Drug carrier capable of realizing drug delivery specifically targeting tumor and application thereof
A tumor-targeting and drug-based technology, which is applied in the interdisciplinary fields of bionics, nanotechnology, immunology and biomedicine, can solve the problems of limiting the use of chemotherapy drugs, lack of targeting, side effects, etc., and achieves good application prospects and huge The effect of social and economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
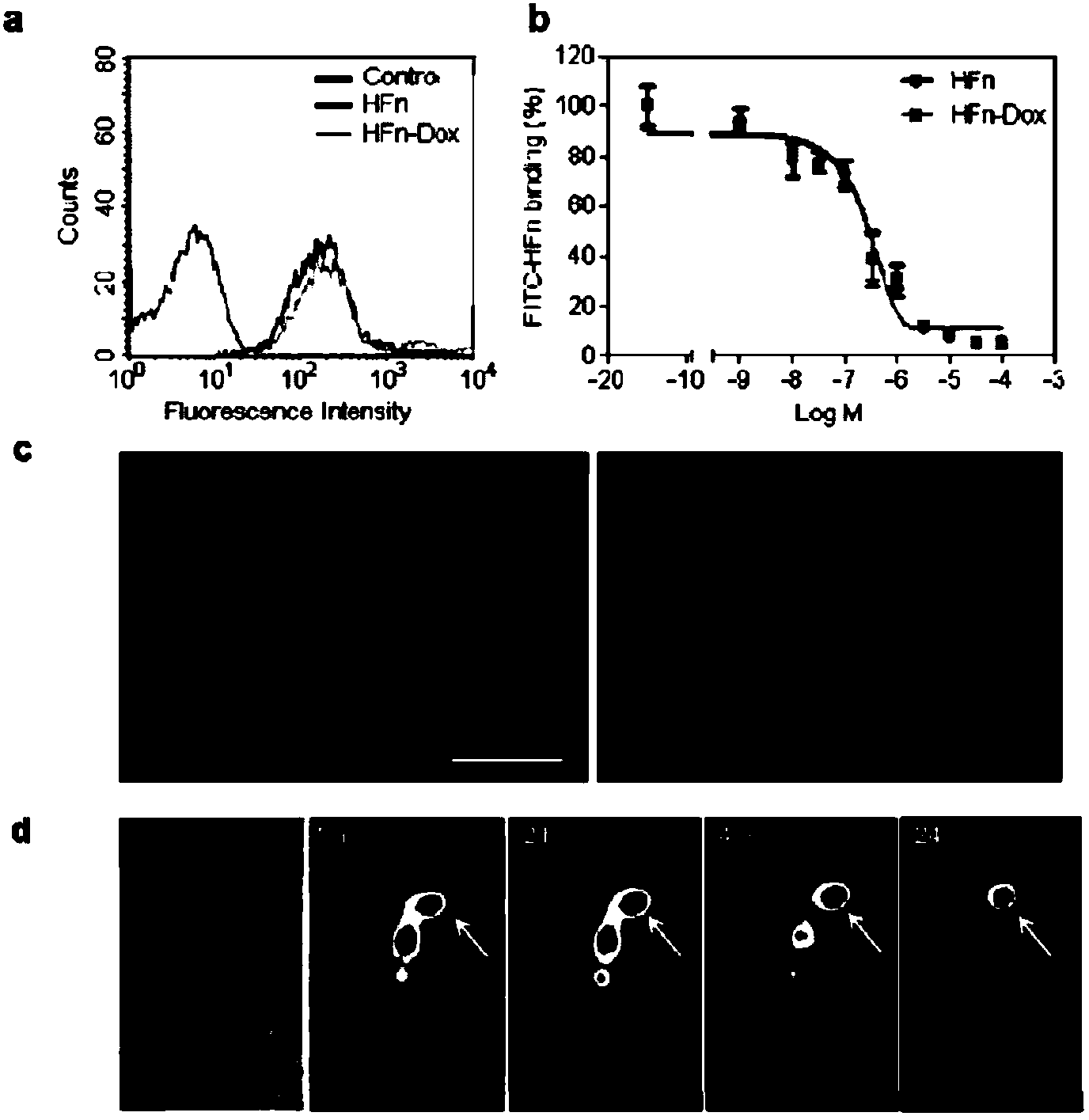
[0040] Example 1. Preparation and characterization of tumor-targeted nano-drug carrier HFn-Dox
specific Embodiment
[0041] As a drug carrier, the first thing to solve is the problem of drug loading. As mentioned above, the currently commonly used method is to load drugs into protein cavities by depolymerization-polymerization of protein shells under pH control. In fact, because of the stability of H-ferritin, it will depolymerize only under the condition of pH=2. Treating the ferritin protein shell under such strong acidic conditions will cause the ferritin subunits to fail to completely reassemble into the original protein shell when the pH value returns to neutral conditions, but will cause some "gap" ( Kim, M. et al., Biomacromolecules, 2011). This will cause the ferritin nanoparticles to be unstable after the drug is loaded, and the drug-encapsulation yield will decrease. Moreover, the incompleteness of the protein shell will affect its targeting to tumors. Another method of loading drugs into ferritin is to use metal ions as drug additives. After chemotherapy drugs are combined with...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2. Research on in vitro release and stability of drug-loaded nano drug carrier HFn-Dox
[0047] (1) In order to study the stability of the targeted drug carrier HFn-Dox loaded with drugs, we put HFn-Dox nanoparticles (500 μmol / L, 500 μL in Dox amount) into the dialysis tube D-tube (MWCO 6-8kDa, Novagen), and then placed in normal saline or normal mouse serum for incubation at 37°C. Samples were taken at incubation times of 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, 36, 48, and 60 hours, and the amount of doxorubicin was determined by HPLC. The results of the assay are expressed in percent dissociation. Drug retention percentage = 100% - dissociation percentage.
[0048] The result is as figure 2 As shown in a, the results of the stability test show that the HFn-Dox drug carrier system is very stable in mouse serum at 37°C. Less than 10% dissociated after 60 hours. This indicated that HFn-Dox could stably exist in mouse serum after administration to mice through tail vein.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com