Power conversion device
A technology of power conversion devices and inverters, which is applied to output power conversion devices, electrical components, and conversion of AC power input to DC power output, etc., which can solve problems such as difficulty in securing the installation site and rising cost of test equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Below, refer to Figure 1 to Figure 3 , the power conversion device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described.
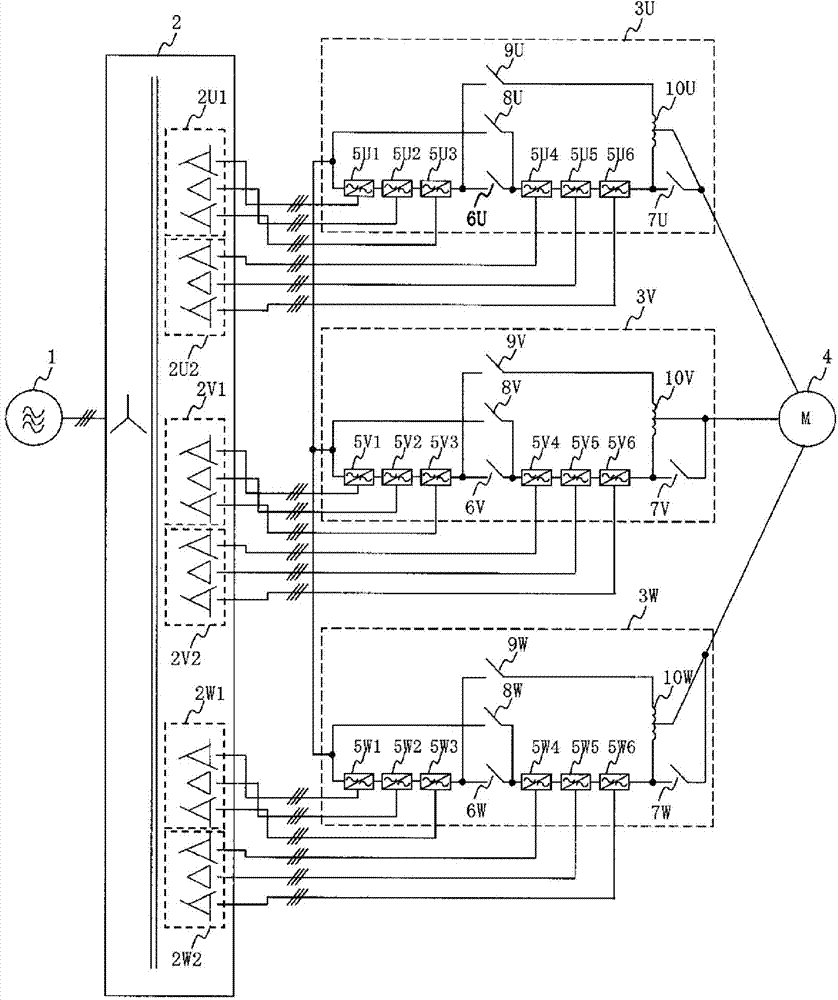
[0025] figure 1 It is a circuit configuration diagram of the power conversion device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. A high-voltage three-phase AC voltage is supplied from the AC power source 1 to the input transformer 2 . The input transformer 2 has secondary winding groups 2U1, 2U2, 2V1, 2V2, 2W1, and 2W2 each having a plurality of insulated secondary windings, and supplies AC power from the secondary winding groups 2U1, 2U2 to the U-phase power converter 3U. Primary winding groups 2V1 and 2V2 supply AC power to V-phase power converter 3V, and secondary winding groups 2W1 and 2W2 supply AC power to W-phase power converter 3W. The U-phase power converter 3U, the V-phase power converter 3V, and the W-phase power converter 3W respectively output single-phase AC voltages with a phase difference of 120° from each...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Figure 5 It is a circuit configuration diagram of a power conversion device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. For each part of this embodiment 2, will be with figure 1 The same parts of the power conversion device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention are denoted by the same symbols, and description thereof will be omitted. The difference between Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 1 is that the number of secondary windings belonging to each secondary winding group of the input transformer 2A is changed from 3 to 2, and the unit inverters of each phase are accordingly The number of units has been changed from 6 to 4.
[0035] The operations of the second embodiment are all the same as those of the first embodiment. In Example 1, the phase voltage obtained by adding six unit inverters 6 is output in the series connection mode, and the output voltage becomes half of the output voltage in the parallel connection mode, but in this Example 2, the ser...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Figure 6 It is a circuit configuration diagram of main parts of a power conversion device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. The main part described here is the U-phase power conversion unit, and illustration of other parts is omitted. For each part of this embodiment 3, with figure 1 In the U-phase power conversion unit of the power conversion device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, the same parts are denoted by the same symbols, and description thereof will be omitted. The difference between the present embodiment 3 and the embodiment 1 is that the unit inverters 5U7, 5U8 and 5U9 are added to the U-phase power converter part 3UB, and the structure of the unit inverters is changed from 6 units to 9 units; Add switches 11U, 12U, and 13U so that three sets of unit inverters can be connected in parallel; and accordingly, the balance reactor 10U is changed to three balance reactors 10UA, 10UB, and 10UC.
[0039] In Example 3, for the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com