Method for lowering COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) of oil refining wastewater by using dibutyl phthalate degrading strain
A technology of dibutyl phthalate and oil refining wastewater is applied in the field of environmental pollution and bio-enhancement, and can solve the problem of high COD in biochemical effluent
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
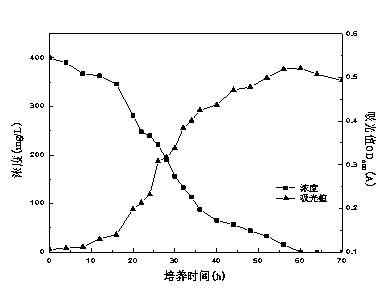
[0020] Isolation and Purification of Strain D8 and Its Degradation of Dibutyl Phthalate
[0021] The bacteria source was collected from the activated sludge of the sewage treatment system of Wuhan Branch of China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation. Take 2 ml of activated sludge and inoculate it into 100 mL of sterilized LB medium, activate and cultivate overnight at 30 °C and 150 r / min. Then take 2mL of the culture solution and transfer it to the inorganic salt medium containing 200 mg / L dibutyl phthalate, cultivate for 1 day under the same conditions, and gradually increase the concentration of dibutyl phthalate (according to 200mg / L L gradient increases). After the acclimatization is completed, the bacterial liquids are serially diluted, respectively spread on inorganic salt solid plates containing dibutyl phthalate, and cultured at 30° C. for 7 days. Pick a single colony and repeat the streaking 3-4 times. Pick out the strains with better degradation ability and store them...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Degradation of Dibutyl Phthalate in Oil Refinery Wastewater by Strain D8
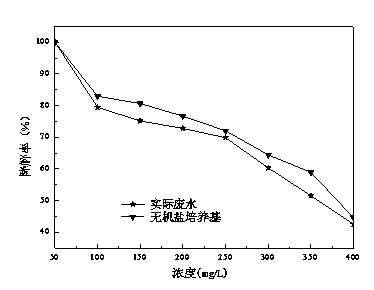
[0027] Two sets of experiments were designed to investigate the removal effect of strain D8 on dibutyl phthalate in oil refinery wastewater: (1) oil refinery wastewater + a certain concentration of dibutyl phthalate; (2) inorganic salt medium + a certain concentration of dibutyl phthalate; concentration of dibutyl phthalate. Inoculate strain D8 into sterilized oil refinery wastewater and inorganic salt medium with an inoculum volume of 2 vol%, and add dibutyl phthalate with a concentration of 50-400 mg / L to two sets of Erlenmeyer flasks respectively, at 30°C And 150r / min shaker culture, after 30h, take a sample and detect the content of dibutyl phthalate, the result is as follows figure 2 shown. Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that the removal effect of strain D8 on dibutyl phthalate in oil refinery wastewater is consistent with the removal effect of dibutyl phthalate in inorganic salt med...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Removal of COD in wastewater after air flotation in refinery biochemical station by strain D8
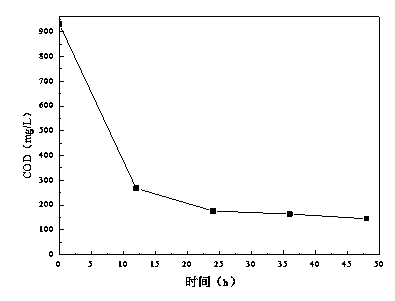
[0030] The strain D8 was inoculated into the sterilized waste water of a biochemical station of an oil refinery after air flotation with an inoculation amount of 2 vol%, and cultured on a shaker at 30°C and 150 r / min. Samples were taken every 12 hours to detect the COD in the waste water. is the abscissa, and the COD concentration in the wastewater is plotted as the ordinate, the result is as follows image 3 shown. Depend on image 3 It can be seen that, from 0 to 24 hours, the COD in the wastewater decreased rapidly with the prolongation of the treatment time. After 24 hours, the COD in the wastewater decreased from 930 mg / L to 176 mg / L, and the removal rate was as high as 81%. The experimental results show that: the strain D8 can quickly adapt to the actual oil refinery wastewater environment, not only can grow and reproduce with dibutyl phthalate as the substrate, but a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com