Method for preparing high-protein forage by utilizing waste cassava vinasse
A technology for high-protein feed and cassava distiller's grains, which is applied in the field of using waste cassava distiller's grains to prepare high-protein feed, can solve the problems of high secondary processing cost, low product nutritional value, high energy consumption, etc., and achieves prevention of secondary pollution and beneficial effects. The effect of rich bacterial content and reducing environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The probiotics used in this example include Saccharomyces cerevisiae, lactic acid bacteria, Bacillus subtilis, acetic acid bacteria, bifidobacteria, and actinomycetes; the probiotic seed liquid is obtained after the probiotics are fermented in the basal medium for 20 hours fermentation broth. Basal medium components include 0.5% peptone, 0.5% sodium chloride, and 1% sodium phosphate. Invertases include glucoamylase, cellulase, mesophilic amylase, acid protease, and β-glucanase.
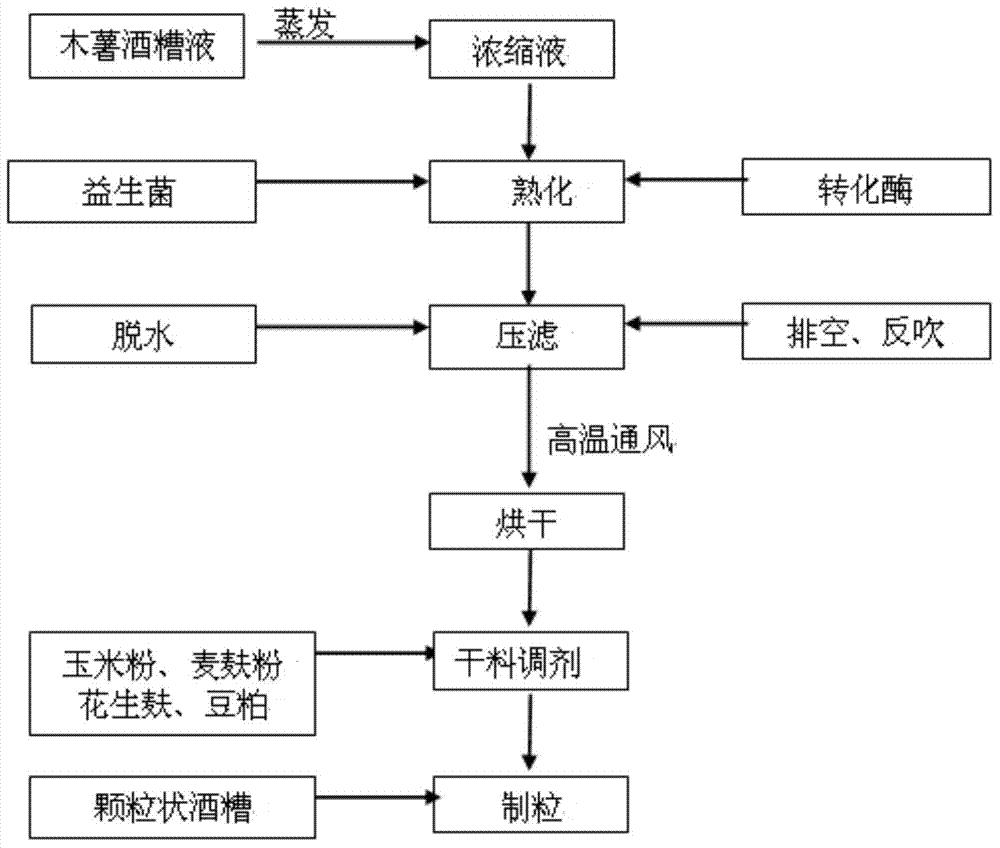
[0028] Step 1) Concentration: use rotary heating and evaporation to concentrate the cassava distiller's grains to a Baume degree of 40°Bé to obtain cassava distiller's grains concentrate.
[0029] Step 2) Ripening: Take 80 parts of the cassava distiller's grain concentrate obtained in step 1) according to the parts by weight, add 20 parts of probiotic seed liquid and 5 parts of invertase, stir evenly, and ferment under anaerobic conditions at 37°C for 25 hours to obtain mature cassava Distill...
Embodiment 2
[0035] The probiotics used in this example include Saccharomyces cerevisiae, lactic acid bacteria, Bacillus subtilis, and bifidobacteria; the probiotic seed liquid is the fermentation liquid obtained after the probiotics were fermented in the basal medium for 24 hours. Basal medium components include 1% peptone, 1% sodium chloride, and 0.5% sodium phosphate. Invertases are glucoamylase, cellulase, acid protease, β-glucanase.
[0036]Step 1) Concentration: use rotary heating and evaporation to concentrate the cassava distiller's grains to a Baume degree of 30°Bé to obtain a cassava distiller's grains concentrate.
[0037] Step 2) Ripening: Take 90 parts of cassava distiller's grain concentrate obtained in step 1) in parts by weight, add 15 parts of probiotic seed liquid and 2 parts of invertase, stir evenly, and ferment under anaerobic conditions at 30°C for 15 hours to obtain mature cassava Distiller's grains. The content of beneficial bacteria in the aged distiller's grains...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The probiotics used in this example include Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Bifidobacterium; the probiotic seed liquid is the fermentation liquid obtained after the probiotics were fermented in the basal medium for 16 hours. Basal medium components include 0.8% peptone, 0.5% sodium chloride, and 1.5% sodium phosphate. Invertases are glucoamylase, acid protease, and β-glucanase.
[0044] Step 1) Concentration: use rotary heating and evaporation to concentrate the cassava distiller's grains to a Baume degree of 40°Bé to obtain cassava distiller's grains concentrate.
[0045] Step 2) Ripening: Take 85 parts of the cassava distiller's grain concentrate obtained in step 1) according to the parts by weight, add 15 parts of probiotic seed liquid and 5 parts of invertase, stir evenly, and ferment under anaerobic conditions at 40°C for 10 hours to obtain mature cassava Distiller's grains. The content of beneficial bacteria in the aged distiller's grains can reach 2-5g / Kg.
[004...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com