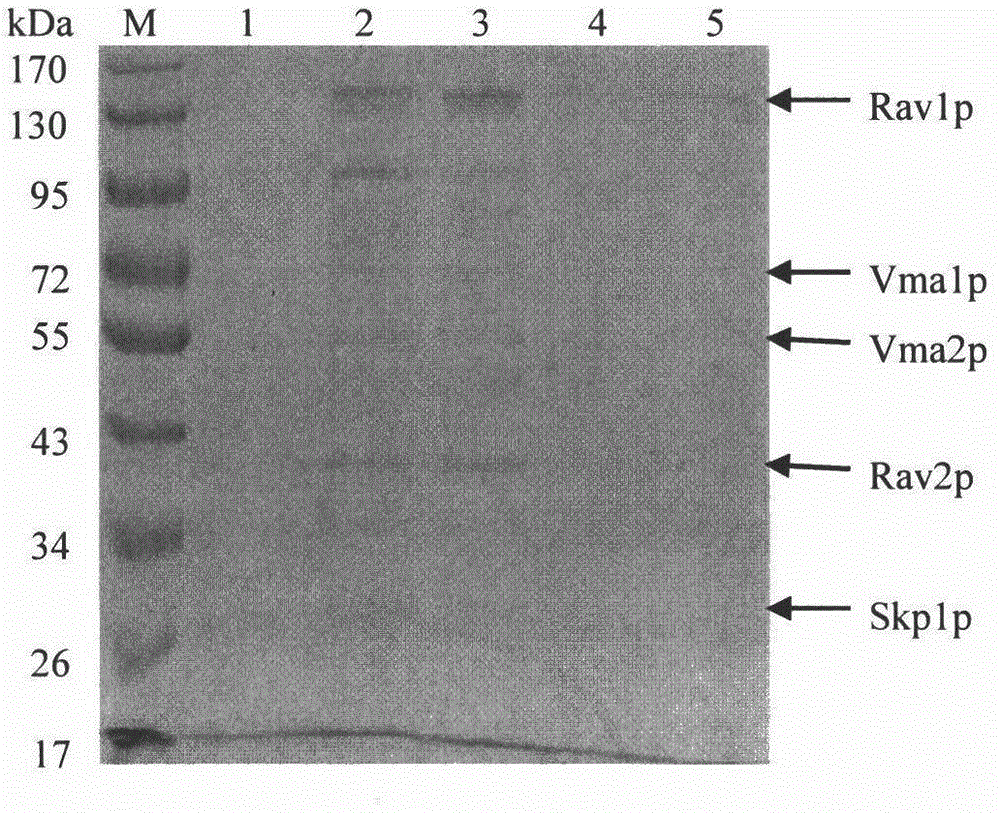
Method for separating RAVE compound from Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells by using FLAG label
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells and complexes, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient content, difficult to make substantial progress, difficult to purify RAVE, etc., to achieve concentration and purity. boosted effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] A method utilizing FLAG tags to separate RAVE complexes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4742rav2-FLAG cells, the steps are as follows:
[0033] A. Large-scale cultivation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant strain BY4742rav2-FLAG:
[0034] (1) Pick a single colony of Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4742rav2-FLAG from the YPD plate containing antibiotics (200 μg / ml G418), inoculate in 8 bottles of Erlenmeyer flasks each containing 200ml of seed medium, and culture at 30°C and 200rpm To mid-logarithmic phase (OD≈1);
[0035] (2) Transfer 8 bottles of seed culture solution to 8 bottles of Erlenmeyer flasks each equipped with ILYPD medium, and cultivate overnight at 30°C and 200 rpm until the middle of the stationary phase (OD ≈ 3.5);
[0036] B. Collect and disrupt cells:
[0037] (1) Collect the cells by centrifugation at 8000xg for 5 minutes at room temperature, resuspend the cells in sterile water at 25°C, and place at room temperature for 5 minutes;
[0038] (2) Cent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com