Semiconductor device
A semiconductor and device technology, applied in the field of semiconductor devices including processors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
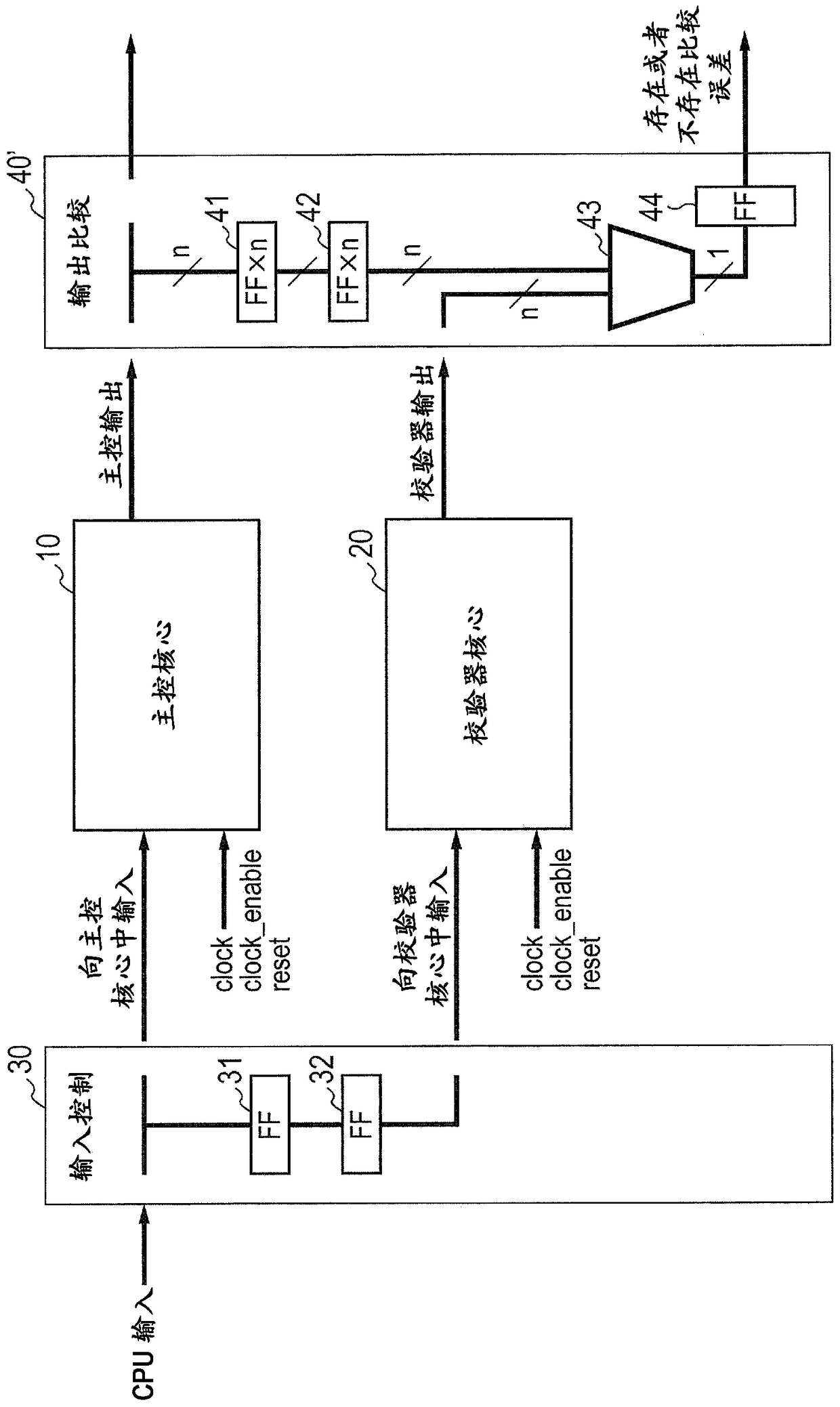
[0046] figure 2 is a diagram showing the configuration of the first embodiment of the present invention. Here, respectively to figure 2 in and figure 1 The units in the same or equivalent units are given to the figure 1 Units in are given the same reference numbers. The following will omit accordingly if necessary figure 2 The difference between figure 1 The description of the section that is repeated in the section. refer to figure 2 , this semiconductor device includes a first processor 10 and a second processor 20, an input control circuit 30 and an output comparison circuit 40 working respectively as a master control core and a checker core of a dual-core lockstep scheme. The input control circuit 30 uses two-stage flip-flops (31, 32) to delay the signal (CPU input) input to the first processor 10 by a predefined clock cycle (for example, two clock cycles) and input it to the second processor 20. delayed signal.
[0047] In the output comparison circuit 40,...
no. 2 example
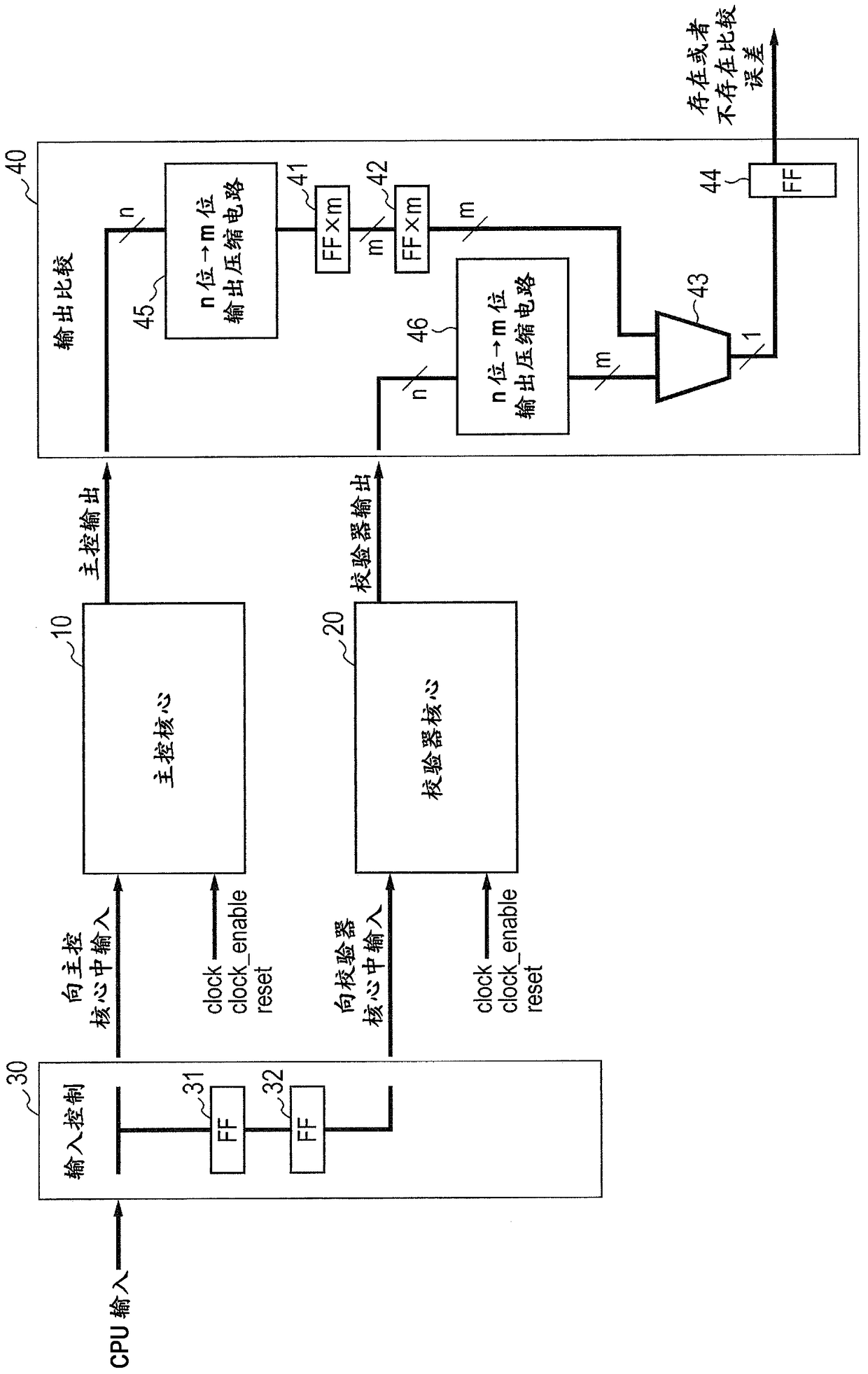
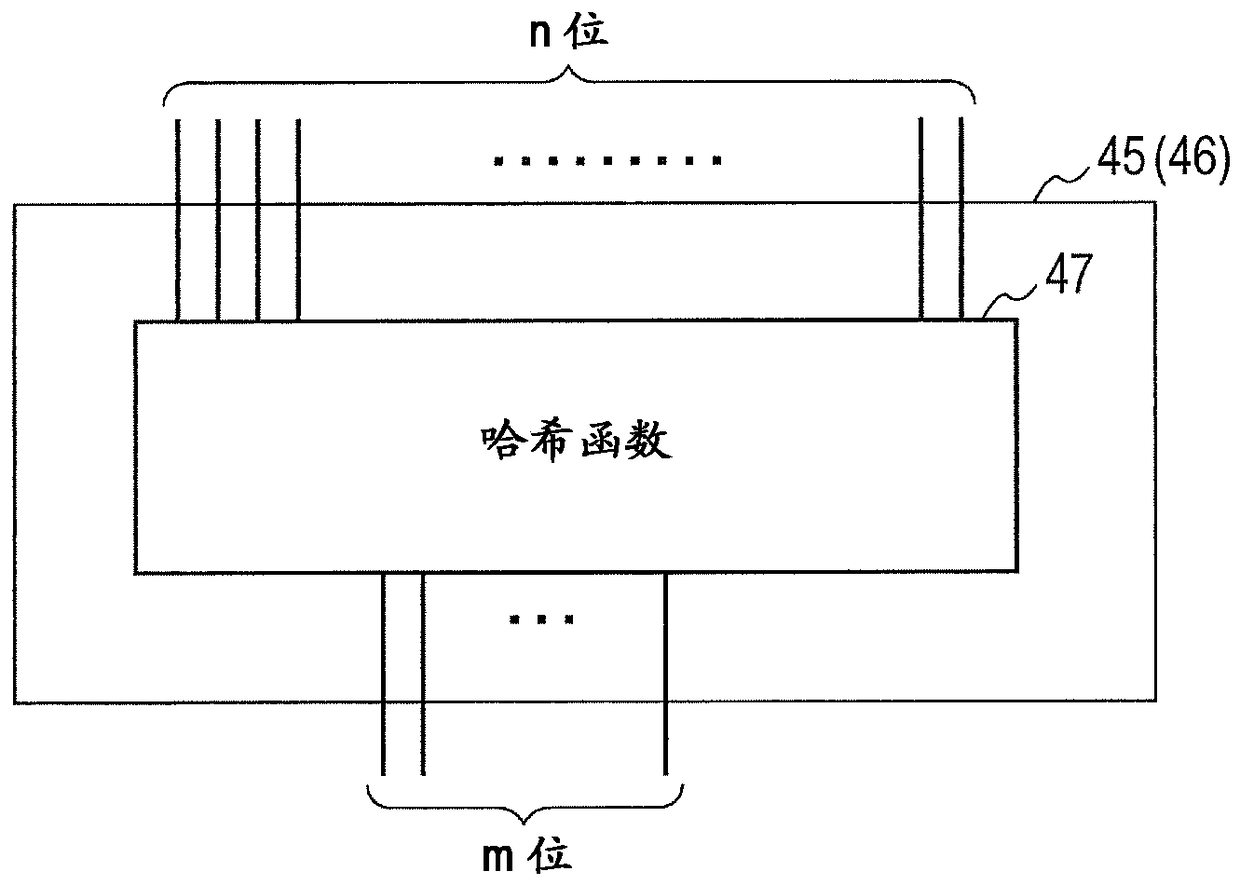
[0054] Figure 4 is a diagram showing an example of the configuration of the n-bit to m-bit output compression circuit 45 (or 46 ) according to the second embodiment. In the second embodiment, the n-bit to m-bit output compression circuit 45 (or 46 ) is configured in such a manner that a signal of n bits is decomposed into groups and the compression level of each group is set variable. In other words, a signal of n-bit width is decomposed into m groups (first group of p1-bit width, second group of p2-bit width to m-th group of pm-bit width). exist Figure 4 The relationship between p1, p2 to pm, m and n in is given by equation (1).
[0055]
[0056] p1 input XOR (exclusive OR) gate 47 1 to pm input XOR gate 47 m is a hash function that maps a p1-bit-wide signal to a pm-bit-wide signal to a 1-bit-wide hash value (1 or 0), respectively. For example input XOR gate 47 to p1 1 Enter the first set of p1 bit widths in . p1 input XOR gate 47 1 Outputs the XOR logical sum (1...
no. 3 example
[0064] Figure 5 is a diagram showing an example of the configuration of the n-bit to m-bit output compression circuit 45 (or 46 ) according to the third embodiment. It will be assumed here that the figure 2 The entire configuration of the semiconductor device according to the third embodiment is shown in . The n-bit to m-bit output compression circuit 45 (or 46) will be described below.
[0065] refer to Figure 5 , in the n-bit to m-bit output compression circuit 45 (or 46) according to the third embodiment, an n-bit-wide signal is decomposed into some signal groups, and the compression level for the groups is set to be variable. However, important signals (of d-bit width) such as address signals, data signals or control signals (for example bus requests or bus responses) are not compressed, for example. Decompose other signals into s groups (where s is the number of groups), that is, p1-bit-wide groups, p2-bit-wide groups to ps-bit-wide groups (group 1 to group s), and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com