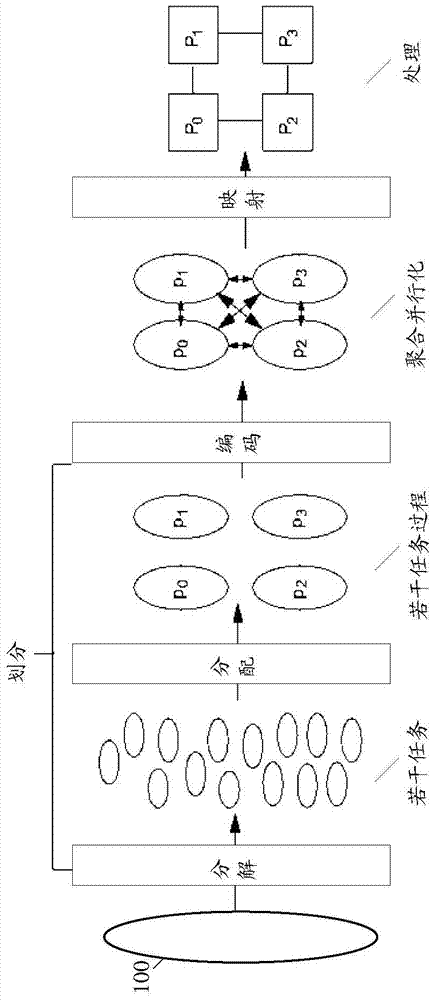
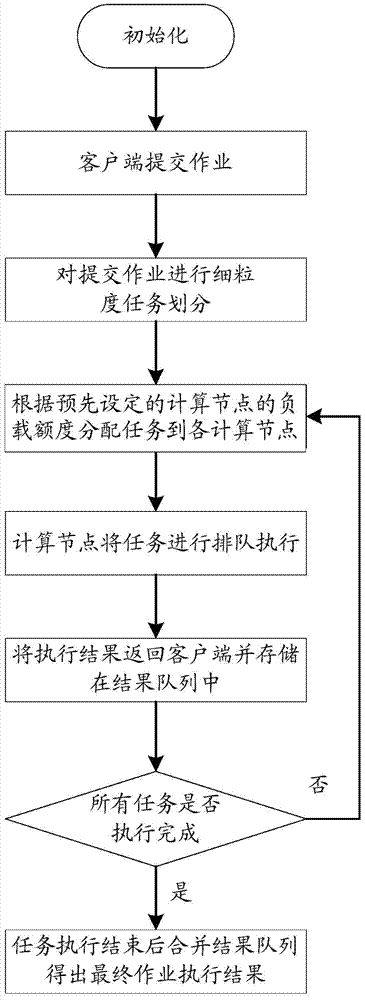
Parallel computation method and system
A parallel computing and computing node technology, applied in the computer field, can solve problems affecting the execution efficiency of parallel computing, average task execution time and task throughput, and unreasonable task allocation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
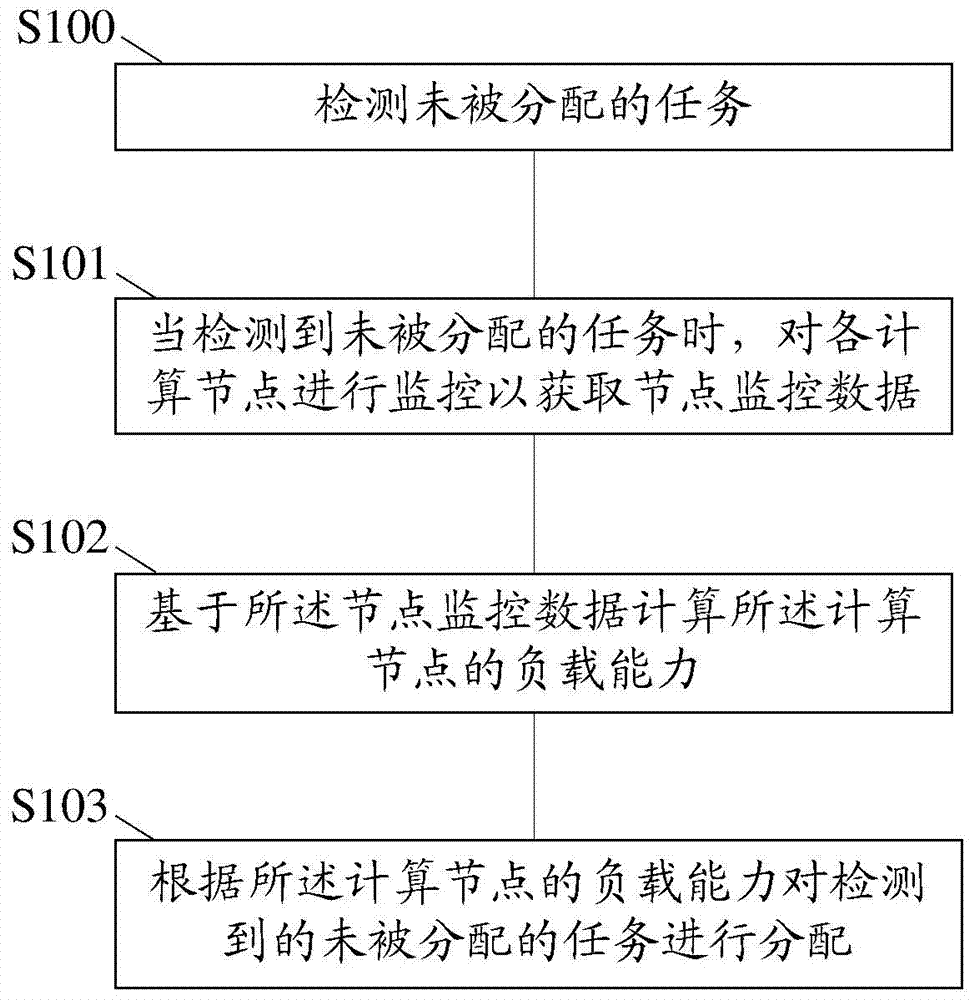
[0084] This embodiment provides a image 3 Parallel computing methods shown, including:
[0085] Step S100, detecting unassigned tasks.
[0086] The unassigned tasks may be generated based on the following process:
[0087] Initialize the system or run the system;
[0088] Submit jobs on the system or system client;
[0089] The submitted job is divided to form tasks.
[0090] The tasks formed in the above process are newly generated tasks by the system and have not been assigned. In this embodiment, the newly generated tasks by the system are referred to as the unassigned tasks.
[0091] Step S101 , when an unassigned task is detected, monitor each computing node to obtain node monitoring data.
[0092] The computing nodes in this step can exist in the virtual environment of the virtual machine. When it is necessary to monitor each computing node to obtain node monitoring data, it can first connect to the virtualization environment through a virtualization connector, and...
Embodiment 2
[0115] This embodiment provides a Figure 5 Parallel computing methods shown, including:
[0116] Step S300, detecting tasks that have been allocated but not processed.
[0117] The tasks that have been assigned but not processed are based on the unassigned tasks described in Embodiment 1, and may be generated by the following process:
[0118] According to the parallel computing method as described in Embodiment 1, the unassigned tasks are assigned to computing nodes;
[0119] The unallocated tasks are left unprocessed for a long time to form the allocated but unprocessed tasks.
[0120] The task formed in the above process is not a new task generated by the system, but has been assigned to the computing node, but because the computing node has not processed the task, the task has been waiting for a long time, and the task has not been processed for a long time. It means that the task has been assigned to the computing node and has not been processed for more than 5 minute...
Embodiment 3
[0128] This embodiment provides a Image 6 The parallel computing method shown is based on Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2. The method includes the process of allocating unallocated node tasks and reassigning allocated but unprocessed node tasks, including:
[0129] Step S400, initialize the system.
[0130] Step S401, detecting whether there is a new task assignment.
[0131] When there is a new task to be assigned, perform steps S402 to S405:
[0132] Step S402, an updating step.
[0133] The updating step is: updating the comprehensive load queue of computing nodes in real time.
[0134] Step S403, check the steps.
[0135] The viewing step is: viewing the node task comprehensive load queue.
[0136] Step S404, the allocation step.
[0137] The respective steps are: selecting the node with the smallest load in the integrated load queue of node tasks, and assigning the new task to the node with the smallest load.
[0138] Step S405, execute the step.
[0139] The execu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com