Anatase type TiO2 nano particle based pH sensor and pH value detection method
A nanoparticle and anatase-type technology, which is applied in the field of pH sensors and pH value detection based on anatase-type TiO2 nanoparticles, can solve the problems of complex detection operations and achieve high detection accuracy, good reproducibility, The effect of signal stabilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] The present invention only uses ITO conductive glass as the embodiment of the conductive carrier, and uses the urease catalyzed reaction system as the embodiment of biosensing, but is not limited to the specific content of the embodiment.
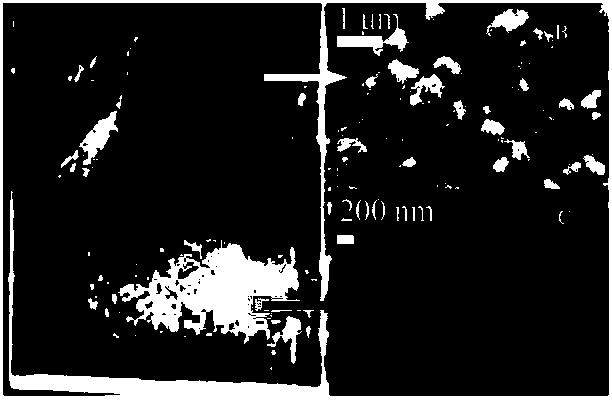
[0042] The first step: commercial anatase TiO 2 The nanoparticles were uniformly dispersed in the water phase by ultrasonication for 30 minutes.
[0043] Step 2: Cut the commercialized ITO conductive glass into appropriate sizes, soak in acetone and ethanol for 2 hours each, rinse thoroughly with double-distilled water, and soak in double-distilled water for later use.
[0044] The third step: ultrasonically dispersed anatase TiO 2 The nanoparticles are drip-coated on the bottom of the ITO glass to form a 0.5cm×1cm film, which is dried at room temperature to form a flat and uniform film, which is constructed as a sensitive element of the pH sensor and stored at room temperature in the dark.
[0045] The fourth step: the constructed...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Following the experimental steps of Example 1, continue to build a biosensor capable of measuring both the pH value and the concentration of the active substance urea in the biological system.
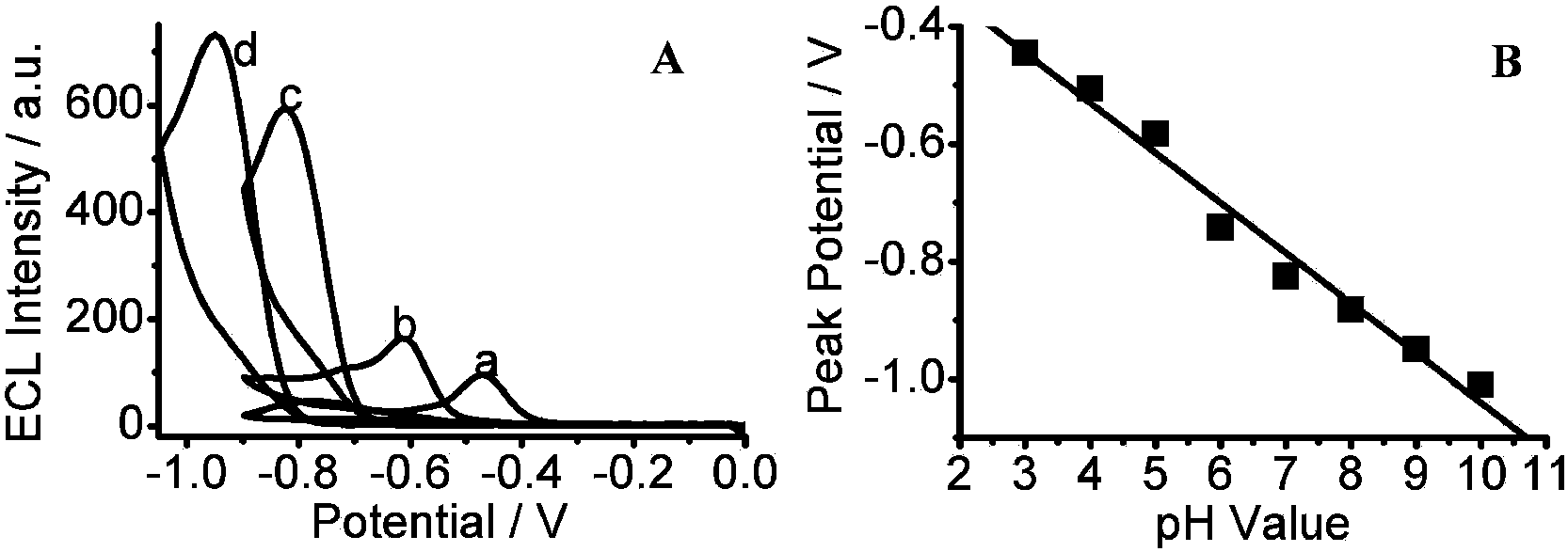
[0049] Step 6: Modify the 0.1%wt chitosan aqueous solution on the pH sensor TiO 2 Above the nanoparticle modification area, form a 0.5cm×1cm film, dry it in a refrigerator at 4°C to form a uniform film; spread 0.1M pH7.4 phosphate buffer solution with urease and 2%wt glutaraldehyde on On the chitosan film, urease was further modified on the ITO conductive glass by amino-amino cross-linking reaction. Apply the three-electrode system mentioned in the third step to obtain a pH biosensor ( figure 2 ).
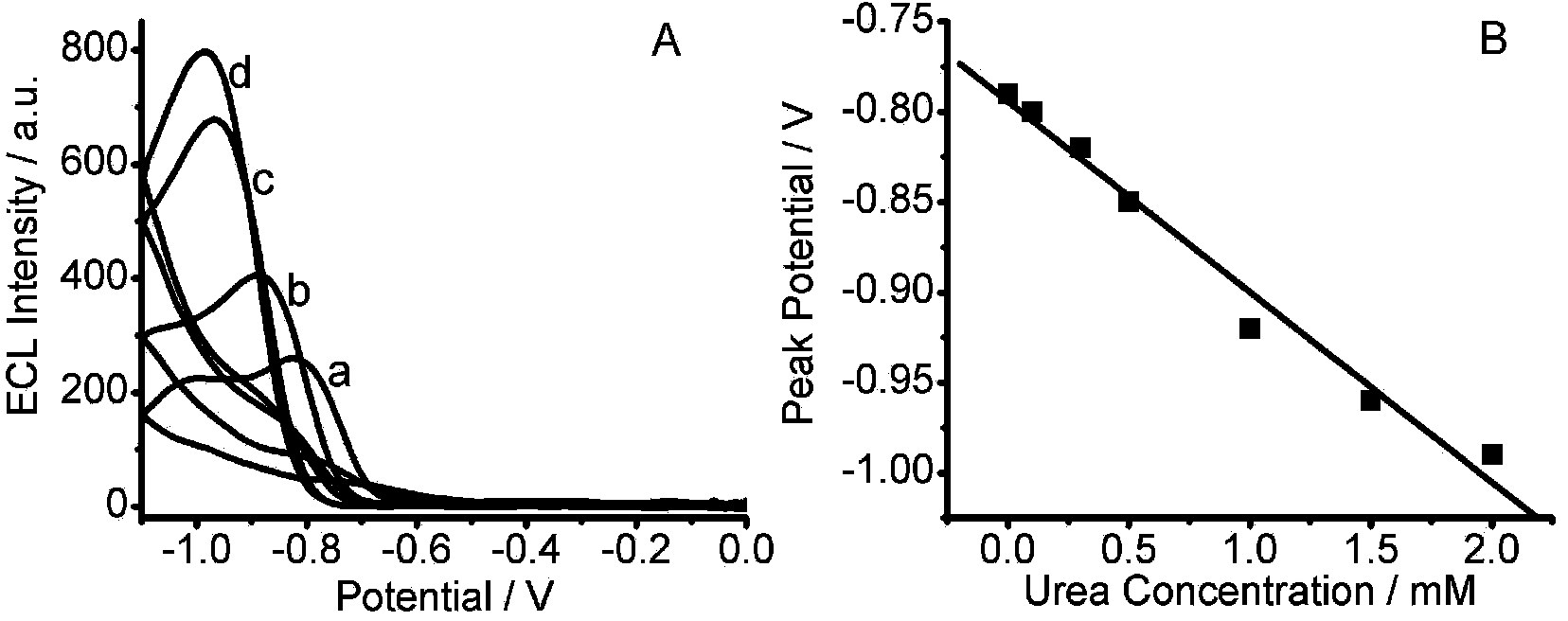
[0050] Step 7: Select a suitable supporting electrolyte. When different concentrations of substrate urea are added to the solution, the enzyme-catalyzed reaction can cause changes in the pH value of the detection environment, and the electrochemiluminescence peak potential of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The present invention only uses ITO conductive glass as the embodiment of the conductive carrier, and uses the acetylcholinesterase catalytic reaction system as the embodiment of biosensing, but is not limited to the specific content of the embodiment. Following the experimental steps of Example 1, continue to construct a biosensor capable of measuring both the pH value and the concentration of the active substance acetylcholine in the biological system.
[0053] Step 6: Modify the 0.1%wt chitosan aqueous solution on the pH sensor TiO 2 Form a 0.5cm×1cm film on the surface of the nanoparticle modification area, and dry it in a refrigerator at 4°C to form a uniform film; put 0.1M pH7.4 phosphate buffer dissolved in acetylcholinesterase and 2%wt glutaraldehyde Spread on the chitosan film, and further modify the urease on the ITO conductive glass through amino-amino cross-linking reaction. Apply the three-electrode system mentioned in the third step to obtain a pH biosens...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com