Phase change memory unit and method for manufacturing phase change memory unit
A phase change memory and phase change technology, applied in electrical components and other directions, can solve the problems of high operating power consumption, poor thermal stability, slow phase change speed, etc., to achieve the effects of ensuring reliability, prolonging life, and low power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
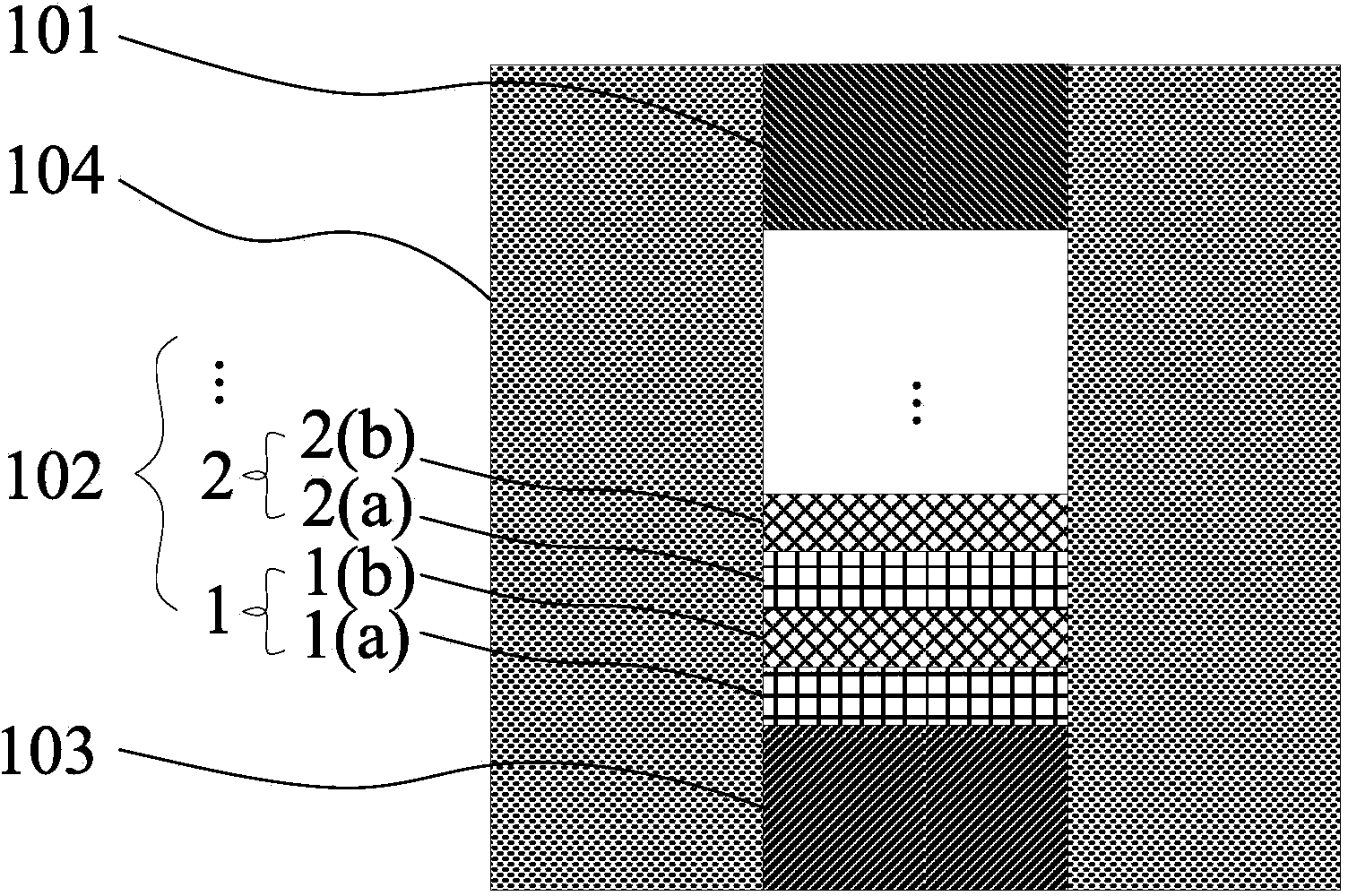
[0039] The present invention provides a phase change memory cell, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a growth substrate, a lower electrode 103 , a dielectric cladding layer 104 , a phase change material layer (that is, a phase change superlattice film structure 102 ), and an upper electrode 101 .
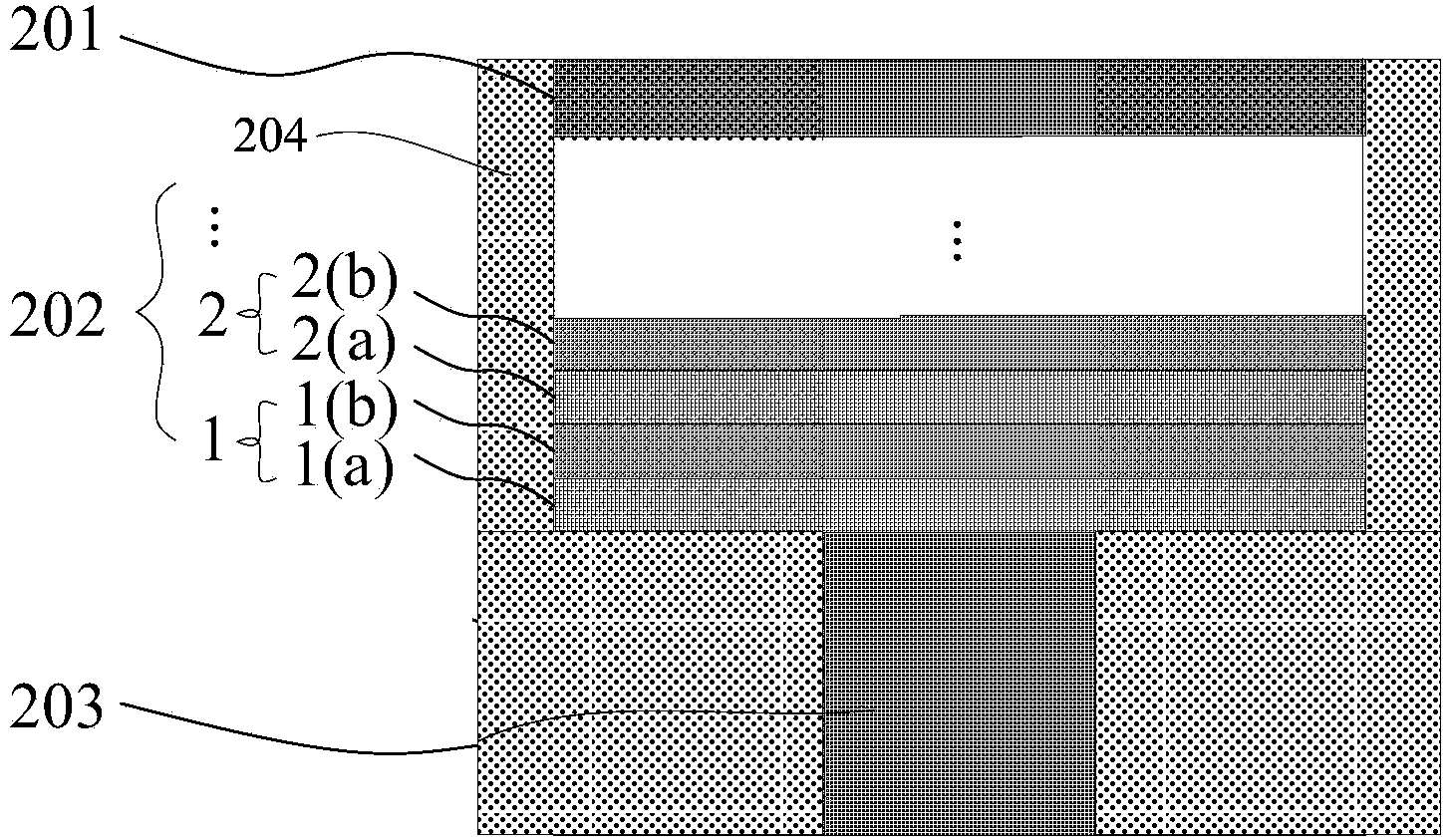
[0040]As an example, the phase-change memory cell may be a restricted structure or a T-shaped structure, such as figure 1 The structure of the restricted phase-change memory cell provided for the present invention; as figure 2 The structure of the T-type phase-change memory unit provided by the present invention.
[0041] The growth substrate can be a glass sheet or a silicon oxide substrate. In this embodiment, the growth substrate is a silicon oxide substrate.
[0042] The lower electrode 103 is fabricated in the growth substrate. The material of the lower electrode 103 can be Al, W, TiN or other conductive materials, and the thickness is in the range of 50-200 nm. In a sp...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The preparation method of the phase-change memory unit of the above-mentioned restricted structure comprises the following steps:
[0047] First, a growth substrate on which the lower electrode 103 is fabricated is provided.
[0048] Before performing subsequent processes, the growth substrate is cleaned to remove impurities such as organic matter, metal ions, and oxides on the surface of the growth substrate, which is beneficial to improving the stability of the device. The lower electrode 103 is a tungsten electrode with a thickness of 50-200 nm, and in a specific implementation process, it is 100 nm.
[0049] Then, a dielectric cladding layer 104 is deposited on the surface of the growth substrate.
[0050] The deposited dielectric cladding layer 104 may be SiO 2 or Si 3 N 4 . In this embodiment, the dielectric cladding layer is preferably Si 3 N 4 .
[0051] Next, the dielectric cladding layer 104 is etched by an exposure-etching process until a deposition h...
Embodiment 3
[0065] figure 2 The preparation method of the phase-change memory unit of T-type structure comprises the following steps:
[0066] Firstly, a growth substrate on which the lower electrode 203 is fabricated is provided.
[0067] Before performing subsequent processes, the growth substrate is cleaned to remove impurities such as organic matter, metal ions, and oxides on the surface of the growth substrate, which is beneficial to improving the stability of the device. The lower electrode 203 is a tungsten electrode with a thickness of 50-200 nm, and in a specific implementation process, it is 100 nm.
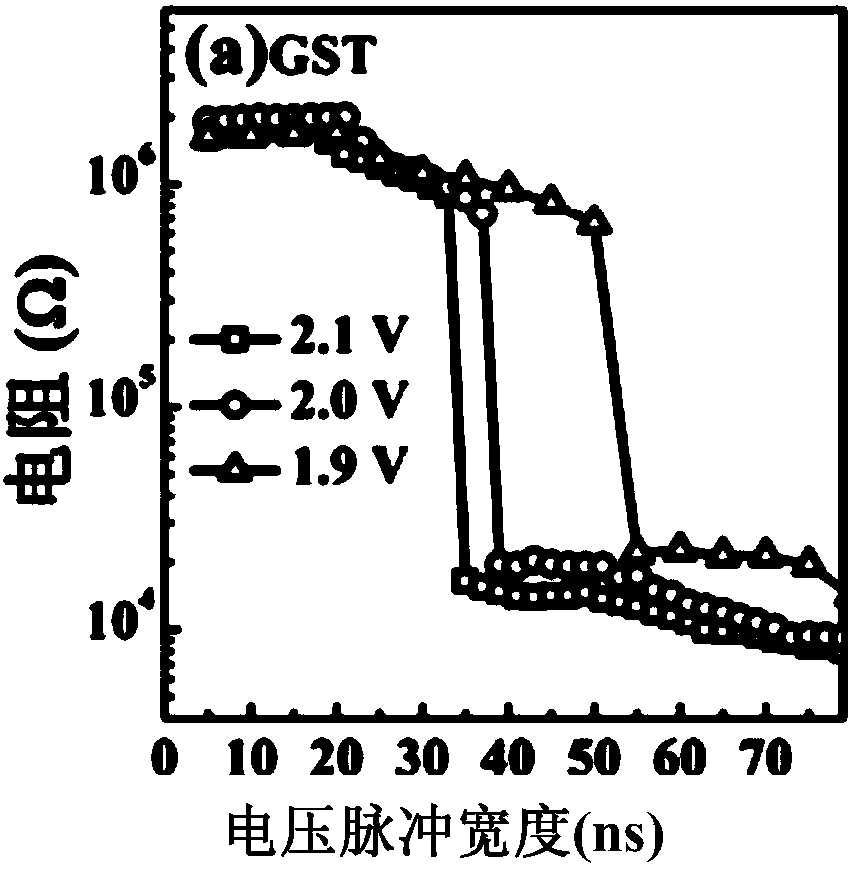
[0068] A phase-change material layer (phase-change superlattice film structure 202) and an upper electrode 201 are sequentially deposited in the deposition hole, and the phase-change material layer is composed of a single-layer phase-change material Sb x Te 1-x layer and monolayer compound Tiy Te 1-y A phase-change superlattice film structure formed by alternately vertically s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com